Abstract
Aim:
To determine the effects of the centrally antihypertensive drug moxonidine injected into the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) on baroreflex function in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR).
Methods:
Baroreflex sensitivity control of renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) and barosensitivity of the RVLM presympathetic neurons were determined following application of different doses of moxonidine within the RVLM.
Results:
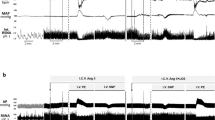
Three doses (0.05, 0.5, and 5 nmol in 50 nL) of moxonidine injected bilaterally into the RVLM dose-dependently reduced the baseline blood pressure (BP) and RSNA in SHR. At the highest dose (5 nmol) of moxonidine injection, the maximum gain (1.24%±0.04%/mmHg) of baroreflex control of RSNA was significantly decreased. However, the lower doses (0.05 and 0.5 nmol) of moxonidine injection into the RVLM significantly enhanced the baroreflex gain (2.34%±0.08% and 2.01%±0.07%/mmHg). The moxonidine-induced enhancement in baroreflex function was completely prevented by the imidazoline receptor antagonist efaroxan but not by the α2-adrenoceptor antagonist yohimbine. A total of 48 presympathetic neurons were recorded extracellularly in the RVLM of SHR. Iontophoresis of applied moxonidine (30–60 nA) dose-dependently decreased the discharge of RVLM presympathetic neurons but also significantly increased the barosensitivity of RVLM presympathetic neurons.
Conclusion:
These data demonstrate that a low dose of moxonidine within the RVLM has a beneficial effect on improving the baroreflex function in SHR via an imidazoline receptor-dependent mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ernsberger P, Damon TH, Graff LM, Schafer SG, Christen MO . Moxonidine, a centrally acting antihypertensive agent, is a selective ligand for I1-imidazoline sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1993; 264: 172–82.
Dampney RA . Functional organization of central pathways regulating the cardiovascular system. Physiol Rev 1994; 74: 323–64.
Haxhiu MA, Dreshaj I, Schafer SG, Ernsberger P . Selective antihypertensive action of moxonidine is mediated mainly by I1-imidazoline receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1994; 24 Suppl 1: S1–S8.
Reis DJ . Neurons and receptors in the rostroventrolateral medulla mediating the antihypertensive actions of drugs acting at imidazoline receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1996; 27 Suppl 3: S11–S18.
Collier DJ, Bernardi L, Angell-James JE, Caulfield MJ, Sleight P . Baroreflex sensitivity and heart rate variability as predictors of cardiovascular outcome in hypertensive patients with multiple risk factors for coronary disease. J Hum Hypertens 2001; 15 Suppl 1: S57–S60.
Johansson M, Gao SA, Friberg P, Annerstedt M, Carlstrom J, Ivarsson T, et al. Baroreflex effectiveness index and baroreflex sensitivity predict all-cause mortality and sudden death in hypertensive patients with chronic renal failure. J Hypertens 2007; 25: 163–8.
Su DF, Miao CY . Reduction of blood pressure variability: a new strategy for the treatment of hypertension. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2005; 26: 388–90.
Head GA . Baroreflexes and cardiovascular regulation in hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1995; 26 Suppl 2: S7–16.
Harron DW . Antihypertensive drugs and baroreflex sensitivity. Effects of rilmenidine. Am J Med 1989; 87: 57S–62S.
Medvedev OS, Kunduzova OR, Murashev AN, Medvedeva NA . Influence of sino-aortic barodenervation on the cardiovascular effects of imidazoline-like drugs. J Auton Nerv Syst 1998; 72: 205–9.
Mancia G, Ferrari A, Gregorini L, Zanchetti A . Clonidine and carotid baroreflex in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1979; 1: 362–70.
Head GA, Burke SL, Sannajust FJ . Involvement of imidazoline receptors in the baroreflex effects of rilmenidine in conscious rabbits. J Hypertens 2001; 19: 1615–24.
Mayorov DN, Burke SL, Head GA . Relative importance of rostral ventrolateral medulla in sympathoinhibitory action of rilmenidine in conscious and anesthetized rabbits. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2001; 37: 252–61.
Head GA, Burke SL . Comparison of renal sympathetic baroreflex effects of rilmenidine and alpha-methylnoradrenaline in the ventrolateral medulla of the rabbit. J Hypertens 2000; 18: 1263–76.
Tank J, Jordan J, Diedrich A, Obst M, Plehm R, Luft FC, et al. Clonidine improves spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity in conscious mice through parasympathetic activation. Hypertension 2004; 43: 1042–7.
Ma XJ, Shen FM, Liu AJ, Shi KY, Wu YL, Su DF . Clonidine, moxonidine, folic acid, and mecobalamin improve baroreflex function in stroke-prone, spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28: 1550–8.
Wang LG, Zeng J, Yuan WJ, Su DF, Wang WZ . Comparative study of NMDA and AMPA/kainate receptors involved in cardiovascular inhibition produced by imidazoline-like drugs in anaesthetized rats. Exp Physiol 2007; 92: 849–58.
Wang WZ, Yuan WJ, Tang CS, Su DF . Electrophysiological evidences for the contribution of NMDA receptors to the inhibition of clonidine on the RVLM presympathetic neurons. Brain Res 2004; 1023: 163–6.
Brown DL, Guyenet PG . Electrophysiological study of cardiovascular neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in rats. Circ Res 1985; 56: 359–69.
Lipski J, Kanjhan R, Kruszewska B, Rong W . Properties of presympathetic neurones in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in the rat: an intracellular study "in vivo". J Physiol 1996; 490 (Pt 3): 729–44.
Goodchild AK, Dampney RA, Bandler R . A method for evoking physiological responses by stimulation of cell bodies, but not axons of passage, within localized regions of the central nervous system. J Neurosci Methods 1982; 6: 351–63.
