Abstract
Aim:
The aim was to study the anti-tumor activities and mechanisms of two synthetic peptide fragments of tumstatin (alpha3 (IV) NC1 domain) in human gastric carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.
Methods:
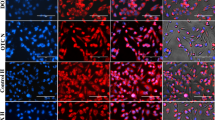
MTT assay and cell cycle assay were used to study the anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic activities of two peptide fragments in vitro. Apoptosis induced by the two peptide fragments was demonstrated by TUNEL assay and morphological observation. The orthotopic tumor model was established to investigate the activities of two peptide fragments in vivo. Intratumor vascularization and the expressions of VEGF, bFGF, Fas, FasL, Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase 3 were determined using immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis.
Results:
Peptide 19 inhibited SGC-7901 proliferation and induced apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo. Notably, peptide 21 suppressed the proliferation of HUVEC-12 cells in vitro. Each peptide arrested both cell lines at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle, and they also synergistically suppressed in vitro and in vivo tumor growth. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis revealed the strong expression of Fas, FasL and caspase 3 in orthotopic tumor tissues treated with peptide 19 alone or in combination with peptide 21. Decreased expressions of VEGF and bFGF and decreased microvessel density (MVD) in orthotopic tumor tissues were seen in mice treated with peptide 21 alone or in combination with peptide 19.
Conclusion:
Two tumstatin peptide fragments facilitate two unique antitumor activities. Thus, they are drug candidates in the treatment of gastric carcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Folkman J . Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1995; 1: 27–31.
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G, et al. Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 1994; 79: 1157–64.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK . Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000; 407: 249–57.
Folkman J, Merler E, Abernathy C, Williams G . Isolation of a tumor factor responsible for angiogenesis. J Exp Med 1971; 133: 275–88.
Hanahan D, Folkman J . Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996; 86: 353–64.
Sauer G, Deissler H . Angiogenesis: prognostic and therapeutic implications in gynecologic and breast malignancies. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 2003; 15: 45–9.
Hamano Y, Kalluri R . Tumstatin, the NC1 domain of alpha3 chain of type IV collagen, is an endogenous inhibitor of pathological angiogenesis and suppresses tumor growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 333: 292–8.
Maeshima Y, Colorado PC, Kalluri R . Two RGD-independent αvβ3 integrin binding sites on tumstatin regulate distinct anti-tumor properties. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 23745–50.
Maeshima Y, Colorado PC, Torre A, Holthaus KA, Grunkemeyer JA, Ericksen MB, et al. Distinct antitumor properties of a type IV collagen domain derived from basement membrane. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 21340–8.
Mundel TM, Kalluri R . Type IV collagen-derived angiogenesis inhibitors. Microvasc Res 2007; 74: 85–9.
Maeshima Y, Manfredi M, Reimer C, Holthaus KA, Hopfer H, Chandamuri BR, et al. Identification of the anti-angiogenic site within vascular basement membrane-derived tumstatin. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 15240–8.
Maeshima Y, Yerramalla UL, Dhanabal M, Holthaus KA, Barbashov S, Kharbanda S, et al. Extracellular matrix-derived peptide binds to αvβ3 integrin and inhibits angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 31959–68.
Han J, Ohno N, Pasco S, Monboisse JC, Borel JP, Kefalides NA . A cell binding domain from the alpha3 chain of type IV collagen inhibits proliferation of melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 20395–401.
Monboisse JC, Garnotel R, Bellon G, Ohno N, Perreau C, Borel JP, et al. The alpha 3 chain of type IV collagen prevents activation of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 25475–82.
Shahan TA, Fawzi A, Bellon G, Monboisse JC . KefalidesNA. Regulation of tumor cell chemotaxis by type IV collagen is mediated by a Ca2+-dependent mechanism requiring CD47 and the integrin alpha(V)beta(3). J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 4796–802.
O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, et al. Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 1997; 88: 277–85.
Zhu B, Lu L, Cai W, Yang X, Li C, Yang Z, et al. Kallikrein-bindin protein inhibits growth of gastric carcinoma by reducing vascular endothelial growth factor production and angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther 2007; 6: 3297–306.
Soares AB, Juliano PB, Araujo VC, Metze K, Altemani A . Angiogenic switch during tumor progression of carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma. Virchows Arch 2007; 451: 65–71.
Folkman J, Kalluri R . Cancer without disease. Nature 2004; 427: 787.
Kalluri R . Basement membranes: structure, assembly and role in tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 422–33.
Folkman J . Angiogenesis inhibitors generated by tumors. Mol Med 1995; 1: 120–2.
Sudhakar A, Boosani CS . Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by tumstatin: insights into signaling mechanisms and implications in cancer regression. Pharm Res 2008; 25: 2731–9.
Cao JG, Peng SP, Sun L, Li H, Wang L, Deng HW . Vascular basement membrane-derived multifunctional peptide, a novel inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2006; 38: 514–22.
Pedchenko V, Zent R, Hudson BG . Alpha(v)beta3 and alpha(v)beta5 integrins bind both the proximal RGD site and non-RGD motifs within noncollagenous (NC1) domain of the alpha3 chain of type IV collagen: implication for the mechanism of endothelial cell adhesion. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 2772–80.
Boosani CS, Mannam AP, Cosgrove D, Silva R, Hodivala-Dilke KM, Keshamouni VG, et al. Regulation of COX-2 mediated signaling by alpha3 type IV noncollagenous domain in tumor angiogenesis. Blood 2007; 110: 1168–77.
Floquet N, Pasco S, Ramont L, Derreumaux P, Laronze JY, Nuzillard JM, et al. The antitumor properties of the alpha3(IV)-(185-203) peptide from the NC1 domain of type IV collagen(tumstatin) are conformation-dependent. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 2091–100.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30472035), the Key Program of Heilongjiang Science and Technology Foundation (ZJY04-0102), Heilongjiang Innovation Program in Graduate Education (YJSCX2007-0201HLJ), a grant from the Department of Education of Heilongjiang Province (11531089), and the Youth Program of Heilongjiang Science and Technology Foundation (QC08C07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Yj., Sun, Lc., He, Y. et al. The anti-tumor properties of two tumstatin peptide fragments in human gastric carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 1307–1315 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.111
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.111
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Is gastrointestinal dysfunction induced by gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis relevant to impairment of interstitial cells of Cajal?
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2011)