Abstract
Aim:
To evaluate the effects and elucidate the mechanisms of a series of indoloquinazolines as novel anticancer agents.
Methods:
Condensation of the substituted isatoic anhydride with the substituted isatin was performed to prepare compounds 1–4, followed by adding malononitrile to prepare compounds 5–7. Cytotoxicity was measured by MTT assays. Apoptosis induction was evaluated using DNA fragmentation, cell cycle assay, caspase 3/7 activity and Western blot.
Results:
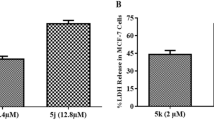
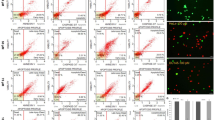
Compounds 3, 4, and 5 display cytotoxicity against MCF-7, HeLa, SKOV3, and A498 cancer cells. DNA ladders appear in cells treated with compounds 3, 4, and 5. Within those, compound 4 exhibits the greatest activity in regards to sub-G1 accumulations in the cell cycle and the activation of caspase-3/7. Furthermore, Fas and Fas ligand levels are elevated by compound 4, implying that the apoptosis is in part mediated through the signals. On the other hand, compounds 1 and 7 display chemosensitizing activity since cytotoxicity of doxorubicine and etoposide is enhanced in combination with compound 1 and 7, respectively, in MCF-7/adr (doxorubicin-resistant) and MCF-7/vp (etoposide-resistant).
Conclusion:
The cytotoxicity of indoloquinazolines is structure-dependent rather than cell type-dependent due to the similar degree of cytotoxicity induced by the individual compounds in all four cell lines. Further modification of the tryptanthrin skeleton is important to develop novel anticancer agents bearing either cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells or drug resistance reversal in MCF-7/adr and MCF-7/vp.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Zakeri Z, Lockshin RA . Cell death: history and future. Adv Exp Med Biol 2008; 615: 1–11.
Debatin KM . Apoptosis pathways in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2004; 53: 153–9.
Thorburn A . Death receptor-induced cell killing. Cell Signal 2004; 16: 139–44.
Nagata S, Golstein P . The Fas death factor. Science 1995; 267: 1449–56.
Hengartner MO . The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 2000; 407: 770–6.
Janicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR, Porter AG . Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 9357–60.
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM . Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 1998; 281: 1305–8.
Liu X, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X . DFF, a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to trigger dna fragmentation during apoptosis. Cell 1997; 89: 175–84.
Luqmani YA . Mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Med Princ Pract 2005; 14: 35–48.
Honda G, Tabata M . Isolation of antifungal principle tryptanthrin, from Strobilanthes cusia O. Kuntze. Planta Med 1979; 36: 85–90.
Honda G, Tabata M, Tsuda M . The antimicrobial specificity of tryptanthrin. Planta Med 1979; 37: 172–4.
Schrenk D, Riebniger D, Till M, Vetter S, Fiedler H-P . Tryptanthrins: A novel class of agonists of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Biochem Pharmacol 1997; 54: 165–71.
Ishihara T, Kohno K, Ushio S, Iwaki K, Ikeda M, Kurimoto M . Tryptanthrin inhibits nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 synthesis by murine macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol 2000; 407: 197–204.
Kimoto T, Hino K, Koya-Miyata S, Yamamoto Y, Takeuchi M, Nishizaki Y, et al. Cell differentiation and apoptosis of monocytic and promyelocytic leukemia cells (U-937 and HL-60) by tryptanthrin, an active ingredient of Polygonum tinctorium Lour. Pathol Int 2001; 51: 315–25.
Sharma VM, Prasanna P, Seshu KV, Renuka B, Rao CV, Kumar GS, et al. Novel indolo[2,1-b]quinazoline analogues as cytostatic agents: synthesis, biological evaluation and structure-activity relationship. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2002; 12: 2303–7.
Yu ST, Chen TM, Tseng SY, Chen YH . Tryptanthrin inhibits MDR1 and reverses doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 358: 79–84.
Chen GS, Bhagwat BV, Liao PY, Chen HT, Lin SB, Chern JW . Specific stabilization of DNA triple helices by indolo[2,1-b]quinazolin-6,12-dione derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2007; 17: 1769–72.
Gibson S, Tu S, Oyer R, Anderson SM, Johnson GL . Epidermal growth factor protects epithelial cells against Fas-induced apoptosis. requirement for Akt activation. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 17612–8.
Nagata S . Fas ligand-induced apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet 1999; 33: 29–55.
Reimer T, Herrnring C, Koczan D, Richter D, Gerber B, Kabelitz D, et al. FasL: Fas ratio -- a prognostic factor in breast carcinomas. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 822–8.
Gottesman MM, Ling V . The molecular basis of multidrug resistance in cancer: The early years of P-glycoprotein research. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 998–1009.
Kimura Yasuhisa MS-yMMUK . Mechanism of multidrug recognition by MDR1/ABCB1. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 1303–10.
Xu D, Hyunmin K, Michael F, Juliano RL . Strategies for inhibition of MDR1 gene expression. Mol Pharmacol 2004; 66: 268–75.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Science Council grant NSC 89-2320-B-002-232. We thank Dr Chih-hsin YANG for kindly providing drug-sensitive and drug-resistant cell lines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, St., Chern, Jw., Chen, Tm. et al. Cytotoxicity and reversal of multidrug resistance by tryptanthrin-derived indoloquinazolines. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31, 259–264 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.198
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.198
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A convenient synthesis of spiroindolo[2,1-b]quinazoline-6,2′-[1,3,4]oxadiazoles from tryptanthrin and nitrile imines
Monatshefte für Chemie - Chemical Monthly (2019)
-
Progress in the studies on tryptanthrin, an alkaloid of history
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2013)
-
Synthesis and properties of 6,6-di(indol-3-yl)-indolo[2,1-b]quinazolin-12(6H)-one and its 2,8-dimethyl and 2,8-dibromo derivatives
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds (2013)
-
Increased indigoid accumulation by plant defense activators in Polygonum tinctorium Lour.
Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry (2012)