Abstract
Aim:
A growing body of evidence suggests that α-synuclein accumulation may play an important role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. The aim of this study was to investigate the roles of the proteasome and autophagy pathways in the clearance of wild-type and mutant α-synuclein in PC12 cells.
Methods:
PC12 cells overexpressing either wild-type or A30P mutant α-synuclein were treated with the proteasome inhibitor epoxomicin, the macroautophagy inhibitor 3-MA and the macroautophagy activator rapamycin alone or in combination. The cell viability was assessed using MTT assay. Immunofluorescence and Western blot analysis were used to detect the level of α-synuclein, LAMP-2A, E1 activase, and E2 ligase in the cells. Chymotrypsin-like proteasomal activity was measured using a commercial kit.
Results:
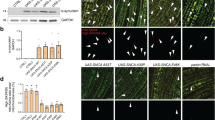
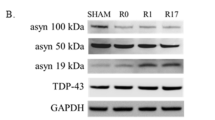
When the proteasome and macroautophagy in the wild-type and mutant cells were inhibited with epoxomicin and 3-MA, respectively, the cell viability was significantly decreased, and the α-synuclein level was increased. Both epoxomicin and 3-MA activated the chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) by increasing the level of the CMA-limiting enzyme LAMP-2A. Furthermore, 3-MA or epoxomicin significantly decreased chymotrypsin-like proteasomal activity. 3-MA or epoxomicin did not change E1 activase expression in either mutant or wild-type cells, but increased E2 ligase expression, especially when used together. Macroautophagy inducer rapamycin increased the cell viability and reduced epoxomicin-induced α-synuclein accumulation. Interestingly, CMA was also activated by rapamycin.
Conclusion:
Our results demonstrate the existence of complex crosstalk between different forms of autophagy and between autophagy and the proteasome pathway in the clearance of α-synuclein in PC12 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ozansoy M, Basak AN . The central theme of Parkinson's disease: alpha-synuclein. Mol Neurobiol 2013; 47: 460–52.
Kahle PJ, Haass C, Kretzschmar HA, Neumann M . Structure/function of alpha-synuclein in health and disease: rational development of animal models for Parkinson's and related diseases. J Neurochem 2002; 82: 449–57.
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 1997; 276: 2045–7.
Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet 1998; 18: 106–8.
Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D . Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science 2004; 305: 1292–5.
Feany MB, Bender WW . A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature 2000; 404: 394–8.
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Takeda A, et al. Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 2000; 287: 1265–9.
Chung KK, Dawson VL, Dawson TM . The role of the ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway in Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 2001; 24: S7–14.
Bence NF, Sampat RM, Kopito RR . Impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by protein aggregation. Science 2001; 292: 1552–5.
Webb JL, Ravikumar B, Atkins J, Skepper JN, Rubinsztein DC . Alpha-Synuclein is degraded by both autophagy and the proteasome. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 25009–13.
Li K, Ito H, Tanaka K, Hirano A . Immunocytochemical co-localization of the proteasome in ubiquitinated structures in neurodegenerative diseases and the elderly. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1997; 56: 125–31.
Ravikumar B, Duden R, Rubinsztein DC . Aggregate-prone proteins with polyglutamine and polyalanine expansions are degraded by autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 1107–17.
Engelender S . alpha-Synuclein fate: proteasome or autophagy. Autophagy 2012; 8: 418–20.
Dice JF . Peptide sequences that target cytosolic proteins for lysosomal proteolysis. Trends Biochem Sci 1990; 15: 305–9.
Berger Z, Ravikumar B, Menzies FM, Oroz LG, Underwood BR, Pangalos MN, et al. Rapamycin alleviates toxicity of different aggregate-prone proteins. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 433–42.
Qian JJ, Cheng YB, Yang YP, Mao CJ, Qin ZH, Li K, et al. Differential effects of overexpression of wild-type and mutant human alpha-synuclein on MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 2008; 435: 142–6.
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T, et al. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J 2000; 19: 5720–8.
Tanida I, Ueno T, Kominami E . LC3 conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2004; 36: 2503–18.
Gonzalez-Polo RA, Boya P, Pauleau AL, Jalil A, Larochette N, Souquere S, et al. The apoptosis/autophagy paradox: autophagic vacuolization before apoptotic death. J Cell Sci 2005; 118: 3091–102.
Massey AC, Kaushik S, Sovak G, Kiffin R, Cuervo AM . Consequences of the selective blockage of chaperone-mediated autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006; 103: 5805–10.
Yue X, Song W, Zhang W, Chen L, Xi Z, Xin Z, et al. Mitochondrially localized EGFR is subjected to autophagic regulation and implicated in cell survival. Autophagy 2008; 4: 641–9.
Bennett MC, Bishop JF, Leng Y, Chock PB, Chase TN, Mouradian MM . Degradation of alpha-synuclein by proteasome. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 33855–8.
McNaught KS, Mytilineou C, Jnobaptiste R, Yabut J, Shashidharan P, Jennert P, et al. Impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome system causes dopaminergic cell death and inclusion body formation in ventral mesencephalic cultures. J Neurochem 2002; 81: 301–6.
Tofaris GK, Layfield R, Spillantini MG . Alpha-synuclein metabolism and aggregation is linked to ubiquitin-independent degradation by the proteasome. FEBS Lett 2001; 509: 22–6.
Rideout HJ, Larsen KE, Sulzer D, Stefanis L . Proteasomal inhibition leads to formation of ubiquitin/alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive inclusions in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 2001; 78: 899–908.
Ancolio K, Alves da Costa C, Ueda K, Checler F . Alpha-synuclein and the Parkinson's disease-related mutant Ala53Thr-alpha-synuclein do not undergo proteasomal degradation in HEK293 and neuronal cells. Neurosci Lett 2000; 285: 79–82.
Yang F, Yang YP, Mao CJ, Cao BY, Cai ZL, Shi JJ, et al. Role of autophagy and proteasome degradation pathways in apoptosis of PC12 cells overexpressing human alpha-synuclein. Neurosci Lett 2009; 454: 203–8.
Kiffin R, Christian C, Knecht E, Cuervo AM . Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy during oxidative stress. Mol Biol Cell 2004; 15: 4829–40.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81171213) and the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Province of China (No BK2010228). We are grateful to Professor IC Bruce for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, F., Yang, Yp., Mao, Cj. et al. Crosstalk between the proteasome system and autophagy in the clearance of α-synuclein. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34, 674–680 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2013.29
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2013.29
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Autophagy and UPS pathway contribute to nicotine-induced protection effect in Parkinson’s disease
Experimental Brain Research (2024)
-
Ubiquilin-2 regulates pathological alpha-synuclein
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Early-onset impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in dopaminergic neurons caused by α-synuclein
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2020)
-
Replication of multiple system atrophy prions in primary astrocyte cultures from transgenic mice expressing human α-synuclein
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2019)
-
Inhibition of Protein Ubiquitination by Paraquat and 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium Impairs Ubiquitin-Dependent Protein Degradation Pathways
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)