Abstract
Aim:
To investigate the effects of salvianolate, a water-soluble active compound from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, on reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in mouse cardiomyocytes in vitro.
Methods:
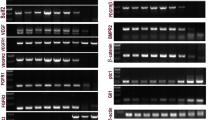
Primary ventricular cardiomyocytes were prepared from neonatal mouse. The cell viability was determined using MTT assay. Culture medium for each treatment was collected for measuring the levels of NO, iNOS, total antioxidant capacity (TAOC) and transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1). TGFβ1 and Smad2/3 expression in the cells was detected with Western blotting.
Results:
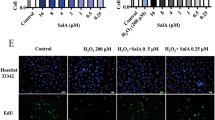
H2O2 (1.25 mmol/L) did not significantly affect the cell viability, whereas the high concentration of salvianolate (5 g/L) alone dramatically suppressed the cell viability. Treatment of the cells with H2O2 (1.25 mmol/L) markedly increased ROS and iNOS production, and decreased the levels of NO, TAOC and TGFβ1 in the culture medium. Furthermore, the H2O2 treatment significantly increased TGFβ1 and Smad2/3 expression in the cells. Addition of salvianolate (0.05, 0.1, and 0.5 g/L) concentration-dependently reversed the H2O2-induced alterations in the culture medium; addition of salvianolate (0.05 g/L) reversed the H2O2-induced increases of TGFβ1 and Smad2/3 expression in the cells. Blockage of TGFβ1 with its antibody (1 mg/L) abolished the above mentioned effects of salvianolate.
Conclusion:
Salvianolate inhibits ROS and iNOS production and increases TAOC and NO levels in H2O2-treated cardiomyocytes in vitro via downregulation of Smad2/3 and TGFβ1 expression. High concentration of salvianolate causes cytotoxicity in mouse cardiomyocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Sorescu D, Griendling KK . Reactive oxygen species, mitochondria, and NAD(P)H oxidases in the development and progression of heart failure. Congest Heart Fail 2002; 8: 132–40.
Guzman Mentesana G, Baez A, Cordoba R, Dominguez R, Lo Presti S, Rivarola W, et al. Role of mitochondria and reactive oxygen species in the progression of heart failure. Rev Fac Cien Med Univ Nac Cordoba 2010; 67: 150–8.
Yoon YS, Lee JH, Hwang SC, Choi KS, Yoon G . TGF beta1 induces prolonged mitochondrial ROS generation through decreased complex IV activity with senescent arrest in Mv1Lu cells. Oncogene 2005; 24: 1895–903.
Buday A, Orsy P, Godo M, Mozes M, Kokeny G, Lacza Z, et al. Elevated systemic TGF-beta impairs aortic vasomotor function through activation of NADPH oxidase-driven superoxide production and leads to hypertension, myocardial remodeling, and increased plaque formation in apoE(−/−) mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2010; 299: H386–95.
Yang DH, Ye ZY, Jin B, He XJ, Zhang Q, Zhou WM, et al. Salvianolate inhibits cytokine gene expression in small intestine of cirrhotic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17: 1903–9.
Wu WY, Wang YP . Pharmacological actions and therapeutic applications of Salvia miltiorrhiza depside salt and its active components. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2012; 33: 1119–30.
Wang MW, Zhang DF, Tang JJ, Chen B, Wang LS, Yang ZJ, et al. Effects of salvianolate on cardiomyocytic apoptosis and heart function in a swine model of acute myocardial infarction. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2009; 7: 140–4.
Nabeebaccus A, Zhang M, Shah AM . NADPH oxidases and cardiac remodelling. Heart Fail Rev 2011; 16: 5–12.
Redout EM, Wagner MJ, Zuidwijk MJ, Boer C, Musters RJ, van Hardeveld C, et al. Right-ventricular failure is associated with increased mitochondrial complex II activity and production of reactive oxygen species. Cardiovasc Res 2007; 75: 770–81.
Seddon M, Looi YH, Shah AM . Oxidative stress and redox signalling in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Heart 2007; 93: 903–7.
Cingolani HE, Plastino JA, Escudero EM, Mangal B, Brown J, Perez NG . The effect of xanthine oxidase inhibition upon ejection fraction in heart failure patients: La Plata Study. J Card Fail 2006; 12: 491–8.
Pociask DA, Sime PJ, Brody AR . Asbestos-derived reactive oxygen species activate TGF-beta1. Lab Invest 2004; 84: 1013–23.
Jiao B, Wang YS, Cheng YN, Gao JJ, Zhang QZ . Valsartan attenuated oxidative stress, decreased MCP-1 and TGF-beta1 expression in glomerular mesangial and epithelial cells induced by high-glucose levels. Biosci Trends 2011; 5: 173–81.
Iglesias-De La Cruz MC, Ruiz-Torres P, Alcami J, Diez-Marques L, Ortega-Velazquez R, Chen S, et al. Hydrogen peroxide increases extracellular matrix mRNA through TGF-beta in human mesangial cells. Kidney Int 2001; 59: 87–95.
Sui XB, Zhang Q, Qiu HS, Zhou JC, Gu XD, Lu ZX, et al. Mechanism of salvianolate in preventing postoperative intestinal adhesion in rats. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2007; 5: 521–5.
Xu J, Fan WH . Effect of salvianolate on migration of human vascular endothelial cells. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2003; 1: 211–4.
Xu M, Wang YP, Luo WB, Xuan LJ . Salvianolate inhibits proliferation and endothelin release in cultured rat mesangial cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2001; 22: 629–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fei, Ah., Cao, Q., Chen, Sy. et al. Salvianolate inhibits reactive oxygen species production in H2O2-treated mouse cardiomyocytes in vitro via the TGFβ pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34, 496–500 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.209
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.209
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of salvianolate on microcirculatory disturbance in patients with stable coronary heart disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Trials (2021)
-
Protective Effects of Salvianolate on Myocardial Injury or Myocardial Infarction after Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in NSTE-ACS Patients: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2020)
-
A Prospective Randomized Multicenter Controlled Trial on Salvianolate for Treatment of Unstable Angina Pectoris in A Chinese Elderly Population
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2019)
-
Cost-consequence analysis of salvianolate injection for the treatment of coronary heart disease
Chinese Medicine (2018)
-
Salvianolate reduces murine myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury via ERK1/2 signaling pathways in vivo
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2017)