Abstract
Aim:
To study the protective effects of tiopronin against high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats.
Methods:
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were given a high-fat diet for 10 weeks. The rats were administered tiopronin (20 mg/kg) or a positive control drug ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA, 15 mg/kg) via gavage daily from week 5 to week 10. After the rats were sacrificed, serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), free fatty acids (FFA), high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C), and liver homogenate FFA, superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were measured using commercial analysis kits. The expression levels of CYP2E1 mRNA and protein were determined using RT-PCR and immunoblot assays, respectively.
Results:
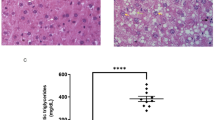
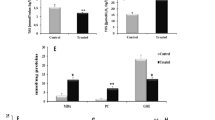
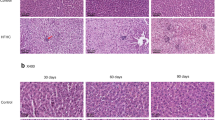
Tiopronin significantly lowered both the serum ALT and AST levels, while only the serum ALT level was lowered by UDCA. Tiopronin significantly decreased the serum and liver levels of TG, TC and FFA as well as the serum LDL-C level, and increased the serum HDL-C level, while UDCA decreased the serum and liver TC levels as well as the serum LDL-C level, but did not change the serum levels of TG, FFA and HDL-C. Tiopronin apparently ameliorated the hepatocyte degeneration and the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the livers, but UDCA did not affect the pathological features of the livers. Both tiopronin and UDCA ameliorated the mitochondrial abnormality in the livers. The benefits of tiopronin were associated with increased SOD and GSH-Px activities, and with decreased MDA activity and CYP2E1 expression in the livers.
Conclusion:
Tiopronin exerts protective effects against non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats, which may be associated with its antioxidant properties and regulation of lipid metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Day CP, James OF . Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998; 114: 842–5.
Te Sligte K, Bourass I, Sels JP, Driessen A, Stockbrugger RW, Koek GH . Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: review of a growing medical problem. Eur J Intern Med 2004; 15: 10–21.
Huang MA, Greenson JK, Chao C, Anderson L, Peterman D, Jacobson J, et al. One-year intense nutritional counseling results in histological improvement in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a pilot study. Am J Gastroenterol 2005; 100: 1072–81.
Stratopoulos C, Papakonstantinou A, Terzis I, Spiliadi C, Dimitriades G, Komesidou V, et al. Changes in liver histology accompanying massive weight loss after gastroplasty for morbid obesity. Obes Surg 2005; 15: 1154–60.
Luyckx FH, Lefebvre PJ, Scheen AJ . Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: association with obesity and insulin resistance, and influence of weight loss. Diabetes Metab 2000; 26: 98–106.
Dioguardi N, Ideo G, De Franchis R, Ronchi G . Controlled clinical trial of 2-mercapto-propionyl-glycine in chronic hepatopathies. Minerva Med 1976; 67: 676–81.
Ichikawa H, Imaizumi K, Tazawa Y, Obara Y, Ishikawa Y, Tobari I, et al. Effect of tiopronin on senile cataracts. A double-blind clinical study. Ophthalmologica 1980; 180: 293–8.
Sany J, Combe B, Verdie-Petibon D, Tagemouati A, Daures JP . Long-term tolerability of tiopronin (Acadione) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Apropos of 140 personal cases. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic 1990; 57: 105–11.
Ichida F, Shibasaki K, Takino T, Suzuki H, Fujisawa K, Inoue K, et al. Therapeutic effects of tiopronin on chronic hepatitis: a double-blind clinical study. J Int Med Res 1982; 10: 325–32.
Kim ES, Glisson BS . Treatment of metastatic head and neck cancer: chemotherapy and novel agents. Cancer Treat Res 2003; 114: 295–314.
Hirayama C, Kishimoto Y, Wakushima T, Murawaki Y . Mechanism of the protective action of thiol compounds in ethanol-induced liver injury. Biochem Pharmacol 1983; 32: 321–5.
Yilong C . Clinical evaluation on the effect of tiopronin in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. China Modern Doctor 2008; 46: 37–8.
Surrenti C, Arcangeli A, Casini A . The antisteatosic activity of 2-MPG (Thiola). Study with the (BSF) dynamic test and with liver biopsy before and after the treatment. Minerva Med 1978; 69: 4251–6.
Ljubuncic P, Tanne Z, Bomzon A . Ursodeoxycholic acid suppresses extent of lipid peroxidation in diseased liver in experimental cholestatic liver disease. Dig Dis Sci 2000; 45: 1921–8.
Buko VU, Lukivskaya OY, Zavodnik LV, Sadovnichy VV, Petushok NE, Tauschel ND . Antioxidative effect of ursodeoxycholic acid in the liver of rats with oxidative stress caused by gamma-irradiation. Ukr Biokhim Zh 2002; 74: 88–92.
