Abstract
Aim:
7,8-Dihydroxy-4-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-2H-chromen-2-one (DW532) is one of simplified analogues of hematoxylin that has shown broad-spectrum inhibition on tyrosine kinases and in vitro anti-cancer activities. The aim of this study was to identify DW532 as a agent targeting both kinases and tubulin, and to investigate its anti-cancer and anti-angiogenesis activities.
Methods:
In vitro tyrosine kinases activity was examined with ELISA, and tyrosine kinases activity in cells was evaluated with Western blot analysis. Tubulin turbidity assay, surface plasmon resonance and immunofluorescence technique were used to characterize the tubulin inhibitory activity. Cell proliferation was examined with SRB assay, and cell apoptosis and cell cycle distribution were analyzed with Annexin-V/PI staining and flow cytometry. Tube formation, aortic ring and chick chorioallantoic membrane assays were used to evaluate the anti-angiogenesis efficacy.
Results:
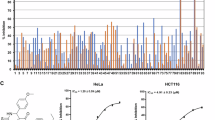
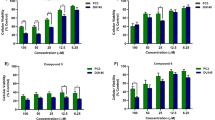
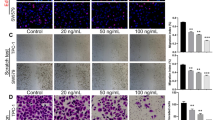
DW532 inhibited EGFR and VEGFR2 in vitro kinase activity (the IC50 values were 4.9 and 5.5 μmol/L, respectively), and suppressed their downstream signaling. DW532 dose-dependently inhibited tubulin polymerization via direct binding to tubulin, thus disrupting the mitotic spindle assembly and leading to abnormal cell division. In a panel of human cancer cells, DW532 (1 and 10 μmol/L) induced G2/M phase arrest and cell apoptosis, which subsequently resulted in cytotoxicity. Knockdown of BubR1 or Mps1, the two core proteins of the spindle assembly checkpoint dramatically decreased DW532-induced cell cycle arrest in MDA-MB-468 cells. Moreover, treatment with DW532 potently and dose-dependently suppressed angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion:
DW532 is a dual inhibitor against tubulin and tyrosine kinases, and deserves further development as a novel anti-cancer agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Giamas G, Man YL, Hirner H, Bischof J, Kramer K, Khan K, et al. Kinases as targets in the treatment of solid tumors. Cell Signalling 2010; 22: 984–1002.
Yarden Y, Pines G . The ERBB network: at last, cancer therapy meets systems biology. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 553–63.
Shibuya M . Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system: physiological functions in angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases. J Biochem 2013; 153: 13–9.
Jordan MA, Wilson L . Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 253–65.
Liu ZL, Tian W, Wang Y, Kuang S, Luo XM, Yu Q . A novel sulfonamide agent, MPSP-001, exhibits potent activity against human cancer cells in vitro through disruption of microtubule. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2012; 33: 261–70.
Chan KS, Koh CG, Li HY . Mitosis-targeted anti-cancer therapies: where they stand. Cell Death Dis 2012; 3: e411.
Gossage L, Eisen T . Targeting multiple kinase pathways: a change in paradigm. Clin Cancer Res: offic J Am Assoc Cancer Res 2010; 16: 1973–8.
Di Leo A, Gomez HL, Aziz Z, Zvirbule Z, Bines J, Arbushites MC, et al. Phase III, double-blind, randomized study comparing lapatinib plus paclitaxel with placebo plus paclitaxel as first-line treatment for metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 5544–52.
Antonarakis ES, Heath EI, Posadas EM, Yu EY, Harrison MR, Bruce JY, et al. A phase 2 study of KX2-391, an oral inhibitor of Src kinase and tubulin polymerization, in men with bone-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2013; 71: 883–92.
Katayama R, Aoyama A, Yamori T, Qi J, Oh-hara T, Song Y, et al. Cytotoxic activity of tivantinib (ARQ 197) is not due solely to c-MET inhibition. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 3087–96.
Ren X, Dai M, Lin LP, Li PK, Ding J . Anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting effects of C9, a new microtubule-depolymerizing agent. Br J Pharmacol 2009; 156: 1228–38.
Lin LG, Xie H, Li HL, Tong LJ, Tang CP, Ke CQ, et al. Naturally occurring homoisoflavonoids function as potent protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors by c-Src0based high-throughput screening. J Med Chem 2008; 51: 4419–29.
Zhang X, Peng T, Ji X, Li J, Tong L, Li Z, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-anilinoquinazolines with C-6 urea-linked side chains as inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Bioorg Med Chem 2013; 21: 7988–98.
Zhang Z, Meng T, He J, Li M, Tong LJ, Xiong B, et al. MT7, a novel compound from a combinatorial library, arrests mitosis via inhibiting the polymerization of microtubules. Investigat New Drugs 2010; 28: 715–28.