Paxions G WC . The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates (4th ed). New York: Academic press; 1998.
Wang LG, Zeng J, Yuan WJ, Su DF, Wang WZ . Comparative study of NMDA and AMPA/kainate receptors involved in cardiovascular inhibition produced by imidazoline-like drugs in anaesthetized rats. Exp Physiol 2007; 92: 849–58.
Wang WZ, Yuan WJ, Ren AJ, Pan YX, Tang CS, Su DF . Role of I1-imidazoline receptors within the caudal ventrolateral medulla in cardiovascular responses to clonidine in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2003; 42: 1–9.
Tank J, Jordan J, Diedrich A, Obst M, Plehm R, Luft FC, et al. Clonidine improves spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity in conscious mice through parasympathetic activation. Hypertension 2004; 43: 1042–7.
Harron DW . Antihypertensive drugs and baroreflex sensitivity. Effects of rilmenidine. Am J Med 1989; 87: 57S–62S.
Mancia G, Ferrari A, Gregorini L, Zanchetti A . Clonidine and carotid baroreflex in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1979; 1: 362–70.
Su DF, Miao CY . Reduction of blood pressure variability: a new strategy for the treatment of hypertension. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2005; 26: 388–90.
Head GA, Burke SL, Sannajust FJ . Involvement of imidazoline receptors in the baroreflex effects of rilmenidine in conscious rabbits. J Hypertens 2001; 19: 1615–24.
Mayorov DN, Burke SL, Head GA . Relative importance of rostral ventrolateral medulla in sympathoinhibitory action of rilmenidine in conscious and anesthetized rabbits. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2001; 37: 252–61.
Head GA, Burke SL . Comparison of renal sympathetic baroreflex effects of rilmenidine and alpha-methylnoradrenaline in the ventrolateral medulla of the rabbit. J Hypertens 2000; 18: 1263–76.
Anderson EA, Sinkey CA, Lawton WJ, Mark AL . Elevated sympathetic nerve activity in borderline hypertensive humans. Evidence from direct intraneural recordings. Hypertension 1989; 14: 177–83.
Judy WV, Watanabe AM, Henry DP, Besch HR Jr, Murphy WR, Hockel GM . Sympathetic nerve activity: role in regulation of blood pressure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Circ Res 1976; 38: 21–9.
Johansson M, Gao SA, Friberg P, Annerstedt M, Carlstrom J, Ivarsson T, et al. Baroreflex effectiveness index and baroreflex sensitivity predict all-cause mortality and sudden death in hypertensive patients with chronic renal failure. J Hypertens 2007; 25: 163–8.
La Rovere MT, Pinna GD, Hohnloser SH, Marcus FI, Mortara A, Nohara R, et al. Baroreflex sensitivity and heart rate variability in the identification of patients at risk for life-threatening arrhythmias: implications for clinical trials. Circulation 2001; 103: 2072–7.
Su DF, Miao CY . Reduction of blood pressure variability: a new strategy for the treatment of hypertension. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2005; 26: 388–90.
Ernsberger P, Damon TH, Graff LM, Schafer SG, Christen MO . Moxonidine, a centrally acting antihypertensive agent, is a selective ligand for I1-imidazoline sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1993; 264: 172–82.
Goldberg MR, Robertson D . Yohimbine: a pharmacological probe for study of the alpha 2-adrenoreceptor. Pharmacol Rev 1983; 35: 143–80.
Dampney RA . Functional organization of central pathways regulating the cardiovascular system. Physiol Rev 1994; 74: 323–64.
Head GA, Burke SL . Comparison of renal sympathetic baroreflex effects of rilmenidine and alpha-methylnoradrenaline in the ventrolateral medulla of the rabbit. J Hypertens 2000; 18: 1263–76.
Head GA, Burke SL, Sannajust FJ . Involvement of imidazoline receptors in the baroreflex effects of rilmenidine in conscious rabbits. J Hypertens 2001; 19: 1615–24.
Ma XJ, Shen FM, Liu AJ, Shi KY, Wu YL, Su DF . Clonidine, moxonidine, folic acid, and mecobalamin improve baroreflex function in stroke-prone, spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28: 1550–8.
Mancia G, Ferrari A, Gregorini L, Zanchetti A . Clonidine and carotid baroreflex in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1979; 1: 362–70.
Tank J, Jordan J, Diedrich A, Obst M, Plehm R, Luft FC, et al. Clonidine improves spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity in conscious mice through parasympathetic activation. Hypertension 2004; 43: 1042–7.
Moreira TS, Takakura AC, Menani JV, Colombari E . Involvement of central alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoceptors on cardiovascular responses to moxonidine. Eur J Pharmacol 2007; 563: 164–71.
Bruban V, Estato V, Schann S, Ehrhardt JD, Monassier L, Renard P, et al. Evidence for synergy between alpha(2)-adrenergic and nonadrenergic mechanisms in central blood pressure regulation. Circulation 2002; 105: 1116–21.
Head GA, Burke SL . Comparison of renal sympathetic baroreflex effects of rilmenidine and alpha-methylnoradrenaline in the ventrolateral medulla of the rabbit. J Hypertens 2000; 18: 1263–76.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30670759 and 30971061) and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (No 2006CB503807). This work was also supported by the grant from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai (No 06QB14029 and 09PJ1400100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Jl., Wang, L., Wu, Zt. et al. Low dose of moxonidine within the rostral ventrolateral medulla improves the baroreflex sensitivity control of sympathetic activity in hypertensive rat. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 1594–1600 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.165
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.165
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of vascular KATP channels in blood pressure variability after sinoaortic denervation in rats
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2011)
-
The features of reserpine-induced gastric mucosal lesions
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2010)