Abstract
Aim:
The aim of this study was to explore the effects and mechanism of berbamine on imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL-positive human leukemia K562 (K562-r) cells in vitro and in vivo.
Methods:
Cell viability was measured by MTT assay, and apoptotic morphology changes were detected by fluorescence microscopy. The apoptosis rate was measured by flow cytometric assay. mdr-1 mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR. Bcl-2 family proteins, cytochrome c(cyt C), poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP), and P-glycoprotein were detected by Western blot. BALB/c nu/nu mice were injected with K562-r cells subcutaneously. Tumor-bearing mice were treated intravenously with berbamine.
Results:
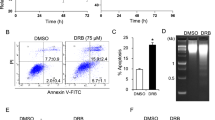
MTT tests revealed that berbamine significantly inhibited K562-r cell proliferation and increased the chemo-sensitivity of K562-r cells to imatinib. The apoptosis rate was significantly increased following treatment with 21.2 μmol/L berbamine; formation of typical apoptotic blebs was apparent, as observed by fluorescence microscopy. Expression levels of mdr-1 mRNA and P-gp protein were high in untreated K562-r cells and significantly down-regulated by berbamine treatment. Berbamine-treated K562-r cells also exhibited down-regulated expression of the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, up-regulated expression of the apoptotic proteins Bax and cytoplasmic cyt C, and stimulated proteolytic cleavage of PARP. In addition, berbamine also suppressed the growth of K562-r xenotransplanted tumors in vivo.
Conclusion:
Berbamine inhibited proliferation of K562-r cells both in vitro and in vivo. Berbamine-induced apoptosis in K562-r cells appeared to occur through a mechanism involving Bcl-2 family proteins, as well as mdr-1 mRNA and P-gp protein. Berbamine in combination with imatinib restored the chemo-sensitivity of K562-r cells to imatinib. Our findings suggest that berbamine may be useful in treating imatinib-resistant CML patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Nowell P, Hungerford D . A minute chromosome in human chronic granulocytic leukemia. Science 1960; 132: 1497.
Konopka JB, Watanabe SM, Witte ON . An alteration of the human c-ABL protein in K562 leukemia-cells unmasks associated tyrosine kinase-activity. Cell 1984; 37: 1035–42.
Kirchner D, Duyster J, Ottmann O, Schmid RM, Bergmann L, Munzert G . Mechanisms of bcr-Abl-mediated NF-kappa B/Re1 activation. Exp Hematol 2003; 31: 504–11.
Steelman LS, Pohnert SC, Shelton JG, Franklin RA, Bertrand FE, McCubrey JA . JAK/STAT, Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/Akt and BCR-ABL in cell cycle progression and leukemogenesis. Leukemia 2004; 18: 189–218.
Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O'Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. New Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2408–17.
Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN, et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 2001; 293: 876–80.
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Pei XY, Dent P, Grant S . Bortezomib and flavopiridol interact synergistically to induce apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells resistant to imatinib mesylate through both Bcr/Abl-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Blood 2004; 104: 509–18.
von Bubnoff N, Veach DR, Miller WT, Li WQ, Peschel C, Bornmann WG, et al. Inhibition of wild-type and mutant Bcr-Abl by pyrido-pyrimidine-type small molecule kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6395–404.
Hait WN, Lazo JS . Calmodulin — a potential target for cancer chemotherapeutic-agents. J Clin Oncol 1986; 4: 994–1012.
Xu RZ, Dong QH, Yu YZ, Zhao XY, Gan XX, Wu D, et al. Berbamine: A novel inhibitor of bcr/abl fusion gene with potent anti-leukemia activity. Leukemia Res 2006; 30: 17–23.
Wu D, Lin MF, Cai Z, Zhao XY . Effects of berbamine on Jurkat cells and its mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. Chin J Hematol 2004; 25: 754–6.
He ZW, Zhao XY, Xu RZ, Wu D . Effects of berbamine on growth of leukemia cell line NB4 and its mechanism. J Zhejiang Univ (Medical Sci) 2006; 35: 209–14.
