Abstract
Aim:
To investigate the protection and the anti-oxidative mechanism afforded by chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia (CIHH) against ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in guinea pig hearts.
Methods:
Adult male guinea pigs were exposed to CIHH by mimicking a 5000 m high altitude (pB=404 mmHg, pO2=84 mmHg) in a hypobaric chamber for 6 h/day for 28 days. Langendorff-perfused isolated guinea pig hearts were used to measure variables of left ventricular function during baseline perfusion, ischemia and the reperfusion period. The activity and protein expression of antioxidant enzymes in the left myocardium were evaluated using biochemical methods and Western blotting, respectively. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) were assessed using ROS-sensitive fluorescence.
Results:
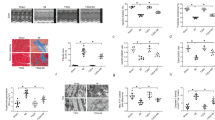
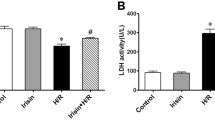
After 30 min of global no-flow ischemia followed by 60 min of reperfusion, myocardial function had better recovery rates in CIHH guinea pig hearts than in control hearts. The activity and protein expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) were significantly increased in the myocardium of CIHH guinea pigs. Pretreatment of control hearts with an antioxidant mixture containing SOD and CAT exerted cardioprotective effects similar to CIHH. The irreversible CAT inhibitor aminotriazole (ATZ) abolished the cardioprotection of CIHH. Cardiac contractile dysfunction and oxidative stress induced by exogenous hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) were attenuated by CIHH and CAT.
Conclusions:
These data suggest that CIHH protects the heart against I/R injury through upregulation of antioxidant enzymes in guinea pig.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Zhuang J, Zhou ZN . Protective effects of intermittent hypoxic adaptation on myocardium and its mechanism. Biol Signals Recept 1999; 8: 316–22.
Zhang Y, Yang HT, Zhou ZN . Cardioprotection of intermittent hypoxia. Acta Physiol Sin 2007; 59: 601–13.
Zhang Y, Zhong N, Zhou ZN . Effects of intermittent hypoxia on action potential and contraction in non-ischemic and ischemic rat papillary muscle. Life Sci 2000; 67: 2465–71.
Zhang Y, Zhong N, Zhu HF, Zhou ZN . Antiarrhythmic and antioxidative effects of intermittent hypoxia exposure on rat myocardium. Acta Physiol Sin 2000; 52: 89–92.
Zong P, Setty S, Sun W, Martinez R, Tune JD, Ehrenburg IV, et al. Intermittent hypoxic training protects canine myocardium from infarction. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2004; 229: 806–12.
Zhong N, Zhang Y, Fang QZ, Zhou ZN . Intermittent hypoxia exposure-induced heat-shock protein 70 expression increases resistance of rat heart to ischemic injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2000; 21: 467–72.
Zhong N, Zhang Y, Zhu HF, Wang JC, Fang QZ, Zhou ZN . Myocardial capillary angiogenesis and coronary flow in ischemia tolerance rat by adaptation to intermittent high altitude hypoxia. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2002; 23: 305–10.
Ding HL, Zhu HF, Dong JW, Zhu WZ, Zhou ZN . Intermittent hypoxia protects the rat heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating protein kinase C. Life Sci 2004; 75: 2587–603.
Zhu HF, Dong JW, Zhu WZ, Ding HL, Zhou ZN . ATP-dependent potassium channels involved in the cardiac protection induced by intermittent hypoxia against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Life Sci 2003; 73: 1275–87.
Bansal P, Gupta SK, Ojha SK, Nandave M, Mittal R, Kumari S, et al. Cardioprotective effect of lycopene in the experimental model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem 2006; 289: 1–9.
Makazan Z, Saini H K, Dhalla NS . Role of oxidative stress in alterations of mitochondrial function in ischemic-reperfused hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2007; 292: H1986–94.
Kourie JI . Interaction of reactive oxygen species with ion transport mechanisms. Am J Physiol 1998; 275: C1–24.
Eigel BN, Gursahani H, Hadley RW . ROS are required for rapid reactivation of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in hypoxic reoxygenated guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2004; 286: H955–63.
Yun YS, Lee YN . Production of superoxide dismutase by Deinococcus radiophilus. J Biochem Mol Biol 2003; 36: 282–7.
Chen CF, Tsai SY, Ma MC, Wu MS . Hypoxic preconditioning enhances renal superoxide dismutase levels in rats. J Physiol 2003; 552: 561–9.
Kim CH, Hong C, Chun YS, Kim GT, Park JW, Kim MS . Hyperbaric oxygenation pretreatment induces catalase and reduces infarct size in ischemic rat myocardium. Eur J Physiol 2001; 442: 519–25.
Zhu WZ, Dong JW, Ding HL, Yang HT, Zhou ZN . Postnatal development in intermittent hypoxia enhances resistance to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in male rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 2004; 91: 716–22.
Nakanishi K, Tajima F, Nakamura A, Yagura S, Ookawara T, Yamashita H, et al. Effects of hypobaric hypoxia on antioxidant enzymes in rats. J Physiol 1995; 489: 869–76.
Kolar F, Jezkova J, Balkova P, Breh J, Neckar J, Novak F, et al. Role of oxidative stress in PKC- upregulation and cardioprotection induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2007; 292: H224–30.
Turek Z, Ringnalda BE, Moran O, Kreuzer F . Oxygen transport in guinea pigs native to high altitude. Pflugers Arch 1980; 384: 109–15.