DiStefano JF, Cotto CA, Lane B, Hagag N . Role of epidermal growth factor in the expression of A431 cancer cell protease and red blood cell cytotoxicity. Cancer Res 1989; 49: 179–84.
Imaizumi T, Itaya H, Nasu S, Yoshida H, Matsubara Y, Fujimoto K, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human umbilical vein endothelial cells stimulated with interleukin-1alpha — an autocrine regulation of angiogenesis and inflammatory reactions. Thromb Haemost 2000; 83: 949–55.
Kline-Smith SL, Walczak CE . Mitotic spindle assembly and chromosome segregation: refocusing on microtubule dynamics. Mol Cell 2004; 15: 317–27.
Gan PP, McCarroll JA, Po'uha ST, Kamath K, Jordan MA, Kavallaris M . Microtubule dynamics, mitotic arrest, and apoptosis: drug-induced differential effects of betaIII-tubulin. Mol Cancer Ther 2010; 9: 1339–48.
Ma YM, Zhou YB, Xie CM, Chen DM, Li J . Novel microtubule-targeted agent 6-chloro-4-(methoxyphenyl) coumarin induces G2-M arrest and apoptosis in HeLa cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2012; 33: 407–17.
Ling YH, Li T, Yuan Z, Haigentz M Jr, Weber TK, Perez-Soler R . Erlotinib, an effective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces p27KIP1 up-regulation and nuclear translocation in association with cell growth inhibition and G1/S phase arrest in human non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Mol Pharmacol 2007; 72: 248–58.
De Antoni A, Pearson CG, Cimini D, Canman JC, Sala V, Nezi L, et al. The Mad1/Mad2 complex as a template for Mad2 activation in the spindle assembly checkpoint. Curr Biol 2005; 15: 214–25.
Hauf S, Cole RW, LaTerra S, Zimmer C, Schnapp G, Walter R, et al. The small molecule Hesperadin reveals a role for Aurora B in correcting kinetochore-microtubule attachment and in maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol 2003; 161: 281–94.
Weiss E, Winey M . The Saccharomyces cerevisiae spindle pole body duplication gene MPS1 is part of a mitotic checkpoint. J Cell Biol 1996; 132: 111–23.
Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers H, Van Oosterom AT, De Bruijn EA . Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev 2004; 56: 549–80.
Bijman MN, Amerongen GP, Laurens N, van Hinsbergh VW, Boven E . Microtubule-targeting agents inhibit angiogenesis at subtoxic concentrations, a process associated with inhibition of Rac1 and Cdc42 activity and changes in the endothelial cytoskeleton. Mol Cancer Ther 2006; 5: 2348–57.
Nicosia RF, Ottinetti A . Growth of microvessels in serum-free matrix culture of rat aorta. A quantitative assay of angiogenesis in vitro. Laboratory investigation; J Tech Methods Pathol 1990; 63: 115–22.
Auerbach R, Arensman R, Kubai L, Folkman J . Tumor-induced angiogenesis: lack of inhibition by irradiation. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer 1975; 15: 241–5.
Anbalagan M, Ali A, Jones RK, Marsden CG, Sheng M, Carrier L, et al. Peptidomimetic Src/pretubulin inhibitor KX-01 alone and in combination with paclitaxel suppresses growth, metastasis in human ER/PR/HER2-negative tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 2012; 11: 1936–47.
Rochais C, Cresteil T, Perri V, Jouanne M, Lesnard A, Rault S, et al. MR22388, a novel anti-cancer agent with a strong FLT–3 ITD kinase affinity. Cancer Lett 2013; 331: 92–8.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M . Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 153–66.
Dumontet C, Jordan MA . Microtubule-binding agents: a dynamic field of cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010; 9: 790–803.
Kubota Y . Tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapy. The Keio J Med 2012; 61: 47–56.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81173080, 81273365, and 81321092) and the National Science and Technology Major Project “Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program” of the People's Republic of China (No 2012ZX09103101-024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, T., Wu, Jr., Tong, Lj. et al. Identification of DW532 as a novel anti-tumor agent targeting both kinases and tubulin. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35, 916–928 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.33
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2014.33
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
New antiproliferative 3-substituted oxindoles inhibiting EGFR/VEGFR-2 and tubulin polymerization
Molecular Diversity (2024)
-
DW10075, a novel selective and small-molecule inhibitor of VEGFR, exhibits antitumor activities both in vitro and in vivo
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2016)
-
Antitumor action of CDK inhibitor LS-007 as a single agent and in combination with ABT-199 against human acute leukemia cells
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2016)
-
Deacetylisovaltratum disrupts microtubule dynamics and causes G2/M-phase arrest in human gastric cancer cells in vitro
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2016)