Abstract
Aim:
Antofloxacin hydrochloride is a new fluoroquinolone antibiotic with broad-spectrum in vitro activity. Using the neutropenic murine thigh infection model, we defined the pharmacodynamic profile and property of antofloxacin hydrochloride against Staphylococcus aureus.
Methods:
Single-dose pharmacokinetic studies of antofloxacin hydrochloride were carried out in thigh infected mice. Therapy was initiated at 2 h postinoculation with 5–640 mg/kg per d fractionated for different dosing regimens. The thighs were removed for bacterial measurement after 24 h of therapy, the best pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) index correlated with the efficacy was determined by nonlinear regression analysis. A sigmoid Emax dose-response model was used to estimate the daily dose and AUC24 h/MIC (minimal inhibitory concentration) required to achieve a static effect.
Results:
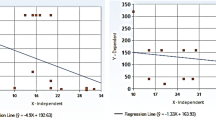
The PK was linear with similar elimination half-life over the dose range studied. The AUC24 h/MIC ratio was the PK/PD parameter that best correlated with efficacy (R2=92.3%, 90.8% for the two organisms, compared with Cmax/MIC and T>MIC [%], respectively). The 24 h static dose ranged from 34.3 to 153.7 mg/kg per d for all S aureus strains, the total AUC24 h/MIC ratio to achieve bacteriostatic effect varied from 31.7 to 122.5 (mean, 65.7±30.6).
Conclusion:
Antofloxacin hydrochloride showed powerful antibacterial activity against the S aureus isolates used in our neutropenicinfected mice model. Our data suggested that the AUC/MIC ratio appeared to be most closely linked to the bacterial outcome (R2>90%), and a total AUC24 h/MIC ratio of 65.7 appears to be the target value to achieve a net bactericidal activity against S aureus, similar to the results of other fluoroquinolones.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Andes D, Craig WA . Pharmacodynamics of the new fluoroquinolone gatifloxacin in murine thigh and lung infection models. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2002; 46: 1665–70.
Andes D, Craig WA . Pharmacodynamics of the new des-f(6)-qui-nolone garenoxacin in a murine thigh infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2003; 47: 3935–41.
Drusano GL, Johnson DE, Rosen M, Standiford HC . Pharmacodynamics of a fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent in a neutropenic rat model of Pseudomonas sepsis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1993; 37: 483–90.
Andes D, Craig WA . In vivo activities of amoxicillin and amoxicillin-clavulanate against Streptococcus pneumoniae: application to breakpoint determinations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1998; 42: 2375–9.
Joly-Guillou ML, Wolff M, Pocidalo JJ, Walker F, Carbon C . Use of a new mouse model of Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia to evaluate the postantibiotic effect of imipenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1997; 41: 345–51.
Onyeji CO, Bui KQ, Owens RC Jr, Nicolau DP, Quintiliani R, Nightingale CH . Comparative efficacies of levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin against Streptococcus pneumoniae in a mouse model of experimental septicaemia. Int J Antimicrob Agents 1999; 12: 107–14.
Xiao XM, Xiao YH . Establishment of a neutropenic-mouse thigh model with S aureus infection. Chin J Clin Pharmacol 2007; 23: 45–9.
Forrest A, Nix DE, Ballow CH, Goss TF, Birmingham MC, Schentag JJ . Pharmacodynamics of intravenous ciprofloxacin in seriously ill patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1993; 37: 1073–81.
Lister PD, Sanders CC . Pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin against Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother 1999; 43: 79–86.
Lister PD, Sanders CC . Pharmacodynamics of trovafloxacin, ofloxa-cin, and ciprofloxacin against Streptococcus pneumoniae in an in vitro pharmacokinetic model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1999; 43: 1118–23.
Andes DR, Craig WA . Pharmacodynamics of fluoroquinolones in experimental models of endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 1998; 27: 47–50.
Forrest A, Chodosh S, Amantea MA, Collins DA, Schentag JJ . Phar-macokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral grepafloxacin in patients with acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. J Antimicrob Chemother 1997; 40 Suppl A: 45–57.
Blaser J, Stone BB, Groner MC, Zinner SH . Comparative study with enoxacin and netilmicin in a pharmacodynamic model to determine importance of ratio of antibiotic peak concentration to MIC for bactericidal activity and emergence of resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1987; 31: 1054–60.
Drusano GL, Preston SL, Owens RC Jr, Ambrose PG . Fluoroquino-lone pharmacodynamics. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 33: 2091–6.
Craig WA . Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters: rationale for antibacterial dosing of mice and men. Clin Infect Dis 1998; 26: 1–10; quiz 11–2.
Dudley MN, Blaser J, Gilbert D, Mayer KH, Zinner SH . Combination therapy with ciprofloxacin plus azlocillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: effect of simultaneous versus staggered administration in an in vitro model of infection. J Infect Dis 1991; 164: 499–506.
Vogelman B, Gudmundsson S, Leggett J, Turnidge J, Ebert S, Craig WA . Correlation of antimicrobial pharmacokinetic parameters with therapeutic efficacy in an animal model. J Infect Dis 1988; 158: 831–47.
Dudley MN . Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of antibiotics with special reference to the fluoroquinolones. Am J Med 1991; 91: 45S–50S.
He YC, He, YJ, Xu L, Lv YH, Liu HX, Sun RY, Zheng QS . Design of a clinical trial of non-inferiority for treating acute bacterial infections and its quantitative analysis. J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007; 11: 1299–305.
Lv Y, Xiao YH, Liu Y, Xia YH Li TY Tolerance of antofloxacin hy-drochloride after ascending single oral dose administration in healthy male volunteers. Chin J Clin Pharmacol 2008; 24: 17–20.
Leggett JE, Ebert S, Fantin B, Craig WA . Comparative dose-effect relations at several dosing intervals for beta-lactam, aminoglycoside and quinolone antibiotics against Gram-negative bacilli in murine thigh-infection and pneumonitis models. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl 1990; 74: 179–84.
Quintiliani R, Owens RC, Grant EM . Clinical role of fluoroquinolones in patients with respiratory tract infections. Infect Dis Clin Prac 1999; 8 ( suppl 1): S28–S41.
Preston SL, Drusano GL, Berman AL, Fowler CL, Chow AT, Dorn-seif B, et al. Pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin: a new paradigm for early clinical trials. JAMA 1998; 279: 125–9.
Andes D, Craig WA . Pharmacodynamics of a new streptogramin, XRP 2868, in murine thigh and lung infection models. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006; 50: 243–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Xm., Xiao, Yh. Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of antofloxacin hydrochloride in a neutropenic murine thigh model of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29, 1253–1260 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00872.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00872.x