Abstract
Aim:
To determine the efficacy and toxicities of sorafenib in the treatment of patients with multiple recurrences of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after liver transplantation in a Chinese population.
Methods:
Twenty patients with multiple recurrences of HCC after liver transplantation were retrospectively studied. They received either transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) or TACE combined with sorafenib.
Results:
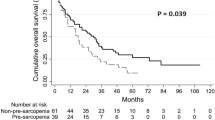
The median survival times (MST) after multiple recurrences was 14 months (TACE+sorafenib group) and 6 months (TACE only group). The difference was significant in MST between the two groups (P=0.005). The TACE + sorafenib group had more stable disease (SD) patients than the TACE group. The most frequent adverse events of sorafenib were hand–foot skin reaction and diarrhea. In the univariate analysis, preoperative bilirubin and CHILD grade are found to be significantly associated with tumor-free survival time, the survival time after multiple recurrences and overall survival time. TACE+sorafenib group showed a better outcome than single TACE treatment group. In the multivariate COX regression modeling, the preoperative high CHILD grade was found to be a risk factor of tumor-free survival time. In addition, the preoperative high bilirubin grade was also found to be a risk factor of survival time after recurrence and overall survival time. Furthermore, survival time after recurrence and overall survival time were also associated with therapeutic schedule, which was indicated by the GROUP.
Conclusion:
Treatment with TACE and sorafenib is worthy of further study and may have more extensive application prospects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P . Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2005; 55: 74–108.
Yates MS, Kensler TW . Keap1 eye on the target: chemoprevention of liver cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28: 1331–42.
Sherman M . Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors, and screening. Semin Liver Dis 2005; 25: 143–54.
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J . Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2003; 362: 1907–17.
Mi JX, Wang GF, Wang HB, Sun XQ, Ni XY, Zhang XW, et al. Synergistic antitumoral activity and induction of apoptosis by novel pan Bcl-2 proteins inhibitor apogossypolone with adriamycin in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2008; 29: 1467–77.
Llovet JM, Schwartz M, Mazzaferro V . Resection and liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 2005; 25: 181–200.
Pan QW, Zhong SY, Liu BS, Liu J, Cai R, Wang YG, et al. Enhanced sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to chemotherapy with a Smac-armed oncolytic adenovirus. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28: 1996–2004.
Bruix J, Sherman M . Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2005; 42: 1208–36.
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J . Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2003; 362: 1907–17.
Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M, Llovet JM . Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2004; 5: 215–9.
Thomas MB, Zhu AX . Hepatocellular carcinoma: the need for progress. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 2892–9.
Llovet JM, Bruix J . Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003; 37: 429–42.
Lopez PM, Villanueva A, Llovet JM . Systematic review: evidence-based management of hepatocellular carcinoma- an updated analysis of randomized controlled trials. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006; 23: 1535–47.
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 7099–109.
Chang YS, Adnane J, Trail PA, Levy J, Henderson A, Xue D, et al. Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006) inhibits tumor growth and vascularization and induces tumor apoptosis and hypoxia in RCC xenograft models. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2007; 59: 561–74.
Ito Y, Sasaki Y, Horimoto M, Wada S, Tanaka Y, Kasahara A, et al. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases/ extracellular signal-regulated kinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1998; 27: 951–8.
Villanueva A, Newell P, Chiang DY, Friedman SL, Llovet JM . Genomics and signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 2007; 27: 55–76.
Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, Farina M, Conner EA, Lee JS, et al. Ubiquitous activation of Ras and Jak/Stat pathways in human HCC. Gastroenterology 2006; 130: 1117–28.
Semela D, Dufour JF . Angiogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2004; 41: 864–80.
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A, Wilkie D, et al. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 11851–8.
Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R, Pivetta G, Ragazzi R, Baldan A, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): the role of angiogenesis and invasiveness. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103: 914–21.
Strebel BM, Dufour JF . Combined approach to hepatocellular carcinoma: a new treatment concept for nonresectable disease. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2008; 8: 1743–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Wf., Qiu, Zq., Yu, Y. et al. Sorafenib extends the survival time of patients with multiple recurrences of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31, 1643–1648 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.124
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.124
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Outcomes of Systemic Treatment in Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinomas Following Liver Transplants
Advances in Therapy (2021)
-
The combination therapy of transarterial chemoembolisation and sorafenib is the preferred palliative treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2020)
-
Galectin-1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma and the combined therapeutic effect of OTX008 galectin-1 inhibitor and sorafenib in tumor cells
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
The role of metronomic capecitabine for treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Sorafenib enhances effects of transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2014)