Abstract
Aim:
To investigate the effect of systemic administration dexmedetomidine, a selective alpha 2 adrenergic receptor (α2AR) agonist, on thermal hyperalgesia and spinal glial activation evoked by monoarthritis (MA).
Methods:
MA was induced by an intra-articular injection of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA). Thermal hyperalgesia was measured by Hargreaves' test. The spinal glial activation status was analyzed by GFAP (an astrocytic marker) and Iba-1 (a microglial marker) immunohistochemistry or immunoblotting.
Results:
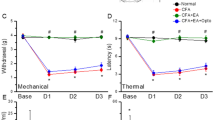
Unilateral intra-articular injection of CFA produced a robust glial activation of astrocytes and microglia in the spinal cord, which was associated with the development and maintenance of thermal hyperalgesia. Intraperitoneal (ip) injection of dexmedetomidine (2.5 and 10 μg/kg) was repeatedly given once daily for 5 days with the first injection 60 min before intra-articular CFA. At the dose of 10 μg/kg, dexmedetomidine significantly attenuated MA-induced ipsilateral hyperalgesia from day 2 to day 5. MA-induced up-regulation of GFAP expression on both sides of the spinal dorsal horn was significantly suppressed by day 5 post-MA following dexmedetomidine application, whereas MA-induced Iba-1 up-regulation was only partially suppressed.
Conclusion:
Systemic dexmedetomidine inhibits the activation of spinal glia, which is possibly associated with its antihyperalgesia in monoarthritic rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Schaible HG, Ebersberger A, Von Banchet GS . Mechanisms of pain in arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2002; 966: 343–54.
Cao H, Zhang YQ . Spinal glial activation contributes to pathological pain states. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2008; 32: 972–83.
Deleo JA, Yezierski RP . The role of neuroinflammation and neuroimmune activation in persistent pain. Pain 2001: 90; 1–6.
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF . Glial activation: a driving force for pathological pain. Trends Neurosci 2001; 24: 450–5.
Hua XY, Svensson CI, Matsui T, Fitzsimmons B, Yaksh TL, Webb M . Intrathecal minocycline attenuates peripheral inflammation-induced hyperalgesia by inhibiting p38 MAPK in spinal microglia. Eur J Neurosci 2005; 22: 2431–40.
Raghavendra V, Tanga FY, DeLeo JA . Complete Freunds adjuvant-induced peripheral inflammation evokes glial activation and proinflammatory cytokine expression in the CNS. Eur J Neurosci 2004; 20: 467–73.
Sun S, Mao Ying QL, Cao H, Li TT, Han M, Pang HL, et al. Is functional state of spinal microglia involved in the anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects of electroacupuncture in rat model of monoarthritis? Neurobiol Dis 2007; 26: 558–68.
Sun S, Cao H, Han M, Li TT, Zhao ZQ, Zhang YQ . Evidence for suppression of electroacupuncture on spinal glial activation and behavioral hypersensitivity in a rat model of monoarthritis. Brain Res Bull 2008; 75: 83–93.
Sun S, Cao H, Han M, Li TT, Pan HL, Zhao ZQ, et al. New evidence for the involvement of spinal fractalkine receptor in pain facilitation and spinal glial activation in rat model of monoarthritis. Pain 2007; 129: 64–75.
Ledeboer A, Sloane EM, Milligan ED, Frank MG, Mahony JH, Maier SF, et al. Minocycline attenuates mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in rat models of pain facilitation. Pain 2005; 115: 71–83.
Milligan ED, Twining C, Chacur M, Biedenkapp J, O'Connor K, Poole S, et al. Spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines mediate mirror-image neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 1026–40.
Sun S, Chen WL, Wang PF, Zhao ZQ, Zhang YQ . Disruption of glial function enhances electroacupuncture analgesia in arthritic rats. Exp Neurol 2006: 198; 294–302.
Al-Metwalli RR, Mowafi HA, Ismail SA, Siddiqui AK, Al-Ghamdi AM, Shafi MA, et al. Effect of intra-articular dexmedetomidine on postoperative analgesia after arthroscopic knee surgery. Br J Anaesth 2008; 101: 395–9.
Jaakola ML, Salonen M, Lehtinen R, Scheinin H . The analgesic action of dexmedetomidine — a novel alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist — in healthy volunteers. Pain 1991; 46: 281–5.
