Abstract
Aim:
Localized delivery of growth factors has significant potential as a future therapeutic strategy in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. A nanoparticle vehicle was created and evaluated in this study with the intent to deliver growth factors for periodontal regeneration.
Methods:
Novel composite nanoparticles based on glycidyl methacrylate derivatized dextrans (Dex-GMA) and gelatin were fabricated by a facile method without using any organic solvents. The configurations of the resultant nanoparticles were evaluated by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and atomic force microscope. Their surfaces were characterized by zeta-potential measurements, after which their properties including swelling, degradation, drug release, and cytotoxicity were also investigated using in vitro models.
Results:
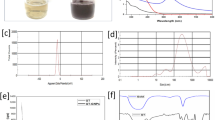
The particle size of Dex-GMA/gelatin nanoparticles (DG-NPs) ranged from 20 to 100 nm and showed a mono-disperse size distribution (mean diameter 53.7 nm) and a strongly negative surface zeta potential (−20 mV). The DG-NPs were characterized by good swelling and degradation properties in media including dextranase. The in vitro drug release studies showed that the efficient bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) release from DG-NPs was maintained for more than 12 d under degradation conditions, where more than 90% of the loaded BMP was released. No any relevant cell damage caused by DG-NPs was found in the cytotoxicity tests for a period of 24 h.
Conclusion:
These combined results demonstrate that DG-NPs fulfill the basic prerequisites for growth factor delivery. With further in vivo studies, those nanoparticles may offer a promising vehicle for the delivery of active drugs to the periodontium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Tabata Y . Significance of release technology in tissue engineering. Drug Discov Today 2005; 10: 1639–46.
Vasita R, Katti DS . Growth factor-delivery systems for tissue engineering: a materials perspective. Expert Rev Med Devices 2006; 3: 29–47.
Chen FM, Shelton RM, Jin Y, Chapple IL . Localized delivery of growth factors for periodontal tissue regeneration: role, strategies, and perspectives. Med Res Rev 2009; 29 (in print). doi: 10.1002/med.20144.
Mundargi RC, Babu VR, Rangaswamy V, Patel P, Aminabhavi TM . Nano/micro technologies for delivering macromolecular therapeutics using poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) and its derivatives. J Control Release 2008;125: 193–209.
Jabr-Milane L, van Vlerken L, Devalapally H, Shenoy D, Komareddy S, Bhavsar M, et al. Multi-functional nanocarriers for targeted delivery of drugs and genes. J Control Release 2008; 130: 121–8.
Chen FM, Wu ZF, Wang QT, Wu H, Zhang YJ, Nie X, et al. Preparation and biological characteristics of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2-loaded dextran-co-gelatin hydrogel microspheres, in vitro and in vivo studies. Pharmacology 2005; 75: 133–44.
Chen FM, Wu ZF, Wang QT, Wu H, Zhang YJ, Nie X, et al. Preparation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded dextran-based microspheres and their characteristics. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005; 26: 1093–103.
Chen FM, Wu ZF, Sun HH, Wu H, Xin SN, Wang QT, et al. Release of bioactive BMP from dextran-derived microspheres: a novel delivery concept. Int J Pharm 2006; 307: 23–32.
Chen FM, Zhao YM, Wu H, Deng ZH, Wang QT, Zhou W, et al. Enhancement of periodontal tissue regeneration by locally controlled delivery of insulin-like growth factor-I from dextran-co-gelatin microspheres. J Control Release 2006; 114: 209–22.
Huang S, Deng T, Wu H, Chen F, Jin Y . Wound dressings containing bFGF-impregnated microspheres. J Microencapsul 2006; 23: 277–90.
Tang MH, Dou HJ, Sun K . One-step synthesis of dextran-based stable nanoparticles assisted by self-assembly. Polymer 2006; 47: 728–34.
Young S, Wong M, Tabata Y, Mikos AG . Gelatin as a delivery vehicle for the controlled release of bioactive molecules. J Control Release 2005; 109: 256–74.