Rivera CM, Lebn VF, Huicho L, Monge CC . Ventilatory response to severe acute hypoxia in guinea pigs and rats with low hemoglobin-oxygen affinity induced by phytic acid. Comp Biochem Physiol 1995; 112: 411–6.
Su SW, Wang YL, Li JX, Mei HS, Yin JX . Relationship between cardiotonic effects and inhibition on cardiac sarcolemmal Na+,K+-ATPase of strophanthidin at low concentrations. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2003; 24: 1103–7.
Kirshenbaum LA, Singal PK . Increase in endogenous antioxidant enzymes protects hearts against reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol 1993; 265: H484–93.
Maczewski M, Duda M, Pawlak W, Beresewicz A . Endothelial protection from reperfusion injury by ischemic preconditioning and diazoxide involves a SOD-like anti O2− mechanism. J Physiol Pharmacol 2004; 55: 537–50.
Zang Q, Maass DL, White J, Jureta W, Horton JW . Cardiac mitochondrial damage and loss of ROS defense after burn injury: the beneficial effects of antioxidant therapy. J Appl Physiol 2007; 102: 103–12.
Wang Y, Gao J, Mathias RT, Cohen IS, Sun X, Baldo GJ . alpha-Adrenergic effects on Na+-K+ pump current in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol 1998; 509: 117–28.
Jun J, Savransky S, Nanayakkara A, Bevans S, Li J, Smith L, et al. Intermittent hypoxia has organ-specific effects on oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2008; 295: R1274–81.
Bychkov R, Pieper K, Ried C, Milosheva M, Bychkov E, Luft FC . Hydrogen peroxide, potassium currents, and membrane potential in human endothelial cells. Circulation 1999; 99: 1719–25.
Nie H, Xiong LZ, Lao N, Chen SY, Xu N, Zhu ZH . Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning induces tolerance against spinal cord ischemia by upregulation of antioxidant enzymes in rabbits. J Cerebr Blood F Met 2006; 26: 666–74.
Sekili S, McCay PB, Li XY, Zughaib M, Sun JZ, Tang L . Direct evidence that the hydroxyl radical plays a pathogenetic role in myocardial “stunning” in the conscious dog and demonstration that stunning can be markedly attenuated without subsequent adverse effects. Circ Res 1993; 73: 705–23.
Woo YJ, Zhang JC, Vijayasarathy C, Zwacka RM, Englehardt JF, Gardner TJ . Recombinant adenovirus-mediated cardiac gene transfer of superoxide dismutase and catalase attenuates postischemic contractile dysfunction. Circulation 1998; 98: II255–60.
Ostadal P, Elmoselhi AB, Zdobnicka I, Lukas A, Elimban V, Dhalla NS . Role of oxidative stress in ischemia-reperfusion-induced changes in Na+,K+-ATPase isoform expression in rat heart. Antioxid Redox Sign 2004; 6: 914–23.
Marklund SL, Westman NG, Lundgren E, Roos G . Copper- and zinc-containing superoxide dismutase, manganese-containing superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase in normal and neoplastic human cell lines and normal human tissues. Cancer Res 1982; 42: 1955–61.
Hoshida S, Yamashita N, Otsu K, Hori M . The importance of manganese superoxide dismutase in delayed preconditioning: involvement of reactive oxygen species and cytokines. Cardiovasc Res 2002; 55: 495–505.
Park AM, Suzuki YJ . Effects of intermittent hypoxia on oxidative stress-induced myocardial damage in mice. J Appl Physiol 2007; 102: 1806–14.
Kaplan P, Matejovicova M, Herijgers P, Flameng W . Lack of the effect of superoxide dismutase and catalase on Na+,K+-ATPase activity in stunned rabbit hearts. Physiol Res 2008; 57: S61–6.
Jones SP, Hoffmeyer MR, Sharp BR, Ho YS, Lefer DJ . Role of intracellular antioxidant enzymes after in vivo myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Physiol 2003; 284: H277–82.
Storz G, Tartaglia LA . OxyR: a regulator of antioxidant genes. J Nutr 1992; 122: 627–30.
Storz G, Tartaglia LA, Ames BN . Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science 1990; 248: 189–94.
Budas GR, Churchill EN, Rosen DM . Cardioprotective mechanisms of PKC isozyme-selective activators and inhibitors in the treatment of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Res 2007; 55: 523–36.
Sukmawan R, Yada T, Toyota E, Neishi Y, Kume T, Shinozaki Y, et al. Edaravone preserves coronary microvascular endothelial function after ischemia/reperfusion on the beating canine heart in vivo. J Pharmacol Sci 2007; 104: 341–8.
Auyeung Y, Sievers RE, Weng D, Barbosa V, Wolfe CL . Catalase inhibition with 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole does not abolish infarct size reduction in heat-shocked rats. Circulation 1995; 92: 3318–22.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (No 301360).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Hc., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Ln. et al. Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury through upregulation of antioxidant enzymes in adult guinea pigs. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30, 947–955 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.57
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2009.57
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The effect of chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia improving liver damage in metabolic syndrome rats through ferritinophagy
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2023)
-
Bloodletting Acupuncture at Jing-Well Points Alleviates Myocardial Injury in Acute Altitude Hypoxic Rats by Activating HIF-1α/BNIP3 Signaling-Mediated Mitochondrial Autophagy and Decreasing Oxidative Stress
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2023)
-
Short-term exercise provides left ventricular myocardial protection against intermittent hypoxia-induced apoptosis in rats
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2011)