Abstract
Aim:
Ferulic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid, FA) provides neuroprotection against apoptosis in a transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) model. This study was to further investigate the anti-apoptotic effect of FA during reperfusion after cerebral ischemia.
Methods:
Rats were subjected to 90 min of cerebral ischemia followed by 3 or 24 h of reperfusion after which they were sacrificed.
Results:
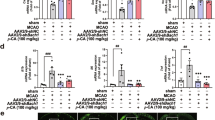
Intravenous FA (100 mg/kg) administered immediately after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) or 2 h after reperfusion effectively abrogated the elevation of postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95), neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), nitrotyrosine, and cleaved caspase-3 levels as well as apoptosis in the ischemic cortex at 24 h of reperfusion. FA further inhibited Bax translocation, cytochrome c release, and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase phosphorylation. Moreover, FA enhanced the expression of gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 1 (GABAB1) in the ischemic cortex at 3 and 24 h of reperfusion. In addition, nitrotyrosine-positive cells colocalized with cleaved caspase-3-positive cells, and phospho-p38 MAP kinase-positive cells colocalized with nitrotyrosine- and Bax-positive cells, indicating a positive relationship among the expression of nitrotyrosine, phospho-p38 MAP kinase, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3. The mutually exclusive expression of GABAB1 and nitrotyrosine revealed that there is a negative correlation between GABAB1 and nitrotyrosine expression profiles. Additionally, pretreatment with saclofen, a GABAB receptor antagonist, abolished the neuroprotection of FA against nitric oxide (NO)-induced apoptosis.
Conclusion:
FA significantly enhances GABAB1 receptor expression at early reperfusion and thereby provides neuroprotection against p38 MAP kinase-mediated NO-induced apoptosis at 24 h of reperfusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kirino T . Delayed neuronal death. Neuropathology 2000; 20: S95–7.
Friedlander RM . Apoptosis and caspases in neurodegenerative diseases. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1365–75.
Kermer P, Liman J, Weishaupt JH, Bahr M . Neuronal apoptosis in neurodegenerative diseases: from basic research to clinical application. Neurodegener Dis 2004; 1: 9–19.
Liu C, Lin N, Wu B, Qiu Y . Neuroprotective effect of memantine combined with topiramate in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Brain Res 2009; 1282: 173–82.
Cardenas A, Moro MA, Hurtado O, Leza JC, Lorenzo P, Castrillo A, et al. Implication of glutamate in the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase after oxygen and glucose deprivation in rat forebrain slices. J Neurochem 2000; 74: 2041–8.
Shen YC, Wang YH, Chou YC, Liou KT, Yen JC, Wang WY, et al. Dimemorfan protects rats against ischemic stroke through activation of sigma-1 receptor-mediated mechanisms by decreasing glutamate accumulation. J Neurochem 2008; 104: 558–72.
Thiyagarajan M, Kaul CL, Sharma SS . Neuroprotective efficacy and therapeutic time window of peroxynitrite decomposition catalysts in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Br J Pharmacol 2004; 142: 899–911.
Abulrob A, Tauskela JS, Mealing G, Brunette E, Faid K, Stanimirovic D . Protection by cholesterol-extracting cyclodextrins: a role for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor redistribution. J Neurochem 2005; 92: 1477–86.
Hsiao G, Lee JJ, Chen YC, Lin JH, Shen MY, Lin KH, et al. Neuroprotective effects of PMC, a potent alpha-tocopherol derivative, in brain ischemia-reperfusion: reduced neutrophil activation and anti-oxidant actions. Biochem Pharmacol 2007; 73: 682–93.
Han D, Zhang QG, Yong L, Li C, Zong YY, Yu CZ, et al. Co-activation of GABA receptors inhibits the JNK3 apoptotic pathway via the disassembly of the GluR6-PSD95-MLK3 signaling module in cerebral ischemic-reperfusion. FEBS Lett 2008; 582: 1298–306.
Elibol B, Soylemezoglu F, Unal I, Fujii M, Hirt L, Huang PL, et al. Nitric oxide is involved in ischemia-induced apoptosis in brain: a study in neuronal nitric oxide synthase null mice. Neuroscience 2001; 105: 79–86.
Kawasaki T, Kitao T, Nakagawa K, Fujisaki H, Takegawa Y, Koda K, et al. Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in cultured rat astrocytes: protection by edaravone, a radical scavenger. Glia 2007; 55: 1325–33.
Wang Q, Chen SY, Xiong LZ, Jin WL, Yang J . Neuroprotective effect of sodium ferulate on transient focal cerebral ischemia by weakening activation of postsynaptic density-95 in rats. Chin J Traumatol 2005; 8: 297–302.
Cheng CY, Su SY, Tang NY, Ho TY, Chiang SY, Hsieh CL . Ferulic acid provides neuroprotection against oxidative stress-related apoptosis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ICAM-1 mRNA expression in rats. Brain Res 2008; 1209: 136–50.
Jin Y, Yan EZ, Fan Y, Guo XL, Zhao YJ, Zong ZH, et al. Neuroprotection by sodium ferulate against glutamate-induced apoptosis is mediated by ERK and PI3 kinase pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28: 1881–90.
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R . Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989; 20: 84–91.
