Abstract
Aim:
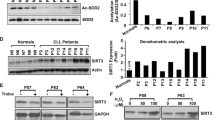
The phosphorylation of histone H2AX, a novel tumor suppressor protein, is involved in regulation of cancer cell apoptosis. The aim of this study was to examine whether H2AX phosphorylation was required for resveratrol-induced apoptosis of human chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells in vitro.
Methods:
K562 cells were tested. Cell apoptosis was analyzed using flow cytometry, and the phosphorylation of H2AX and other signaling proteins was examined with Western blotting. To analyze the signaling pathways, the cells were transfected with lentiviral vectors encoding H2AX-wt or specific siRNAs.
Results:
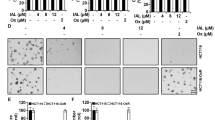
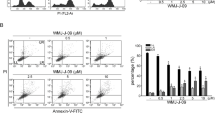
Treatment of K562 cells with resveratrol (20–100 μmol/L) induced apoptosis and phosphorylation of H2AX at Ser139 in time- and dose-dependent manners, but reduced phosphorylation of histone H3 at Ser10. Resveratrol treatment activated two MAPK family members p38 and JNK, and blocked the activation of another MAPK family member ERK. Pretreatment with the p38 inhibitor SB202190 or the JNK inhibitor SP600125 dose-dependently reduced resveratrol-induced phosphorylation of H2AX, which were also observed when the cells were transfected with p38- or JNK-specific siRNAs. Overexpression of H2AX in K562 cells markedly increased resveratrol-induced apoptosis, whereas overexpression of H2AX-139m (Ser139 was mutated to block phosphorylation) inhibited resveratrol-induced apoptosis. K562 cells transfected with H2AX-specific siRNAs were resistant to resveratrol-induced apoptosis.
Conclusion:
H2AX phosphorylation at Ser139 in human CML cells, which is regulated by p38 and JNK, is essential for resveratrol-induced apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Goldman JM, Melo JV . Chronic myeloid leukemia--advances in biology and new approaches to treatment. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 1451–64.
Goldman JM, Melo JV . Targeting the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 1084–6.
Dumka D, Puri P, Carayol N, Lumby C, Balachandran H, Schuster K, et al. Activation of the p38 Map kinase pathway is essential for the antileukemic effects of dasatinib. Leuk Lymphoma 2009; 50: 2017–29.
Horita M, Andreu EJ, Benito A, Arbona C, Sanz C, Benet I, et al. Blockade of the Bcr-Abl kinase activity induces apoptosis of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells by suppressing signal transducer and activator of transcription 5-dependent expression of Bcl-xL. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 977–84.
Branford S, Yeung DT, Parker WT, Roberts ND, Purins L, Braley JA, et al. Prognosis for patients with CML and >10% BCR-ABL1 after 3 months of imatinib depends on the rate of BCR-ABL1 decline. Blood 2014; 124: 511–8.
Chu S, Holtz M, Gupta M, Bhatia R . BCR/ABL kinase inhibition by imatinib mesylate enhances MAP kinase activity in chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ cells. Blood 2004; 103: 3167–74.
Lu Z, Jin Y, Chen C, Li J, Cao Q, Pan J . Pristimerin induces apoptosis in imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells harboring T315I mutation by blocking NF-kappaB signaling and depleting Bcr-Abl. Mol Cancer 2010; 9: 112.
Mesa RA . Imatinib and tyrosine kinase inhibition, in the management of BCR-ABL negative myeloproliferative disorders. Biologics 2007; 1: 129–38.
Deguchi Y, Kimura S, Ashihara E, Niwa T, Hodohara K, Fujiyama Y, et al. Comparison of imatinib, dasatinib, nilotinib and INNO-406 in imatinib-resistant cell lines. Leuk Res 2008; 32: 980–3.
Nicolini FE, Ibrahim AR, Soverini S, Martinelli G, Muller MC, Hochhaus A, et al. The BCR-ABLT315I mutation compromises survival in chronic phase chronic myelogenous leukemia patients resistant to tyrosine kinase inhibitors, in a matched pair analysis. Haematologica 2013; 98: 1510–6.
Donato NJ, Wu JY, Stapley J, Gallick G, Lin H, Arlinghaus R, et al. BCR-ABL independence and LYN kinase overexpression in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells selected for resistance to STI571. Blood 2003; 101: 690–8.
Hu Y, Liu Y, Pelletier S, Buchdunger E, Warmuth M, Fabbro D, et al. Requirement of Src kinases Lyn, Hck and Fgr for BCR-ABL1-induced B-lymphoblastic leukemia but not chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 453–61.
