Abstract
Aim:
To investigate the population pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of bivalirudin, a synthetic bivalent direct thrombin inhibitor, in young healthy Chinese subjects.
Methods:
Thirty-six young healthy volunteers were randomly assigned into 4 groups received bivalirudin 0.5 mg/kg, 0.75 mg/kg, and 1.05 mg/kg intravenous bolus, 0.75 mg/kg intravenous bolus followed by 1.75 mg/kg intravenous infusion per hour for 4 h. Blood samples were collected to measure bivalirudin plasma concentration and activated clotting time (ACT). Population PK-PD analysis was performed using the nonlinear mixed-effects model software NONMEM. The final models were validated with bootstrap and prediction-corrected visual predictive check (pcVPC) approaches.
Results:
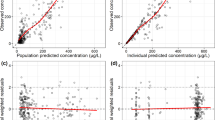
The final PK model was a two-compartment model without covariates. The typical PK population values of clearance (CL), apparent distribution volume of the central-compartment (V1), inter-compartmental clearance (Q) and apparent distribution volume of the peripheral compartment (V2) were 0.323 L·h-1·kg-1, 0.086 L/kg, 0.0957 L·h-1·kg-1, and 0.0554 L/kg, respectively. The inter-individual variabilities of these parameters were 14.8%, 24.2%, fixed to 0% and 15.6%, respectively. The final PK-PD model was a sigmoid Emax model without the Hill coefficient. In this model, a covariate, red blood cell count (RBC*), had a significant effect on the EC50 value. The typical PD population values of maximum effect (Emax), EC50, baseline ACT value (E0) and the coefficient of RBC* on EC50 were 318 s, 2.44 mg/L, 134 s and 1.70, respectively. The inter-individual variabilities of Emax, EC50, and E0 were 6.80%, 46.4%, and 4.10%, respectively.
Conclusion:
Population PK-PD models of bivalirudin in healthy young Chinese subjects have been developed, which may provide a reference for future use of bivalirudin in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kimmel SE, Sekeres M, Berlin JA, Ellison N . Mortality and adverse events after protamine administration in patientsundergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth Analg 2002; 94: 1402–8.
Toschi V, Lettino M, Gallo R, Badimon JJ, Chesebro JH . Biochemistry and biology of hirudin. Coron Artery Dis 1996; 7: 420–8.
Maraganore JM, Bourdon P, Jablonski J, Ramachandran KL, Fenton JW 2nd . Design and characterization of hirulogs: a novelclass of bivalent peptide inhibitors of thrombin. Biochemistry 1990; 29: 7095–101.
Vasquez JC, Vichiendilokkul A, Mahmood S, Baciewicz FA Jr . Anticoagulation with bivalirudin during cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 2002; 74: 2177–9.
Stone GW, McLaurin BT, Cox DA, Bertrand ME, Lincoff AM, Moses JW, et al. Bivalirudin for patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2203–16.
Lincoff AM, Bittl JA, Harrington RA, Feit F, Kleiman NS, Jackman JD, et al. Bivalirudin and provisional glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockade compared with heparin and planned glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockade during percutaneous coronary intervention: REPLACE-2 randomized trial. JAMA 2003; 289: 853–63.
Kastrati A, Neumann FJ, Mehilli J, Byrne RA, Iijima R, Büttner HJ, et al. Bivalirudin versus unfractionated heparin during percutaneous coronary intervention. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 688–96.
Stone GW, Witzenbichler B, Guagliumi G, Peruga JZ, Brodie BR, Dudek D, et al. Bivalirudin during primary PCI in acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 2218–30.
Atkinson AJ Jr, Lalonde RL . Introduction of quantitative methods in pharmacology and clinical pharmacology: a historical overview. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007; 82: 3–6.
Gobburu VS, Marroum PJ . Utilisation of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling and simulation in regulatory decision making. Clin Pharmacokinet 2001; 40: 883–92.
Grasela TH, Dement CW, Kolterman OG, Fineman MS, Grasela DM, Honig P . Pharmacometrics and the transition to model-based development. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007; 82: 137–42.
Zhang LP, Pfister M, Meibohm B . Concepts and challenges in quantitative pharmacology and model-based drug development. AAPS J 2008; 10: 552–9.
Zhang DM, Wang ZN, Zhao X, Lu W, Gu JK, Cui YM . Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, tolerability and safety of single doses of bivalirudin in healthy Chinese subjects. Biol Pharm Bull 2011; 34: 1841–8.
Karlsson MO, Holford N . A tutorial on visual predictive checks. PAGE 2008; 17: Abstr 1434 [www.page-meeting.org/?abstract=1434].
Bergstrand M, Hooker AC, Wallin JE, Karlsson MO . Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. AAPS J 2011; 13: 143–51.
Zhang L, Beal SL, Sheiner LB . Simultaneous vs sequential analysis for population PK/PD data I: best-case performance. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 2003; 30: 387–404.
Brendel K, Dartois C, Comets E, Lemenuel-Diot A, Laveille C, Tranchand B . Are population pharmacokineticand/or pharmacodynamic modelsadequately evaluated? A survey of the literaturefrom 2002 to 2004. Clin Pharmacokinet 2007; 46: 221–34.
The Medicines Company. BivalirudinPrescribing Information (2005).
Robson R . The use of bivalirudin in patients with renal impairment. J Invasive Cardiol 2000; 12: 33F–6.
Robson R, White H, Aylward P, Frampton C . Bivalirudin pharmacokinetics andpharmacodynamics: Effect of renalfunction, dose, and gender. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002; 71: 433–9.
Hooker AC, Staatz CE, Karlsson MO . Conditional weighted residuals (CWRES): a model diagnostic for the FOCE method. Pharm Res 2007; 24: 2187–97.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Shenzhen Main Luck Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The authors would like to thank Jing-kai GU, Min LU, Ling-yue MA, Xiao LIU, Shuo-han TIAN, Xiao-yan SHENG, and Jing-zi LI for their assistance in performing the trial, and Yuan-cheng CHEN for his assistance in data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Dm., Wang, K., Zhao, X. et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of bivalirudin in young healthy Chinese volunteers. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33, 1387–1394 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.37
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.37
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacometrics: a quantitative tool of pharmacological research
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2012)