Abstract
Aim:
To develop a novel gastroretentive drug delivery system based on a self-microemulsifying (SME) lipid mixture for improving the oral absorption of the immunosuppressant tacrolimus.
Methods:
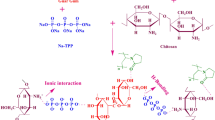
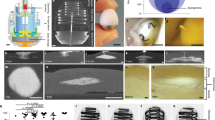
Liquid SME mixture, composed of Cremophor RH40 and monocaprylin glycerate, was blended with polyethylene oxide, chitosan, polyvinylpyrrolidone and mannitol, and then transformed into tablets via granulation, with ethanol as the wetting agent. The tablets were characterized in respect of swelling, bioadhesive and SME properties. In vitro dissolution was conducted using an HCl buffer at pH 1.2. Oral bioavailability of the tablets was examined in fasted beagle dogs.
Results:
The tablet could expand to 13.5 mm in diameter and 15 mm in thickness during the initial 20 min of contact with the HCl buffer at pH 1.2. The bioadhesive strength was as high as 0.98±0.06 N/cm2. The SME gastroretentive sustained-release tablets preserved the SME capability of the liquid SME formations under transmission electron microscope. The drug-release curve was fit to the zero-order release model, which was helpful in reducing fluctuations in blood concentration. Compared with the commercially available capsules of tacrolimus, the relative bioavailability of the SME gastroretentive sustained-release tablets was 553.4%±353.8%.
Conclusion:
SME gastroretentive sustained-release tablets can enhance the oral bioavailability of tacrolimus with poor solubility and a narrow absorption window.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Yamashita K, Nakate T, Okimoto K, Ohike A, Tokunaga Y, Ibuki R, et al. Establishment of new preparation method for solid dispersion formulation of tacrolimus. Int J Pharm 2003; 267: 79–91.
Kino T, Hatanaka H, Hashimoto M, Nishiyama M, Goto T, Okuhara M, et al. FK 506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces I. Fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. J Antibiot 1987; 42: 1249–55.
Plosker GL, Foster RH . Tacrolimus-a further update of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in the management of organ transplantation. Drugs 2000; 59: 323–89.
Borhade V, Nair H, Hegde D . Design and evaluation of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) of tacrolimus. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008; 9: 13–21.
Abdalla A, Klein S, Mader K . A new self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for poorly soluble drugs: characterization, dissolution, in vitro digestion and incorporation into solid pellets. Eur J Pharm Sci 2008; 35: 457–64.
Gursoy RN, Benita S . Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for improved oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Biomed Pharmacother 2004; 58: 173–82.
Abdalla A, Mader K . Preparation and characterization of a self-emulsifying pellet formulation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2007; 66: 220–6.
Nazzal S, Khan MA . Controlled release of a self-emulsifying formulation from a tablet dosage form: stability assessment and optimization of some processing parameters. Int J Pharm 2006; 315: 110–21.
Patil P, Joshi P, Paradkar A . Effect of formulation variables on preparation and evaluation of gelled self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) of ketoprofen. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004; 5: e42.
Joseph S, inventors; AluhaRx Inc., assignee. Solid self-emulsifying dosage form for improved delivery of poorly soluble hydrophobic compounds and the process for preparation there of. US Patent 10252158. 2002 Sep 23.
Tang B, Cheng G, Gu JC, Xu CH . Development of solid self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: preparation techniques and dosage forms. Drug Discovery Today 2008; 13: 606–12.
Serratoni M, Newton M, Booth S, Clarke A . Controlled drug release from pellets containing water-insoluble drugs dissolved in a self-emulsifying system. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2007; 65: 94–8.
Balakrishnan P, Lee BJ, Oh DH, Kim JO, Hong MJ, Jee JP, et al. Enhanced oral bioavailability of dexibuprofen by a novel solid self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2009; 72: 539–45.
Nazzal S, Nutan M, Palamakula A, Shah R, Zaghloul AA, Khan MA . Optimization of a self-nanoemulsified tablet dosage form of ubiquinone using response surface methodology: effect of formulation ingredients. Int J Pharm 2002; 240: 103–14.
Tuleu C, Newton M, Rose J, Euler D, Saklatvala R, Clarke A, et al. Comparative bioavailability study in dogs of a self-emulsifying formulation of progesterone presented in a pellet and liquid form compared with an aqueous suspension of progesterone. J Pharm Sci 2004; 93: 1495–502.
Tamura S, Tokunaga Y, Ibuki R, Amidon GL, Sezaki H, Yamashita S . The site-specific transport and metabolism of tacrolimus in rat small intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 306: 310–6.