Chang CY, Argo CK, Al-Osaimi AM, Caldwell SH . Therapy of NAFLD: antioxidants and cytoprotective agents. J Clin Gastroenterol 2006; 40: S51–60.
Balmer ML, Siegrist K, Zimmermann A, Dufour JF . Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid in combination with vitamin E on adipokines and apoptosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int 2009; 29: 1184–8.
Georgescu EF, Georgescu M . Therapeutic options in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Are all agents alike? Results of a preliminary study. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2007; 16: 39–46.
Laurin J, Lindor KD, Crippin JS, Gossard A, Gores GJ, Ludwig J, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid or clofibrate in the treatment of non-alcohol-induced steatohepatitis: a pilot study. Hepatology 1996; 23: 1464–7.
Dufour JF, Oneta CM, Gonvers JJ, Bihl F, Cerny A, Cereda JM, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of ursodeoxycholic acid with vitamine in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006; 4: 1537–43.
Fan JG, Zhong L, Tia LY, Xu ZJ, Li MS, Wang GL . Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid and/or low-calorie diet on steatohepatitis in rats with obesity and hyperlipidemia. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11: 2346–50.
Zou Y, Li J, Lu C, Wang J, Ge J, Huang Y, et al. High-fat emulsion-induced rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Life Sci 2006; 79: 1100–7.
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH . A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 1957; 226: 497–509.
Kirsch R, Clarkson V, Shephard EG, Marais DA, Jaffer MA, Woodburne VE, et al. Rodent nutritional model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: species, strain and sex difference studies. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003; 18: 1272–82.
Avni Y, Shirin H, Aeed H, Shahmurov M, Birkenfeld S, Bruck R . Thioacetamide-induced hepatic damage in a rat nutritional model of steatohepatitis. Hepatol Res 2004; 30: 141–7.
Begriche K, Igoudjil A, Pessayre D, Fromenty B . Mitochondrial dysfunction in NASH: causes, consequences and possible means to prevent it. Mitochondrion 2006; 6: 1–28.
Weltman MD, Farrell GC, Liddle C . Increased hepatocyte CYP2E1 expression in a rat nutritional model of hepatic steatosis with inflammation. Gastroenterology 1996; 111: 1645–53.
Mavrelis PG, Ammon HV, Gleysteen JJ, Komorowski RA, Charaf UK . Hepatic free fatty acids in alcoholic liver disease and morbid obesity. Hepatology 1983; 3: 226–31.
Feldstein AE, Werneburg NW, Canbay A, Guicciardi ME, Bronk SF, Rydzewski R, et al. Free fatty acids promote hepatic lipotoxicity by stimulating TNF-alpha expression via a lysosomal pathway. Hepatology 2004; 40: 185–94.
Halliwell B . Free radicals, antioxidants, and human disease: curiosity, cause, or consequence? Lancet 1994; 344: 721–4.
Morris AA . Mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders and the liver. Liver 1999; 19: 357–68.
Li Z, Berk M, McIntyre TM, Gores GJ, Feldstein AE . The lysosomal-mitochondrial axis in free fatty acid-induced hepatic lipotoxicity. Hepatology 2008; 47: 1495–503.
Kojima H, Sakurai S, Uemura M, Fukui H, Morimoto H, Tamagawa Y . Mitochondrial abnormality and oxidative stress in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2007; 31: S61–6.
Uzun MA, Koksal N, Kadioglu H, Gunerhan Y, Aktas S, Dursun N, et al. Effects of N-acetylcysteine on regeneration following partial hepatectomy in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Surg Today 2009; 39: 592–7.
Leclercq IA, Farrell GC, Field J, Bell DR, Gonzalez FJ, Robertson GR . CYP2E1 and CYP4A as microsomal catalysts of lipid peroxides in murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Clin Invest 2000; 105: 1067–75.
Lieber CS . Cytochrome P-4502E1: its physiological and pathological role. Physiol Rev 1997; 77: 517–44.
Chalasani N, Gorski JC, Asghar MS, Asghar A, Foresman B, Hall SD, et al. Hepatic cytochrome P450 2E1 activity in nondiabetic patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2003; 37: 544–50.
Yue J, Dong G, He C, Chen J, Liu Y, Peng R . Protective effects of thiopronin against isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicology 2009; 264: 185–91.
Acknowledgements
The research presented in this paper was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 30873081 and 81072686) and Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (No 1208085QH143).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Jq., Zou, Yh., Huang, C. et al. Protective effects of tiopronin against high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33, 791–797 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.19
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.19
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Evaluate the value of prolonging the duration of tiopronin for injection administration in preventing hepatotoxicity
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Allisartan isoproxil reduces mortality of stroke-prone rats and protects against cerebrovascular, cardiac, and aortic damage
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2021)
-
Prospective analysis of tiopronin in prevention of sorafenib and antiviral therapy inducing liver toxicity in advanced hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
Medical Oncology (2015)