Basinska T, Slomkowski S . The direct determination of protein concentration for proteins immobilized on polystyrene microspheres. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 1991; 3: 115–25.
Feng SS, Huang G . Effects of emulsifiers on the controlled release of paclitaxel (Taxol) from nanospheres of biodegradable polymers. J Control Release 2001; 71: 53–69.
Panyam J, Labhasetwar V . Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2003; 55: 329–47.
Biondi M, Ungaro F, Quaglia F, Netti PA . Controlled drug delivery in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2008; 60: 229–42.
Wu H, Zhang Z, Wu D, Zhao H, Yu K, Hou Z . Preparation and drug release characteristics of pingyangmycin-loaded dextran cross-linked gelatin microspheres for embolization therapy. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2006; 78: 56–62.
Chen FM, Zhao YM, Sun HH, Jin T, Wang QT, Zhou W, et al. Novel glycidyl methacrylated dextran (Dex-GMA)/gelatin hydrogel scaffolds containing microspheres loaded with bone morphogenetic proteins: formulation and characteristics. J Control Release 2007; 118: 65–77.
Chen FM, Zhao YM, Zhang R, Jin T, Sun HH, Wu ZF, et al. Periodontal regeneration using novel glycidyl methacrylated dextran (Dex-GMA)/gelatin scaffolds containing microspheres loaded with bone morphogenetic proteins. J Control Release 2007; 121: 81–90.
Huang M, Wu W, Qian J, Wan DJ, Wei XL, Zhu JH . Body distribution and in situ evading of phagocytic uptake by macrophages of long-circulating poly (ethylene glycol) cyanoacrylate-co-n-hexadecyl cyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005; 26: 1512–8.
Jiang B, Hu L, Gao C, Shen J . Crosslinked polysaccharide nanocapsules: preparation and drug release properties. Acta Biomater 2006; 2: 9–18.
Huang ZR, Hua SC, Yang YL, Fang JY . Development and evaluation of lipid nanoparticles for camptothecin delivery: a comparison of solid lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured lipid carriers, and lipid emulsion. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2008; 29: 1094–102.
Satarkar NS, Zach Hilt J . Hydrogel nanocomposites as remote-controlled biomaterials. Acta Biomater 2008; 4: 11–6.
Zhang J, Misra RD . Magnetic drug-targeting carrier encapsulated with thermosensitive smart polymer: core-shell nanoparticle carrier and drug release response. Acta Biomater 2007; 3: 838–50.
Zhang J, Rana S, Srivastava RS, Misra RD . On the chemical synthesis and drug delivery response of folate receptor-activated, polyethylene glycol-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles. Acta Biomater 2008; 4: 40–8.
Li SH, Cai SX, Liu B, Ma KW, Wang ZP, Li XK . In vitro characteristics of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres incorporating gelatin particles loading basic fibroblast growth factor. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2006; 27: 754–9.
Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Schmitt F . Chemical modification of therapeutic drugs or drug vector systems to achieve targeted therapy: looking for the grail. Med Res Rev 2007; 27: 574–90.
Cui LJ, Sun NX, Li XH, Huang J, Yang JG . Subconjunctival sustained release 5-fluorouracil for glaucoma filtration surgery. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2008; 29: 1021–8.
Bailey MM, Berkland CJ . Nanoparticle formulations in pulmonary drug delivery. Med Res Rev 2009; 29: 196–212.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by a grant from the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (No 30700173), as well as grants from the contributor's own institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Fm., Ma, Zw., Dong, Gy. et al. Composite glycidyl methacrylated dextran (Dex-GMA)/gelatin nanoparticles for localized protein delivery. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 485–493 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.15
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.15
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Recent developments of biomaterial scaffolds and regenerative approaches for craniomaxillofacial bone tissue engineering
Journal of Polymer Research (2022)
-
Recent Trends in Drug Delivery System Using Protein Nanoparticles
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2014)
-
Bone regeneration: current concepts and future directions
BMC Medicine (2011)