Xu M, Kontinen VK, Kalso E . Effects of radolmidine, a novel alpha2-adrenergic agonist compared with dexmedetomidine in different pain models in the rat. Anesthesiology 2000; 93: 473–81.
Guneli E, Karabay Yavasoglu NU, Apaydin S, Uyar M, Uyar M . Analysis of the antinociceptive effect of systemic administration of tramadol and dexmedetomidine combination on rat models of acute and neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2007; 88: 9–17.
Shimode N, Fukuoka T, Tanimoto M, Tashiro C, Tokunaga A, Noguchi K . The effects of dexmedetomidine and halothane on Fos expression in the spinal dorsal horn using a rat postoperative pain model. Neurosci Lett 2003; 343: 45–8.
Zhang WS, Xu H, Xu B, Sun S, Deng XM, Zhang YQ . Antihyperalgesic effect of systemic dexmedetomidine and gabapentin in a rat model of monoarthritis. Brain Res 2009; 1264: 57–66.
Malmberg AB, Hedley LR, Jasper JR, Hunter JC, Basbaum AI . Contribution of alpha(2) receptor subtypes to nerve injury-induced pain and its regulation by dexmedetomidine. Br J Pharmacol 2001; 132: 1827–36.
Bourgoin S, Pohl M, Mauborgne A, Benoliel JJ, Collin E, Hamon M, et al. Monoaminergic control of the release of calcitonin gene related peptide- and substance P-like materials from rat spinal cord slices. Neuropharmacology 1993; 32: 633–40.
Holz GG4th, Kream RM, Spiegel A, Dunlap K . G proteins couple alpha-adrenergic and GABAb receptors to inhibition of peptide secretion from peripheral sensory neurons. J Neurosci 1989; 9: 657–66.
Pang IH, Vasko MR . Effect of depletion of spinal cord norepinephrine on morphine-induced antinociception. Brain Res 1986; 371: 171–6.
Takano Y, Yaksh TL . Chronic spinal infusion of dexmedetomidine, ST-91 and clonidine: spinal alpha2 adrenoceptor subtypes and intrinsic activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1993; 264: 327–35.
Enkvist MO, Hämäläinen H, Jansson CC, Kukkonen JP, Hautala R, Courtney MJ, Akerman KE . Coupling of astroglial alpha 2-adrenoreceptors to second messenger pathways. J Neurochem. 1996; 66: 2394–401.
Mori K, Ozaki E, Zhang B, Yang L, Yokoyama A, Takeda I, et al. Effects of norepinephrine on rat cultured microglial cells that express alpha1, alpha2, beta1 and beta2 adrenergic receptors. Neuropharmacology 2002; 43: 1026–34.
Zhuang ZY, Gerner P, Woolf CJ, Ji RR . ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in this neuropathic pain model. Pain 2005; 114: 149–59.
Coursin DB, Coursin DB, Maccioli GA . Dexmedetomidine. Curr Opin Crit Care 2001; 7: 221–26.
Unnerstall JR, Kopajtic TA, Kuhar MJ . Distribution of alpha 2 agonist binding sites in the rat and human central nervous system: analysis of some functional, anatomic correlates of the pharmacologic effects of clonidine and related adrenergic agents. Brain Res 1984; 319: 69–101.
Guo TZ, Jiang JY, Buttermann AE, Maze M . Dexmedetomidine injection into the locus ceruleus produces antinociception. Anesthesiology 1996; 84: 873–81.
Ishii H, Kohno T, Yamakura T, Ikoma M, Baba H . Action of dexmedetomidine on the substantia gelatinosa neurons of the rat spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci 2008; 27: 3182–90.
Nakamura M, Ferreira SH . Peripheral analgesic action of clonidine: mediation by release of endogenous enkephalin-like substances. Eur J pharmacol 1988; 146: 223–8.
Garrison CJ, Dougherty PM, Carlton SM . GFAP expression in lumbar spinal cord of naive and neuropathic rats treated with MK-801. Exp Neurol 1994; 129: 237–43.
Raghavendra V, Rutkowski MD, DeLeo JA . The role of spinal neuroimmune activation in morphine tolerance/hyperalgesia in neuropathic and sham-operated rats. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 9980–9.
