Abstract
Aim:
Interferon-γ inducible protein 16 (IFI16), a DNA sensor for DNA double-strand break (DSB), is expressed in most human hepatocellular carcinoma cell (HCC) lines. In this study we investigated the re-localization of chromatin-bound IFI16 by Nutlin-3, a DNA damage agent, in HCC cells in vitro, and the potential mechanisms.
Methods:
Human HCC SMMC-7721 (wild-type TP53), Huh-7 (mutant TP53), Hep3B (null TP53) and normal fetal liver L02 cell lines were examined. DSB damage in HCC cells was detected via γH2AX expression and foci formation assay. The expression of IFI16 and IFNB mRNA was measured using RT-PCR, and subcellular localization and expression of the IFI16 protein were detected using chromatin fractionation, Western blot analysis, and fluorescence microscopy.
Results:
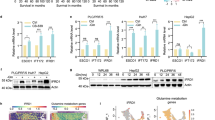
Treatment of SMMC-7721 cells with Nutlin-3 (10 μmol/L) or etoposide (40 μmol/L) induced significant DSB damage. In SMMC-7721 cells, Nutlin-3 significantly increased the expression levels of IFI16 and IFNB mRNA, and partially redistributed chromatin-bound IFI16 protein to the cytoplasm. These effects were blocked by pretreatment with pifithrin-α, a p53 inhibitor. Furthermore, Nutlin-3 did not induce ectopic expression of IFI16 protein in Huh-7 and Hep3B cells. Moreover, the association of IFI16 with chromatin and Nutlin-3-induced changes in localization were not detected in L02 cells.
Conclusion:
Nutlin-3 regulates the subcellular localization of IFI16 in HCC cells in vitro in a p53-dependent manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2013. CA-Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11–30.
Polager S, Ginsberg D . p53 and E2f: partners in life and death. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 738–48.
Liao JC, Lam R, Brazda V, Duan S, Ravichandran M, Ma J, et al. Interferon-inducible protein 16: insight into the interaction with tumor suppressor p53. Structure 2011; 19: 418–29.
Schattgen SA, Fitzgerald KA . The PYHIN protein family as mediators of host defenses. Immunol Rev 2011; 243: 109–18.
Ludlow LE, Johnstone RW, Clarke CJ . The HIN-200 family: more than interferon-inducible genes? Exp Cell Res 2005; 308: 1–17.
Johnstone RW, Wei W, Greenway A, Trapani JA . Functional interaction between p53 and the interferon-inducible nucleoprotein IFI 16. Oncogene 2000; 19: 6033–42.
Dawson MJ, Trapani JA . HIN-200: a novel family of IFN-inducible nuclear proteins expressed in leukocytes. J Leukocyte Biol 1996; 60: 310–6.
Fujiuchi N, Aglipay JA, Ohtsuka T, Maehara N, Sahin F, Su GH, et al. Requirement of IFI16 for the maximal activation of p53 induced by ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 20339–44.
Mazibrada J, Andrea MD, Rittà M, Borgogna C, Pfeffer U, Chiusa L, et al. In vivo growth inhibition of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by the Interferon-inducible gene IFI16. Cancer Lett 2010; 287: 33–43.
Alimirah F, Chen J, Davis FJ, Choubey D . IFI16 in human prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res 2007; 5: 251–9.
Wieland S, Thimme R, Purcell RH, Chisari FV . Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Prod Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004; 101: 6669–74.
Gariano GR, Dell'Oste V, Bronzini M, Gatti D, Luganini A, De Andrea M, et al. The intracellular DNA sensor IFI16 gene acts as restriction factor for human cytomegalovirus replication. PLoS Pathog 2012; 8: e1002498.
Unterholzner L, Keating SE, Baran M, Horan KA, Jensen SB, Sharma S, et al. IFI16 is an innate immune sensor for intracellular DNA. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 997–1004.
Unterholzner L, Bowie AG . IFI16 acts as a nuclear pathogen sensor to induce the inflammasome in response to kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection. Cell Host Microbe 2011; 9: 351–3.