Xu L, Zhao XY, Wu D . Berbamine, a calmodulin antagonist, induces apoptosis in human leukemia K562 cells. Chin J Hematol 2003; 24: 261–2.
Branford S, Rudzki Z, Walsh S, Grigg A, Arthur C, Taylor K, et al. High frequency of point mutations clustered within the adenosine triphosphate-binding region of BCR/ABL in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia or Ph-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia who develop imatinib (STI571) resistance. Blood 2002; 99: 3472–5.
Chen Q, Takeyama N, Brady G, Watson AJM, Dive C . Blood cells with reduced mitochondrial membrane potential and cytosolic cytochrome c can survive and maintain clonogenicity given appropriate signals to suppress apoptosis. Blood 1998; 92: 4545–53.
Amarante-Mendes GP, Kim CN, Liu L, Huang Y, Perkins CL, Green DR, et al. Bcr-Abl exerts its antiapoptotic effect against diverse apoptotic stimuli through blockage of mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and activation of caspase-3. Blood 1998; 91: 1700–5.
Li BX, Gao YR, Li WH . Determination of berbamine in rat plasma by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography. J Harbin Med Univ 1995; 29: 201–3.
Minn AJ, Rudin CM, Boise LH, Thompson CB . Expression of Bcl-x(L) can confer a multidrug-resistance phenotype. Blood 1995; 86: 1903–10.
Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ . BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 1899–911.
Strasser A, O'Connor L, Dixit VM . Apoptosis signaling. Annu Rev Biochem 2000; 69: 217–45.
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EHY, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, et al. Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 2001; 292: 727–30.
Campos L, Rouault JP, Sabido O, Oriol P, Roubi N, Vasselon C, et al. High expression of Bcl-2 protein in acute myeloid-leukemia cells is associated with poor response to chemotherapy. Blood 1993; 81: 3091–6.
Kim CN, Wang XD, Huang Y, Ibrado AM, Liu L, Fang GF, et al. Overexpression of Bcl-x (L), inhibits Ara-C-induced mitochondrial loss of cytochrome c and other perturbations that activate the molecular cascade of apoptosis. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 3115–20.
Baran Y, Ural AU, Gunduz U . Mechanisms of cellular resistance to imatinib in human chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Hematology 2007; 12: 497–503.
Mancini M, Brusa G, Benvenuti M, Mazzacurati L, Campanini F, Barbieri E, et al. The (BCR)-B-p210-ABL tyrosine kinase of chronic myeloid leukemia causes resistance to radio-induced apoptotic death by inhibiting the proapoptotic BAX gene. Leukemia 2004; 18: 370–2.
Ibrado AM, Huang Y, Fang GF, Liu L, Bhalla K . Overexpression of Bcl-2 or Bcl-x(L) inhibits Ara-C-induced CPP32/Yama protease activity and apoptosis of human acute myelogenous leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 4743–8.
Illmer T, Schaich M, Platzbecker U, Freiberg-Richter J, Oelschlagel U, von Bonin M, et al. P-glycoprotein-mediated drug efflux is a resistance mechanism of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to treatment with imatinib mesylate. Leukemia 2004; 18: 401–8.
Rumpold H, Wolf AM, Gruenewald K, Gastl G, Gunsilius E, Wolf D . RNAi-mediated knockdown of P-glycoprotein using a transposon-based vector system durably restores imatinib sensitivity in imatinib-resistant CML cell lines. Exp Hematol 2005; 33: 767–75.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No 491020-N20529).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Yl., Xu, L., Liang, Y. et al. Berbamine exhibits potent antitumor effects on imatinib-resistant CML cells in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 451–457 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.19
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.19
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
STAT3 transcription factor as target for anti-cancer therapy
Pharmacological Reports (2020)
-
Role of Non Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Hematological Malignances and its Targeting by Natural Products
Molecular Cancer (2018)
-
Berbamine inhibited the growth of prostate cancer cells in vivo and in vitro via triggering intrinsic pathway of apoptosis
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2016)
-
Berbamine overcomes imatinib-induced neutropenia and permits cytogenetic responses in Chinese patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2011)
-
Berbamine, a novel nuclear factor κB inhibitor, inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human myeloma cells
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2009)