Sweitzer SM, Colburn RW, Rutkowski M, DeLeo JA . Acute peripheral inflammation induces moderate glial activation and spinal IL-1beta expression that correlates with pain behavior in the rat. Brain Res 1999; 829: 209–21.
Clark AK, Gentry C, Bradbury EJ, McMahon SB, Malcangio M . Role of spinal microglia in rat models of peripheral nerve injury and inflammation. Eur J Pain 2007; 11: 223–30.
Lin T, Li K, Zhang FY, Zhang ZK, Light AR, Fu KY . Dissociation of spinal microglia morphological activation and peripheral inflammation in inflammatory pain models. J Neuroimmunol 2007; 192: 40–8.
Lindia JA, McGowan E, Jochnowitz N, Abbadie C . Induction of CX3CL1 expression in astrocytes and CX3CR1 in microglia in the spinal cord of a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Pain 2005; 6: 434–8.
Raghavendra V, Agrewala JN, Kulkarni SK . Melatonin reversal of lipopolysaccharides-induced thermal and behavioral hyperalgesia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2000; 395: 15–21.
Chacur M, Gutierrez JM, Milligan ED, Wieseler-Frank J, Britto LRG, Maier SF, et al. Snake venom components enhance pain upon subcutaneous injection: an initial examination of spinal cord mediators. Pain 2004; 111: 65–76.
Guo LH, Trautmann K, Schluesener HJ . Expression of P2X4 receptor by lesional activated microglia during formalin-induced inflammatory pain. J Neuroimmunol 2005; 163: 120–7.
Lan L, Yuan H, Duan L, Cao R, Gao B, Shen J, et al. Blocking the glial function suppresses subcutaneous formalin-induced nociceptive behavior in the rat. Neurosci Res 2007; 57: 112–9.
Watkins LR, Martin D, Ulrich P, Tracey KJ, Maier SF . Evidence for the involvement of spinal cord glia in subcutaneous formalin induced hyperalgesia in the rat. Pain 1997; 71: 225–35.
Elmquist JK, Scammell TE, Saper CB . Mechanisms of CNS response to systemic immune challenge: the febrile response. Trends Neurosci. 1997; 20: 565–70.
Huber JD, Witt KA, Hom S, Egleton RD, Mark KS, Davis TP . Inflammatory pain alters blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junctional protein expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2001; 280: H1241–8.
Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG . Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci 1999; 22: 208–15.
Marriott I . The role of tachykinins in central nervous system inflammatory responses. Frontiers in Bioscience 2004; 9: 2153–65.
Tsuda M, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Koizumi S, Mizokoshi A, Kohsaka S, Salter MW, et al. P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 2003; 424: 778–83.
Li X, Eisenach JC . alpha2A-adrenoceptor stimulation reduces capsaicin-induced glutamate release from spinal cord synaptosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001; 299: 939–44.
Garrido E, Perez-Garcia C, Alguacil LF, Diez-Fernandez C . The alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist yohimbine reduces glial fibrillary acidic protein upregulation induced by chronic morphine administration. Neurosci Lett 2005; 383: 141–4.
Alonso E, Garrido E, Diez-Fernandez C, Perez-Garcia C . Herradon G, Ezquerra L, et al. Yohimbine prevents morphine-induced changes of glial fibrillary acidic protein in brainstem and alpha2-adrenoceptor gene expression in hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 2007; 412; 163–7.
Milner TA, Lee A, Aicher SA, Rosin DL . Hippocampal alpha2a-adrenergic receptors are located predominantly presynaptically but are also found postsynaptically and in selective astrocytes. J Comp Neurol. 1998; 395: 310–27.
Stone LS, Broberger C, Vulchanova L, Wilcox GL, Hokfelt T, Riedl MS, et al. Differential distribution of alpha2A and alpha2C adrenergic receptor. Immunoreactivity in the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 1998; 18: 5928–37.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Fundation of China (NSFC, 30870835, and 30821002) and National Basic Research Program of China (2007CB512303, 2007CB512502, and 2006CB500807).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Zhang, Ws., Yang, Jl. et al. Dexmedetomidine blocks thermal hyperalgesia and spinal glial activation in rat model of monoarthritis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31, 523–530 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.32
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.32