Aglipay JA, Lee SW, Okada S, Fujiuchi N, Ohtsuka T, Kwak JC, et al. A member of the Pyrin family, IFI16, is a novel BRCA1-associated protein involved in the p53-mediated apoptosis pathway. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8931–8.
Duan X, Ponomareva L, Veeranki S, Choubey D . IFI16 induction by glucose restriction in human fibroblasts contributes to autophagy through activation of the ATM/AMPK/p53 pathway. PLoS One 2011; 6: e19532.
Xin H, Pereira-Smith OM, Choubey D . Role of IFI 16 in cellular senescence of human fibroblasts. Oncogene 2004; 23: 6209–17.
Xin H, Curry J, Johnstone RW, Nickoloff BJ, Choubey D . Role of IFI 16, a member of the interferon-inducible p200-protein family, in prostate epithelial cellular senescence. Oncogene 2003; 22: 4831–40.
Costa S, Borgogna C, Mondini M, De Andrea M, Meroni P, Berti E, et al. Redistribution of the nuclear protein IFI16 into the cytoplasm of ultraviolet B-exposed keratinocytes as a mechanism of autoantigen processing. Brit J Dermatol 2011; 164: 282–90.
Khalid SS, Hamid S, Siddiqui AA, Qureshi A, Qureshi N . Gene profiling of early and advanced liver disease in chronic hepatitis C patients. Hepa Inter 2011; 5: 782–8.
Shi X, Liu J, Liu Q, Li M . IFI16 mis-localization can be a contributing factor to hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Med Hypotheses 2014; 82: 398–400.
Wang J, Zheng T, Chen X, Song X, Meng X, Bhatta N, et al. MDM2 antagonist can inhibit tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma with different types of p53 in vitro. J Gastroen Hepatol 2011; 26: 371–7.
Shi X, Liu J, Ren L, Mao N, Tan F, Ding N, et al. Nutlin-3 downregulates p53 phosphorylation on serine392 and induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMB Rep 2014; 46: 221–6.
Yu Y, Gu Z, Yin J, Chou W, Kwok C, Qin Z, et al. Ursolic acid induces human hepatoma cell line SMMC-7721 apoptosis via p53-dependent pathway. Chin Med J 2010; 123: 1915–23.
Miao R, Han Y, An L, Yang J, Wang Q . Seleno-podophyllotoxin derivatives induce hepatoma SMMC-7721 cell apoptosis through Bax pathway. Cell Biol Int 2008; 32: 217–23.
Zou L, Cortez D, Elledge SJ . Regulation of ATR substrate selection by Rad17-dependent loading of Rad9 complexes onto chromatin. Gene Dev 2002; 16: 198–208.
Mah LJ, El-Osta A, Karagiannis TC . γH2AX as a molecular marker of aging and disease. Epigenetics 2010; 5: 129–36.
Suzuki M, Suzuki K, Kodama S, Watanabe M . Phosphorylated histone H2AX foci persist on rejoined mitotic chromosomes in normal human diploid cells exposed to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res 2006; 165: 269–76.
Clarke C, Apostolidis V, Hii L, Gough D, Trapani J, Johnstone R . Critical role of the transcription factor AP-1 for the constitutive and interferon-induced expression of IFI 16. J Cell Biochem 2003; 89: 80–93.
Komarov PG, Komarova EA, Kondratov RV, Christov-Tselkov K, Coon JS, Chernov MV, et al. A chemical inhibitor of p53 that protects mice from the side effects of cancer therapy. Science 1999; 285: 1733–7.
Yu F, Hao X, Zhao H, Ge C, Yao M, Yang S, et al. Delta-like 1 contributes to cell growth by increasing the interferon-inducible protein 16 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 2010; 30: 703–14.
Gugliesi F, Bawadekar M, De Andrea M, Dell'Oste V, Caneparo V, Tincani A, et al. Nuclear DNA sensor IFI16 as circulating protein in autoimmune diseases is a signal of damage that impairs endothelial cells through high-affinity membrane binding. PLoS One 2013; 8: e 63045.
