Abstract
Aim:
The aim of this study was to design and synthesize a series of high activity compounds against aspartyl protease β-secretase (BACE-1) bearing hydroxyethylene (HE) framework.
Methods:
First, we designed the small library based on our previous work and rational analysis. Subsequently, thirteen compounds were selected and synthesized using skilled solid phase synthetic methods to explore the relationship between structure and activity. We then used molecular modeling to explain the possible binding mode.
Results:
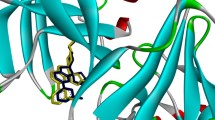
Thirteen new compounds (6-18) have been designed, synthesized and bioassayed. Their structures were determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra, low- and high-resolution mass spectra and optical rotation. Most compounds have shown moderate to excellent activities, and compound 10, which contains fewer amino acids and amide bonds than GRL-7234, was about 5-fold more potent than the control compound 4 discovered by Merck. The molecular modeling results have indicated the possible binding mode and explained the difference between compounds 10 and 16, providing direction for further study.
Conclusion:
This study yielded several high activity compounds bearing fewer amino acids and amide bonds than previous compounds, providing insight into the further development of potent BACE-1 inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
McGeer PL, McGeer EG . Alzheimer's disease: arthritis of the brain?. Drugs News Prospect 1995; 8: 80–3.
Hendriksen JV, Nottet HS, Smits HA . Secretases as targets for drug design in Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Clin Invest 2002; 32: 60–8.
Citron M . Beta-secretase inhibition for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease-promise and challenge. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004; 25: 92–7.
Arendt T . Alzheimer's disease as a disorder of mechanisms underlying structural brain self-organization. Neuroscience 2001; 102: 723–65.
Enz A, Amstutz R, Boddeke H, Gmelin G, Malanowski J . Brain selective inhibition of acetylcholinesterase: a novel approach to therapy for Alzheimer's disease. Prog Brain Res 1993; 98: 431–8.
Monczor M . Diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Curr Med Chem-Central Nervous System Agents 2005; 5: 5–13.
Selkoe DJ . Translating cell biology into therapeutic advances in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 1999; 399 (6738 Suppl): A23–31.
Citron M . β-Secretase inhibition for the treatment of Alzheimer's diseasepromise and challenge. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004; 25: 92–7.
Hardy JA, Higgins GA . Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 1992; 25: 184–5.
Ghosh AK, Hong L, Tang J . β-Secretase as a therapeutic target for inhibitor drugs. Curr Med Chem 2002; 9: 1135–44.
Luo Y, Bolon B, Kahn S, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S, Denis P, et al. Mice deficient in BACE1, the Alzheimer′s beta-secretase, have normal phenotype and abolished beta-amyloid generation. Nat Neurosci 2001; 4: 231–2.
Cai H, Wang Y, McCarthy D, Wen H, Borchelt DR, Price DL, et al. BACE1 is the major beta secretase for generation of Abeta peptides by neurons. Nat Neurosci 2001; 4: 233–4.
Durham TB, Shepherd TA . Progress toward the discovery and development of efficacious BACE inhibitors. Curr Opin Drug Dis 2006; 9: 776–91.
Ghosh AK, Kumaragurubaran N, Hong L, Kulkarni SS, Xu X, Chang W, et al. Design, synthesis, and X-ray structure of potent memapsin 2 (β-secretase) inhibitors with isophthalamide derivatives as the P2-P3-ligands. J Med Chem 2007; 50: 2399–407.
Ghosh AK, Kumaragurubaran N, Hong L, Kulkarni S, Xu X, Miller HB, et al. Potent memapsin 2 (β-secretase) inhibitors: design, synthesis, protein-ligand X-ray structure, and in vivo evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2008; 8: 1031–6.
Ghosh AK, Bilcer G, Harwood C, Kawahama R, Shin D, Hussain KA, et al. Structure-based design: potent inhibitors of human brain memapsin 2 (β-secretase). J Med Chem 2001; 44: 2865–8.
Shuto D, Kasai S, Kimura T, Liu P, Hidaka K, Hamada T, et al. KMI-008, a novel β-secretase inhibitor containing a hydroxymethylcarbonyl isostere as a transition-state mimic: design and synthesis of substrate-based octapeptides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2003; 13: 4273–6.
Kimura T, Shuto D, Kasai S, Liu P, Hidaka K, Hamada T, et al. KMI-358 and KMI-370, highly potent and small-sized BACE1 inhibitors containing phenylnorstatine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2004; 14: 1527–31.
Hanessian S, Yun H, Hou Y, Yang G, Bayrakdarian M, Therrien E, et al. Structure-based design, synthesis, and memapsin 2 (bace) inhibitory activity of carbocyclic and heterocyclic peptidomimetics. J Med Chem 2005; 48: 5175–90.
Hanessian S, Yang G, Rondeau JM, Neumann U, Betschart C, Tintelnot-Blomley M . Structure-based design and synthesis of macroheterocyclic peptidomimetic inhibitors of the aspartic protease β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme (BACE). J Med Chem 2006; 49: 4544–67.
Freskos JN, Fobian YM, Benson TE, Bienkowski MJ, Brown DL, Emmons TL, et al. Design of potent inhibitors of human β-secretase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2007; 17: 73–7.
Plattner JJ, Norbeck DW . In: Drug discovery technologies. Clark CR, Moos WH, Eds. Chichester: Ellis Horwood Limited; 1990. p92–126.
Coburn CA, Stachel SJ, Li YM . Rush DM, Steele TG, Chen-Dodson E, et al. Identification of a small molecule nonpeptide active site β-secretase inhibitor that displays a nontraditional binding mode for aspartyl proteases. J Med Chem 2004; 47: 6117–9.
Stachel SJ, Coburn CA, Steele TG, Jones KG, Loutzenhiser EF, Gregro AR, et al. Structure-based design of potent and selective cell-permeable inhibitors of human β-secretase (bace-1). P J Med Chem 2004; 47: 6447–50.
Iserloh U, Wu Y, Cumming JN, Pan J, Wang LY, Stamford AW, et al. Potent pyrrolidine- and piperidine-based BACE-1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2008; 18: 414–7.
Maillard MC, Hom RK, Benson TE, Moon JB, Mamo S, Bienkowski M, et al. Design, synthesis, and crystal structure of hydroxyethyl secondary amine-based peptidomimetic inhibitors of human β-secretase. J Med Chem 2007; 50: 776–81.
Abdel-Rahman HM, Al-Karamany GS, El-Koussi NA, Youssef AF, Kiso Y . HIV protease inhibitors: peptidomimetic drugs and future perspectives. Curr Med Chem 2002; 9: 1905–22.
Xiao K, Li X, Li JY, Ma LP, Hu B, Yu HP, et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of Leu*Ala hydroxyethylene-based non-peptide β-secretase (BACE) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 2006; 14: 4535–51.
Huey R, Morris GM, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS . A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J Comput Chem 2007; 28: 1145–52.
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, et al. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 1998; 19: 1639–62.
Acknowledgements
Project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No 30672538).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Yp., Xiao, K., Yu, Hp. et al. Discovery of potent β-secretase (bace-1) inhibitors by the synthesis of isophthalamide-containing hybrids. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 259–269 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2008.26
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2008.26