Venkataramanan R, Swaminathan A, Prasad T, Jain A, Zuckerman S, Warty V, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus. Clin Pharmacokinet 1995; 29: 404–30.
Holm P, Norling T, Lademann AM, inventors; LIFECYCLE PHARMA A/S, assignee. Once daily oral dosage form comprising tacrolimus. Patent WO2008/145143. 2008 May 30.
Kagayama A, Tanimoto S, Fujisaki J, Kaibara A, Ohara K, Iwasaki K, et al. Oral absorption of FK506 in rats. Pharm Res 1993; 10: 1446–50.
Shigeki T, Atsuo O, Rinta I, Gordon L, Shinji Y . Tacrolimus is a class II low-solubility high-permeability drug: the effect of P-glycoprotein efflux on regional permeability of tacrolimus in rats. J Pharm Sci 2002; 91: 719–29.
Streubel A, Siepmann J, Bodmeier R . Gastroretentive drug delivery systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2006; 3: 217–33.
Strubing S, Abboud T, Contri RV, Metz H, Mader K . New insights on poly(vinyl acetate)-based coated floating tablets: Characterisation of hydration and CO2 generation by benchtop MRI and its relation to drug release and floating strength. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2008; 69: 708–17.
Ramji AKA, Chandra SRG, Prabhakar RV . Formulation and evaluation of swellable and floating gastroretentive ciprofloxacin hydrochloride tablets. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009; 10: 220–6.
Parikh DC, Amin AF . In vitro and in vivo techniques to assess the performance of gastro-retentive drug delivery systems: a review. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2008; 5: 951–65.
Gusler G, Berner B, Chau M, Berner B, inventors; Depomed, Inc, assignee. Optimal polymer mixtures for gastric. Patent AU2002337974. 2002 Oct 22.
Wu N, Wang LS, Tan DCW, Moochhala SM, Yang YY . Mathematical modeling and in vitro study of controlled drug release via a highly swellable and dissoluble polymer matrix: polyethylene oxide with high molecular weights. J Control Release 2005; 102: 569–81.
Mahalingam R, Jasti B, Birudaraj R, Stefanidis D, Killion R, Alfredson T, et al. Evaluation of polyethylene oxide compacts as gastroretentive delivery systems. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009; 10: 98–103.
Waterman KC . A critical review of gastric retentive controlled drug delivery. Pharm Dev Technol 2007; 12: 1–10.
Klausner EA, Lavy E, Friedman M, Hoffman A . Expandable gastroretentive dosage forms. J Control Release 2003; 90: 143–62.
Werle M, Bernkop SA . Thiolated chitosans: useful excipients for oral drug delivery. J Pharm Pharmacol 2008; 60: 273–81.
Chambin O, Jannin V, Champion D, Chevalier C, Rochat-Gonthier MH, Pourcelot Y . Influence of cryogenic grinding on properties of a self-emulsifying formulation. Int J Pharm 2004; 278: 79–89.
Constantinides PP . Lipid microemulsions for improving drug dissolution and oral absorption: physical and biopharmaceutical aspects. Pharm Res 1995; 12: 1561–72.
Li HT, Hardy RJ, Gu XC . Effect of drug solubility on polymer hydration and drug dissolution from polyethylene oxide (PEO) matrix tablets. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008; 9: 437–43.
Kim CJ . Effects of drug solubility, drug loading, and polymer molecular weight on drug release from Polyox® tablets. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 1998; 24: 645–51.
Shah NH, Carvajal MT, Patel CI, Infeld MH, Malick AW . Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) with polyglycolized glycerides for improving in vitro dissolution and oral absorption of lipophilic drugs. Int J Pharm 1994; 106: 15–23.
Hauss DJ, Fogal SE, Ficorilli JV, Price CA, Roy T, Jayaraj AA, et al. Lipid-based delivery systems for improving the bioavailability and lymphatic transport of a poorly water-soluble LTB4 inhibitor. J Pharm Sci 1998; 87: 164–9.
Fischl MA, Richman DD, Flexner C, Para MF, Jaubrich R, Karim A, et al. Phase I/II study of the toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and activity of the HIV protease inhibitor SC-52151. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol 1997; 15: 28–34.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to DOW Chemical for the generous gift of PEO WSR N60K and to the ISP Corporation for kindly providing PVP K90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Yp., Gan, Y. & Zhang, Xx. Novel gastroretentive sustained-release tablet of tacrolimus based on self-microemulsifying mixture: in vitro evaluation and in vivo bioavailability test. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32, 1294–1302 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2011.90
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2011.90