Johnson KE, Chikoti L, Chandran B . Herpes simplex virus 1 infection induces activation and subsequent inhibition of the IFI16 and NLRP3 inflammasomes. J Virol 2013; 87: 5005–18.
Li T, Diner BA, Chen J, Cristea IM . Acetylation modulates cellular distribution and DNA sensing ability of interferon-inducible protein IFI16. P Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012; 109: 10558–63.
Yuan ZM, Huang Y, Ishiko T, Nakada S, Utsugisawa T, Shioya H, et al. Role for p300 in stabilization of p53 in the response to DNA damage. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 1883–6.
Verma R, Rigatti MJ, Belinsky GS, Godman CA, Giardina C . DNA damage response to the Mdm2 inhibitor Nutlin-3. Biochem Pharmacol 2010; 79: 565–74.
Chen L, Borozan I, Sun J, Guindi M, Fischer S, Feld J, et al. Cell-type specific gene expression signature in liver underlies response to interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis C infection. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 1123–33.
Borgogna C, Toniutto P, Smirne C, Azzimonti B, Rittà M, Avellini C, et al. Expression of the interferon-inducible proteins MxA and IFI16 in liver allografts. Histopathology 2009; 54: 837–46.
Jenner RG, Young RA . Insights into host responses against pathogens from transcriptional profiling. Nat Rev Microbiol 2005; 3: 281–94.
Jin T, Perry A, Jiang J, Smith P, Curry JA, Unterholzner L, et al. Structures of the HIN domain: DNA complexes reveal ligand binding and activation mechanisms of the AIM2 inflammasome and IFI16 receptor. Immunity 2012; 36: 561–71.
Brázda V, Coufal J, Liao JC, Arrowsmith CH . Preferential binding of IFI16 protein to cruciform structure and superhelical DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012; 422: 716–20.
O'Neill LA . Sensing the dark side of DNA. Science 2013; 339: 763–4.
Fontana MF, Vance RE . Two signal models in innate immunity. Immunol Rev 2011; 243: 26–39.
Ansari MA, Singh VV, Dutta S, Veettil MV, Dutta D, Chikoti L, et al. Constitutive interferon-inducible protein 16-inflammasome activation during epstein-barr virus latency I, II and III in B and epithelial cells. J Virol 2013; 87: 8606–23.
Veeranki S, Duan X, Panchanathan R, Liu H, Choubey D . IFI16 protein mediates the anti-inflammatory actions of the type-I interferons through suppression of activation of caspase-1 by inflammasomes. PLoS One 2011; 6: e27040.
Land WG . Transfusion-related acute lung injury: The Work of DAMPs. Transfus Med Hemother 2013; 40: 3–13.
Iyer SS, Pulskens WP, Sadler JJ, Butter LM, Teske GJ, Ulland TK, et al. Necrotic cells trigger a sterile inflammatory response through the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106: 20388–93.
Lill NL, Grossman SR, Ginsberg D, DeCaprio J, Livingston DM . Binding and modulation of p53 by p300/CBP coactivators. Nature 1997; 387: 823–7.
Kondo Y, Nagai K, Nakahata S, Saito Y, Ichikawa T, Suekane A, et al. Overexpression of the DNA sensor proteins, absent in melanoma 2 and interferon-inducible 16, contributes to tumorigenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma with p53 inactivation. Cancer Sci 2012; 103: 782–90.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81071362) and the Youth Foundation of Hebei Educational Committee, China (No QN2014012). We thank Prof Cong LIU (West China Second University Hospital) for kindly supplying us with HCC cell lines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Xl., Yang, J., Mao, N. et al. Nutlin-3-induced redistribution of chromatin-bound IFI16 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro is associated with p53 activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36, 252–258 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.106
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.106
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Blockade of MDM2 with inactive Cas9 prevents epithelial to mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelial cells
Laboratory Investigation (2019)