Abstract
Aim:
NYGGF4 is a novel gene that is abundantly expressed in the adipose tissue of obese patients. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of NYGGF4 on basal and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes and to understand the underlying mechanisms.
Methods:
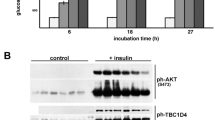
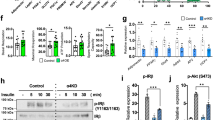
3T3-L1 preadipocytes transfected with either an empty expression vector (pcDNA3.1Myc/His B) or an NYGGF4 expression vector were differentiated into mature adipocytes. Glucose uptake was determined by measuring 2-deoxy-D-[3H]glucose uptake into the adipocytes. Immunoblotting was performed to detect the translocation of insulin-sensitive glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4). Immunoblotting also was used to measure the phosphorylation and total protein contents of insulin signaling proteins such as the insulin receptor (IR), insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1, Akt, ERK1/2, p38, and JNK.
Results:
NYGGF4 over-expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes reduced insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and impaired insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation. It also diminished insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and serine phosphorylation of Akt without affecting the phosphorylation of IR, ERK1/2, p38, and JNK.
Conclusion:
NYGGF4 regulates the functions of IRS-1 and Akt, decreases GLUT4 translocation and reduces glucose uptake in response to insulin. These observations highlight the potential role of NYGGF4 in glucose homeostasis and possibly in the pathogenesis of obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000; 404: 635–43.
Spiegelman BM, Flier JS. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 2001; 104: 531–43.
Visscher TL, Seidell JC. The public health impact of obesity. Annu Rev Public Health 2001; 22: 355–75.
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999-2004. JAMA 2006; 295: 1549–55.
Samaras K, Kelly PJ, Chiano MN, Arden N, Spector TD, Campbell LV. Genes versus environment. The relationship between dietary fat and total and central abdominal fat. Diabetes Care 1998; 21: 2069–76.
Rankinen T, Zuberi A, Chagnon YC, Weisnagel SJ, Argyropoulos G, Walts B, et al. The human obesity gene map: the 2005 update. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006; 14: 529–644.
Wang B, Zhang M, Ni YH, Liu F, Fan HQ, Fei L, et al. Identification and characterization of NYGGF4, a novel gene containing a phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain that stimulates 3T3-L1 preadipocytes proliferation. Gene 2006; 379: 132–40.
Ceddia RB, Somwar R, Maida A, Fanq X, Bikopouls G, Sweeney G. Globular adiponectin increases GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetoloqia 2005; 48: 132–9.
Andreozzi F, Laratta E, Sciacqua A, Perticone F, Sesti G. Angiotensin II impairs the insulin signaling pathway promoting production of nitric oxide by inducing phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 on Ser312 and Ser616 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Circ Res 2004; 94: 1211–8.
Bryant NJ, Govers R, James DE. Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002; 3: 267–77.
K anzaki M. Insulin receptor signals regulating GLUT4 translocation and actin dynamics. Endocr J 2006; 53: 267–93.
Liu YJ, Liu XG, Wang L, Dina C, Yan H, Liu JF, et al. Genome-wide association scans identified CTNNBL1 as a novel gene for obesity. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: 1803–13.
Ducluzeau PH, Fletcher LM, Vidal H, Laville M, Tavaré JM. Molecular mechanisms of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in adipocytes. Diabetes Metab 2002; 28: 85–92.
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 85–96.
Samuelsson AM, Bollano E, Mobini R, Larsson BM, Omerovic E, Fu M. H yperinsulinemia: effect on cardiac mass/function, angiotensin II receptor expression, and insulin signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006; 291: H787–96.
Fujishiro M, Gotoh Y, Katagiri H, Sakoda H, Ogihara T, Anai M, et al. Three mitogen-activated protein kinases inhibit insulin signaling by different mechanisms in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Endocrinol 2003; 17: 487–97.
González-Yanes C, Serrano A, Bermúdez-Silva FJ, Hernández-Dominguez M, Páez-Ochoa MA, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, et al. Oleylethanolamide impairs glucose tolerance and inhibits insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes through p38 and JNK MAPK pathways. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2005; 289: E923–9.
Giovannone B, Scaldaferri ML, Federici M, Porzio O, Lauro D, Fusco A, et al. Insulin receptor substrate (IRS) transduction system: distinct and overlapping signaling protein. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2000; 16: 434–4.
Margolis B, Borg JP, Straight S, Meyer D. The function of PTB domain proteins. Kidney Int 1999; 56: 1230–7.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30571978), Health Bureau of Jiangsu Province (No RC2002061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Cm., Chen, Xh., Wang, B. et al. Over-expression of NYGGF4 inhibits glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via attenuated phosphorylation of IRS-1 and Akt. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 120–124 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2008.9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2008.9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dual role of PID1 in regulating apoptosis induced by distinct anticancer-agents through AKT/Raf-1-dependent pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
PID1 increases chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in medulloblastoma and glioblastoma cells in a manner that involves NFκB
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Gal-geun-dang-gwi-tang improves diabetic vascular complication in apolipoprotein E KO mice fed a western diet
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2014)
-
Overexpression of TFAM Protects 3T3-L1 Adipocytes from NYGGF4 (PID1) Overexpression-Induced Insulin Resistance and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2013)
-
Role of NYGGF4 in insulin resistance
Molecular Biology Reports (2012)