Abstract
Aim:
Multi-drug resistance poses a critical bottleneck in chemotherapy. Given the up-regulation of mTOR pathway in many chemoresistant cancers, we examined whether sirolimus (rapamycin), a first generation mTOR inhibitor, might induce human osteosarcoma (OS) cell apoptosis and increase the sensitivity of OS cells to anticancer drugs in vitro.
Methods:
Human OS cell line MG63/ADM was treated with sirolimus alone or in combination with doxorubicin (ADM), gemcitabine (GEM) or methotrexate (MTX). Cell proliferation and apoptosis were detected using CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry, respectively. MiRNAs in the cells were analyzed with miRNA microarray. The targets of miR-34b were determined based on TargetScan analysis and luciferase reporter assays. The expression of relevant mRNA and proteins was measured using qRT-PCR and Western blotting. MiR-34, PAK1 and ABCB1 levels in 40 tissue samples of OS patients were analyzed using qRT-PCR and in situ hybridization assays.
Results:
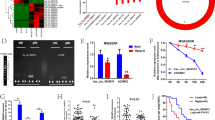
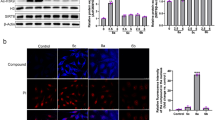
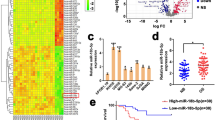
Sirolimus (1–100 nmol/L) dose-dependently suppressed the cell proliferation (IC50=23.97 nmol/L) and induced apoptosis. Sirolimus (10 nmol/L) significantly sensitized the cells to anticancer drugs, leading to decreased IC50 values of ADM, GEM and MTX (from 25.48, 621.41 and 21.72 μmol/L to 4.93, 73.92 and 6.77 μmol/L, respectively). Treatment of with sirolimus increased miR-34b levels by a factor of 7.5 in the cells. Upregulation of miR-34b also induced apoptosis and increased the sensitivity of the cells to the anticancer drugs, whereas transfection with miR-34b-AMO, an inhibitor of miR-34b, reversed the anti-proliferation effect of sirolimus. Two key regulators of cell cycle, apoptosis and multiple drug resistance, PAK1 and ABCB1, were demonstrated to be the direct targets of miR-34b. In 40 tissue samples of OS patients, significantly higher miR-34 ISH score and lower PAK5 and ABCB1 scores were detected in the chemo-sensitive group.
Conclusion:
Sirolimus increases the sensitivity of human OS cells to anticancer drugs in vitro by up-regulating miR-34b interacting with PAK1 and ABCB1. A low miR-34 level is an indicator of poor prognosis in OS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Jaffe N . Osteosarcoma: review of the past, impact on the future. The American experience. Cancer Treat Res 2009; 152: 239–62.
Milosevic Z, Pesic M, Stankovic T, Dinic J, Milovanovic Z, Stojsic J, et al. Targeting RAS-MAPK-ERK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR signal transduction pathways to chemosensitize anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Transl Res 2014; 164: 411–23.
Zhang H, Cohen AL, Krishnakumar S, Wapnir IL, Veeriah S, Deng G, et al. Patient-derived xenografts of triple-negative breast cancer reproduce molecular features of patient tumors and respond to mTOR inhibition. Breast Cancer Res 2014; 16: R36.
Utomo WK, Narayanan V, Biermann K, van Eijck CH, Bruno MJ . mTOR is a promising therapeutical target in a subpopulation of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett 2014; 346: 309–17.
Okazaki H, Matsunaga N, Fujioka T, Okazaki F, Akagawa Y, Tsurudome Y, et al. Circadian regulation of mTOR by the ubiquitin pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 543–51.
Arceci RJ, Stieglitz K, Bierer BE . Immunosuppressants FK506 and rapamycin function as reversal agents of the multidrug resistance phenotype. Blood 1992; 80: 1528–36.
Wang Y, Hu Z, Liu Z, Chen R, Peng H, Guo J, et al. MTOR inhibition attenuates DNA damage and apoptosis through autophagy-mediated suppression of CREB1. Autophagy 2013; 9: 2069–86.
Zhao S, Lu N, Chai Y, Yu X . Rapamycin inhibits tumor growth of human osteosarcomas. J BUON 2015; 20: 588–94.
Ajabnoor GM, Crook T, Coley HM . Paclitaxel resistance is associated with switch from apoptotic to autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 2012; 3: e260.
McCarty MF . mTORC1 activity as a determinant of cancer risk — rationalizing the cancer-preventive effects of adiponectin, metformin, rapamycin, and low-protein vegan diets. Med Hypotheses 2011; 77: 642–8.
Paoloni MC, Mazcko C, Fox E, Fan T, Lana S, Kisseberth W, et al. Rapamycin pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic relationships in osteosarcoma: a comparative oncology study in dogs. PLoS One 2010; 5: e11013.
Navarro F, Lieberman J . miR-34 and p53: new insights into a complex functional relationship. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0132767.
Li W, Han W, Ma Y, Cui L, Tian Y, Zhou Z, et al. P53-dependent miRNAs mediate nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in colonic carcinogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med 2015; 85: 105–13.
Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L, Hermeking H . The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol 2014; 6: 214–30.
Siemens H, Jackstadt R, Kaller M, Hermeking H . Repression of c-Kit by p53 is mediated by miR-34 and is associated with reduced chemoresistance, migration and stemness. Oncotarget 2013; 4: 1399–415.
Bao B, Li Y, Ahmad A, Azmi AS, Bao G, Ali S, et al. Targeting CSC-related miRNAs for cancer therapy by natural agents. Curr Drug Targets 2012; 13: 1858–68.
