Abstract
Aim:
Excessive glutamate release has been proposed to be involved in the pathogenesis of several neurological diseases. In this study, we investigated the effect of HDT-1 (3, 4, 4a, 5, 8, 8a-hexahydro-6,7-dimethyl-4a-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-tosylisoquinolin-l(2H)-one), a novel synthetic compound, on glutamate release in rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals and explored the possible mechanism.
Methods:
The release of glutamate was evoked by the K+ channel blocker 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) or the high external [K+] and measured by one-line enzyme-coupled fruorometric assay. We also determined the loci at which HDT-1 impinges on cerebrocortical nerve terminals by using membrane potential-sensitive dye to assay nerve terminal excitability and depolarization, and Ca2+ indicator Fura-2 to monitor Ca2+ influx.
Results:
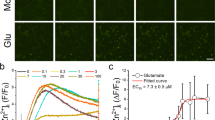
HDT-1 inhibited the release of glutamate evoked by 4-AP and KC1 in a concentration-dependent manner. HDT-1 did not alter the resting synaptosomal membrane potential or 4-AP-evoked depolarization. Examination of the effect of HDT-1 on cytosolic [Ca2+] revealed that the diminution of glutamate release could be attributed to reduction in voltage-dependent Ca2+ influx. Consistent with this, the HDT-1-mediated inhibition of glutamate release was significantly prevented in synaptosomes pretreated with the N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channel blocker ω-conotoxin MVIIC.
Conclusion:
In rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals, HDT-1 inhibits glutamate release through a reduction of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel activity and subsequent decrease of Ca2+ influx into nerve terminals, rather than any upstream effect on nerve terminal excitability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Fonnum F . Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem 1984; 42: 1–11.
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL . A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993; 361: 31–9.
Meldrum B, Garthwaite J . Excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1990; 11: 379–87.
Obrenovitch TP, Urenjak J . Altered glutamatergic transmission in neurological disorders: from high extracellular glutamate to excessive synaptic efficacy. Prog Neurobiol 1997; 51: 39–87.
Chou SSP, Chen PW . Cycloaddition reactions of 4-sulfur-substituted dihydro-2-pyridones and 2-pyridones with conjugated dienes. Tetrahedron 2008; 64: 1879–87.
Cassels BK, Asencio M, Conget P, Speisky H, Videla LA, Lissi EA . Structure-antioxidative activity relationships in benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Pharmacol Res 2004; 31: 103–7.
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P . Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 1993; 262: 689–95.
Markesbery WR . Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer's disease. Free Rad Biol Med 1997; 23: 134–47.
Choi DW, Rothman SM . The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci 1990; 13: 171–82.
Tretter L, Adam-Vizi V . Glutamate release by an Na+ load and oxidative stress in nerve terminals: relevance to ischemia/reperfusion. J Neurochem 2002; 83: 855–62.
Nicholls DG . The glutamatergic nerve terminal. Eur J Biochem 1993; 212: 613–31.
Nicholls DG, Sihra TS, Sanchez-Prieto J . Calcium-dependent and -independent release of glutamate from synaptosomes monitored by continuous fluorometry. J Neurochem 1987; 49: 50–7.
Akerman, KE, Scott IG, Heikkila JE, Heinonen E . Ionic dependence of membrane potential and glutamate receptor-linked responses in synaptoneurosomes as measured with a cyanine dye, DiSC2(5). J Neurochem 1987; 48: 552–9.
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY . A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 1985; 260: 3440–50.
Sihra TS, Bogonez E, Nicholls DG . Localized Ca2+ entry preferentially affects protein dephosphorylation, phosphorylation, and glutamate release. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 1983–9.
Tibbs GR, Barrie AP, Van Mieghem FJ, McMahon HT, Nicholls DG . Repetitive action potentials in isolated nerve terminals in the presence of 4-aminopyridine: effects on cytosolic free Ca2+ and glutamate release. J Neurochem 1989; 53: 1693–9.
Barrie AP, Nicholls DG, Sanchez-Prieto J, Sihra TS . An ion channel locus for the protein kinase C potentiation of transmitter glutamate release from guinea pig cerebrocortical synaptosomes. J Neurochem 1991; 57: 1398–404.
Turner TJ, Dunlap K . Pharmacological characterization of presy-naptic calcium channels using subsecond biochemical measurements of synaptosomal neurosecretion. Neuropharmacology 1995; 34: 1469–78.
Vazquez E, Sanchez-Prieto J . Presynaptic modulation of glutamate release targets different calcium channels in rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals. Eur J Neurosci 1997; 9: 2009–18.
Roeper J, Pongs O . Presynaptic potassium channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1996; 6: 338–41.
Thompson SM, Capogna M, Scanziani M . Presynaptic inhibition in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 1993; 16: 222–7.
Sihra TS, Nichols RA . Mechanisms in the regulation of neurotransmitter release from brain nerve terminals: current hypotheses. Neurochem Res 1993; 18: 47–58.
Nicholls DG . Presynaptic modulation of glutamate release. Prog Brain Res 1998; 116: 15–22.
Sudhof TC . The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu Rev Neurosci 2004; 27: 509–47.
Choi DW . Excitotoxic cell death. J Neurobiol 1992; 23: 1261–76.
Lipton SA, Rosenberg PA . Excitatory amino acid as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med 1994; 330: 613–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Fu Jen Catholic University (109631030991-3) and the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC 96-2628-B-030-001-MY3).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Sj., Chou, Sh., Kuo, Yc. et al. HDT-1, a new synthetic compound, inhibits glutamate release in rat cerebral cortex nerve terminals (synaptosomes). Acta Pharmacol Sin 29, 1289–1295 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00882.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00882.x