Athar M, Back JH, Tang X, Kim KH, Kopelovich L, Bickers DR, et al. Resveratrol: a review of preclinical studies for human cancer prevention. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2007; 224: 274–83.
Li F, Gong Q, Dong H, Shi J . Resveratrol, a neuroprotective supplement for Alzheimer's disease. Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18: 27–33.
Shen M, Jia GL, Wang YM, Ma H . Cardioprotective effect of resvaratrol pretreatment on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion induced injury in rats. Vascul Pharmacol 2006; 45: 122–6.
Park SJ, Ahmad F, Philp A, Baar K, Williams T, Luo H, et al. Resveratrol ameliorates aging-related metabolic phenotypes by inhibiting cAMP phosphodiesterases. Cell 2012; 148: 421–33.
Puissant A, Grosso S, Jacquel A, Belhacene N, Colosetti P, Cassuto JP, et al. Imatinib mesylate-resistant human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell lines exhibit high sensitivity to the phytoalexin resveratrol. Faseb J 2008; 22: 1894–904.
Surh YJ, Hurh YJ, Kang JY, Lee E, Kong G, Lee SJ . Resveratrol, an antioxidant present in red wine, induces apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells. Cancer Lett 1999; 140: 1–10.
Whyte L, Huang YY, Torres K, Mehta RG . Molecular mechanisms of resveratrol action in lung cancer cells using dual protein and microarray analyses. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 12007–17.
Li T, Wang W, Li T . Antileukemic mechanism of resveratrol in vitro and in mice bearing L1210-tumor. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2008; 6: 1267–74. Chinese.
Dorrie J, Gerauer H, Wachter Y, Zunino SJ . Resveratrol induces extensive apoptosis by depolarizing mitochondrial membranes and activating caspase-9 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 4731–9.
Puissant A, Robert G, Fenouille N, Luciano F, Cassuto JP, Raynaud S, et al. Resveratrol promotes autophagic cell death in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells via JNK-mediated p62/SQSTM1 expression and AMPK activation. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 1042–52.
Liu Y, Tseng M, Perdreau SA, Rossi F, Antonescu C, Besmer P, et al. Histone H2AX is a mediator of gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell apoptosis following treatment with imatinib mesylate. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 2685–92.
Zhang YJ, Lu CR, Cao Y, Luo Y, Bao RF, Yan S, et al. Imatinib induces H2AX phosphorylation and apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in vitro via caspase-3/Mst1 pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2012; 33: 551–7.
Dong Y, Xiong M, Duan L, Liu Z, Niu T, Luo Y, et al. H2AX phosphorylation regulated by p38 is involved in Bim expression and apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells induced by imatinib. Apoptosis 2014; 19: 1281–92.
Lu C, Zhu F, Cho YY, Tang F, Zykova T, Ma WY, et al. Cell apoptosis: requirement of H2AX in DNA ladder formation, but not for the activation of caspase-3. Mol Cell 2006; 23: 121–32.
Lu C, Xiong M, Luo Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Dong Y, et al. Genome-wide transcriptional analysis of apoptosis-related genes and pathways regulated by H2AX in lung cancer A549 cells. Apoptosis 2013; 18: 1039–47.
Milella M, Kornblau SM, Estrov Z, Carter BZ, Lapillonne H, Harris D, et al. Therapeutic targeting of the MEK/MAPK signal transduction module in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 851–9.
Banerjee Mustafi S, Chakraborty PK, Raha S . Modulation of Akt and ERK1/2 pathways by resveratrol in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells results in the downregulation of Hsp70. PLoS One 2010; 5: e8719.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81070424 and No 81272303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Xp., Xiong, M., Xu, Cs. et al. Resveratrol induces apoptosis of human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in vitro through p38 and JNK-regulated H2AX phosphorylation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36, 353–361 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.132
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.132
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Homoharringtonine enhances cytarabine-induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukaemia by regulating the p38 MAPK/H2AX/Mcl-1 axis
BMC Cancer (2024)
-
Resveratrol Directly Controls the Activity of Neuronal Ryanodine Receptors at the Single-Channel Level
Molecular Neurobiology (2020)
-
Resveratrol induces apoptosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial cell line (BPH-1) through p38 MAPK-FOXO3a pathway
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2019)
-
Role of Non Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Hematological Malignances and its Targeting by Natural Products
Molecular Cancer (2018)
-
Effect of resveratrol and metformin on ovarian reserve and ultrastructure in PCOS: an experimental study
Journal of Ovarian Research (2018)