Xu X, Zheng X . Potential involvement of calcium and nitric oxide in protective effects of puerarin on oxygen-glucose deprivation in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Ethnopharmacol 2007; 113: 421–6.
Ma J, Zhang GY, Liu Y, Yan JZ, Hao ZB . Lithium suppressed Tyr-402 phosphorylation of proline-rich tyrosine kinase (Pyk2) and interactions of Pyk2 and PSD-95 with NR2A in rat hippocampus following cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Res 2004; 49: 357–62.
Bredt DS . Endogenous nitric oxide synthesis: biological functions and pathophysiology. Free Radic Res 1999; 31: 577–96.
Aarts M, Liu Y, Liu L, Besshoh S, Arundine M, Gurd JW, et al. Treatment of ischemic brain damage by perturbing NMDA receptor- PSD-95 protein interactions. Science 2002; 298: 846–50.
Zhu C, Wang X, Qiu L, Peeters-Scholte C, Hagberg H, Blomgren K . Nitrosylation precedes caspase-3 activation and translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor in neonatal rat cerebral hypoxia-ischaemia. J Neurochem 2004; 90: 462–71.
Jung JY, Han CR, Jeong YJ, Kim HJ, Lim HS, Lee KH, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in rat PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 2007; 411: 222–7.
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG . Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 2009; 40: e331–9.
Bal-Price A, Brown GC . Nitric-oxide-induced necrosis and apoptosis in PC12 cells mediated by mitochondria. J Neurochem 2000; 75: 1455–64.
Love S . Apoptosis and brain ischaemia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2003; 27: 267–82.
Shou Y, Li L, Prabhakaran K, Borowitz JL, Isom GE . p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates Bax translocation in cyanide-induced apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 2003; 75: 99–107.
Choi JM, Shin HK, Kim KY, Lee JH, Hong KW . Neuroprotective effect of cilostazol against focal cerebral ischemia via antiapoptotic action in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2002; 300: 787–93.
Solaroglu I, Tsubokawa T, Cahill J, Zhang JH . Anti-apoptotic effect of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neuroscience 2006; 143: 965–74.
Ghatan S, Larner S, Kinoshita Y, Hetman M, Patel L, Xia Z, et al. p38 MAP kinase mediates bax translocation in nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in neurons. J Cell Biol 2000; 150: 335–47.
Barone FC, Irving EA, Ray AM, Lee JC, Kassis S, Kumar S, et al. SB 239063, a second-generation p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, reduces brain injury and neurological deficits in cerebral focal ischemia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001; 296: 312–21.
Okuno S, Saito A, Hayashi T, Chan PH . The c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase signaling pathway mediates Bax activation and subsequent neuronal apoptosis through interaction with Bim after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 7879–87.
Cheng A, Chan SL, Milhavet O, Wang S, Mattson MP . p38 MAP kinase mediates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of neural progenitor cells. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 43320–27.
Vollenweider F, Bendfeldt K, Maetzler W, Otten U, Nitsch C . GABA(B) receptor expression and cellular localization in gerbil hippocampus after transient global ischemia. Neurosci Lett 2006; 395: 118–23.
Kuramoto N, Wilkins ME, Fairfax BP, Revilla-Sanchez R, Terunuma M, Tamaki K, et al. Phospho-dependent functional modulation of GABA(B) receptors by the metabolic sensor AMP-dependent protein kinase. Neuron 2007; 53: 233–47.
Francis J, Zhang Y, Ho W, Wallace MC, Zhang L, Eubanks JH . Decreased hippocampal expression, but not functionality, of GABAB receptors after transient cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurochem 1999; 72: 87–94.
Ouyang C, Guo L, Lu Q, Xu X, Wang H . Enhanced activity of GABA receptors inhibits glutamate release induced by focal cerebral ischemia in rat striatum. Neurosci Lett 2007; 420: 174–8.
Marinelli S, Federici M, Giacomini P, Bernardi G, Mercuri NB . Hypoglycemia enhances ionotropic but reduces metabotropic glutamate responses in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. J Neurophysiol 2001; 85: 1159–66.
Yang J, Klaidman LK, Chang ML, Kem S, Sugawara T, Chan P, et al. Nicotinamide therapy protects against both necrosis and apoptosis in a stroke model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2002; 73: 901–10.
Hossmann KA . Pathophysiology and therapy of experimental stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2006; 26: 1057–83.
Rondini L, Peyrat-Maillard MN, Marsset-Baglieri A, Berset C . Sulfated ferulic acid is the main in vivo metabolite found after short-term ingestion of free ferulic acid in rats. J Agric Food Chem 2002; 50: 3037–41.
Cheng CY, Ho TY, Lee EJ, Su SY, Tang NY, Hsieh CL . Ferulic acid reduces cerebral infarct through its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Am J Chin Med 2008; 36: 1105–19.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by Taiwan Department of Health Clinical Trial and Research Center of Excellence (DOH99-TD-B-111-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Cy., Su, Sy., Tang, Ny. et al. Ferulic acid inhibits nitric oxide-induced apoptosis by enhancing GABAB1 receptor expression in transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31, 889–899 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.66
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.66
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Date Palm as Source of Nutraceuticals for Health Promotion: a Review
Current Nutrition Reports (2022)
-
Analysis of NaoMaiTong Metabolites Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry in Rat Urine
Chromatographia (2017)