Kim CH, Kim HK, Rettig RL, Kim J, Lee ET, Aprelikova O, et al. miRNA signature associated with outcome of gastric cancer patients following chemotherapy. BMC Med Genomics 2011; 4: 79.
Wang L, Yu J, Xu J, Zheng C, Li X, Du J . The analysis of microRNA-34 family expression in human cancer studies comparing cancer tissues with corresponding pericarcinous tissues. Gene 2014; 554: 1–8.
Zhao J, Lammers P, Torrance CJ, Bader AG . TP53-independent function of miR-34a via HDAC1 and p21 (CIP1/WAF1). Mol Ther 2013; 21: 1678–86.
Wang LG, Ni Y, Su BH, Mu XR, Shen HC, Du JJ . MicroRNA-34b functions as a tumor suppressor and acts as a nodal point in the feedback loop with Met. Int J Oncol 2013; 42: 957–62.
Cannell IG, Bushell M . Regulation of Myc by miR-34c: A mechanism to prevent genomic instability? Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 2726–30.
Tanaka N, Toyooka S, Soh J, Tsukuda K, Shien K, Furukawa M, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-34 induces cell proliferation and invasion of human mesothelial cells. Oncol Rep 2013; 29: 2169–74.
Anderson ME . Update on survival in osteosarcoma. Orthop Clin North Am 2016; 47: 283–92.
Martz CA, Ottina KA, Singleton KR, Jasper JS, Wardell SE, Peraza-Penton A, et al. Systematic identification of signaling pathways with potential to confer anticancer drug resistance. Sci Signal 2014; 7: ra121.
Liesveld JL, O'Dwyer K, Walker A, Becker MW, Ifthikharuddin JJ, Mulford D, et al. A phase I study of decitabine and rapamycin in relapsed/refractory AML. Leuk Res 2013; 37: 1622–7.
Moroney J, Fu S, Moulder S, Falchook G, Helgason T, Levenback C, et al. Phase I study of the antiangiogenic antibody bevacizumab and the mTOR/hypoxia-inducible factor inhibitor temsirolimus combined with liposomal doxorubicin: tolerance and biological activity. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 5796–805.
Pop IV, Pop LM, Ghetie MA, Vitetta ES . Targeting mammalian target of rapamycin to both downregulate and disable the P-glycoprotein pump in multidrug-resistant B-cell lymphoma cell lines. Leuk Lymphoma 2009; 50: 1155–62.
Noh WC, Mondesire WH, Peng J, Jian W, Zhang H, Dong J, et al. Determinants of rapamycin sensitivity in breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 1013–23.
Ramaiah MJ, Pushpavalli SN, Lavanya A, Bhadra K, Haritha V, Patel N, et al. Novel anthranilamide-pyrazolo [1,5-a] pyrimidine conjugates modulate the expression of p53-MYCN associated micro RNAs in neuroblastoma cells and cause cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2013; 23: 5699–706.
Brabletz T . MiR-34 and SNAIL: another double-negative feedback loop controlling cellular plasticity/EMT governed by p53. Cell Cycle 2012; 11: 215–6.
Jin K, Xiang Y, Tang J, Wu G, Li J, Xiao H, et al. miR-34 is associated with poor prognosis of patients with gallbladder cancer through regulating telomere length in tumor stem cells. Tumour Biol 2014; 35: 1503–10.
Ishida H, Li K, Yi M, Lemon SM . p21-activated kinase 1 is activated through the mammalian target of rapamycin/p70 S6 kinase pathway and regulates the replication of hepatitis C virus in human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 11836–48.
Hammer A, Diakonova M . Tyrosyl phosphorylated serine-threonine kinase PAK1 is a novel regulator of prolactin-dependent breast cancer cell motility and invasion. Adv Exp Med Biol 2015; 846: 97–137.
Qing H, Gong W, Che Y, Wang X, Peng L, Liang Y, et al. PAK1-dependent MAPK pathway activation is required for colorectal cancer cellproliferation. Tumour Biol 2012; 33: 985–94.
Maroof H, Salajegheh A, Smith RA, Lam AK . Role of microRNA-34 family in cancer with particular reference to cancer angiogenesis. Exp Mol Pathol 2014; 97: 298–304.
Balça-Silva J, Sousa Neves S, Gonçalves AC, Abrantes AM, Casalta-Lopes J, Botelho MF, et al. Effect of miR-34b overexpression on the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res 2012; 32: 1603–9.
Ye Z, Fang J, Dai S, Wang Y, Fu Z, Feng W, et al. MicroRNA-34a induces a senescence-like change via the down-regulation of SIRT1 and up-regulation of p53 protein in human esophageal squamous cancer cells with a wild-type p53 gene background. Cancer Lett 2016; 370: 216–21.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81172548 and 81372873).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Zhao, Rh., Tseng, KF. et al. Sirolimus induces apoptosis and reverses multidrug resistance in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro via increasing microRNA-34b expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37, 519–529 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.153
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.153
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Multifaceted role of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway in human health and disease
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Association of mTOR Pathway and Conformational Alterations in C-Reactive Protein in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Infections
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Meta analysis of bioactive compounds, miRNA, siRNA and cell death regulators as sensitizers to doxorubicin induced chemoresistance
Apoptosis (2022)
-
miRNA signatures in childhood sarcomas and their clinical implications
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2019)
-
When less may be more: calorie restriction and response to cancer therapy
BMC Medicine (2017)