Abstract
Aim:
M2ES is PEGylated recombinant human endostatin. In this study we investigated the pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and excretion of M2ES in rats.
Methods:
125I-radiolabeled M2ES was administered to rats by intravenous bolus injection at 3 mg/kg. The pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion of M2ES were investigated using the trichloroacetic acid (TCA) precipitation method.
Results:
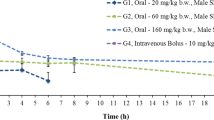
The serum M2ES concentration-time curve after a single intravenous dose of 3 mg/kg in rats was fitted with a non-compartment model. The pharmacokinetic parameters were evaluated as follows: Cmax=28.3 μg·equ/mL, t1/2=71.5 h, AUC(0–∞)=174.6 μg·equ·h/mL, Cl=17.2 mL·h−1·kg−1, MRT=57.6 h, and Vss=989.8 mL/kg for the total radioactivity; Cmax=30.3 μg·equ/mL, t1/2=60.1 h, AUC(0–∞)=146.2 μg·equ·h/mL, Cl=20.6 mL·h−1·kg−1, MRT=47.4 h, and Vss=974.6 mL/kg for the TCA precipitate radioactivity. M2ES was rapidly and widely distributed in various tissues and showed substantial deposition in kidney, adrenal gland, lung, spleen, bladder and liver. The radioactivity recovered in the urine and feces by 432 h post-dose was 71.3% and 8.3%, respectively. Only 0.98% of radioactivity was excreted in the bile by 24 h post-dose.
Conclusion:
PEG modification substantially prolongs the circulation time of recombinant human endostatin and effectively improves its pharmacokinetic behavior. M2ES is extensively distributed in most tissues of rats, including kidney, adrenal gland, lung, spleen, bladder and liver. Urinary excretion was the major elimination route for M2ES.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS . et al. Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 1997; 88: 277–85.
Taddei L, Chiarugi P, Brogelli L, Cirri P, Magnelli L, Raugei G, et al. Inhibitory effect of full-length human endostatin on in vitro angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 263: 340–5.
Shi H, Huang Y, Zhou H, Song X, Yuan S, Fu Y, et al. Nucleolin is a receptor that mediates antiangiogenic and antitumor activity of endostatin. Blood 2007; 110: 2899–906.
Chen Y, Wang S, Lu X, Zhang H, Fu Y, Luo Y . Cholesterol sequestration by nystatin enhances the uptake and activity of endostatin in endothelium via regulating distinct endocytic pathways. Blood 2011; 117: 6392–403.
Song N, Ding Y, Zhuo W, He T, Fu Z, Chen Y, et al. The nuclear translocation of endostatin is mediated by its receptor nucleolin in endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 2012; 15: 697–711.
Guo L, Song N, He T, Qi F, Zheng S, Xu XG, et al. Endostatin inhibits the tumorigenesis of hemangioendothelioma via downregulation of CXCL1. Mol Carcinog 2014. doi: 10.1002/mc.22210.
Ou J, Li J, Pan F, Xie G, Zhou Q, Huang H, et al. Endostatin suppresses colorectal tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis by inhibiting expression of fibronectin extra domain A and integrin alpha9. J Cell Biochem 2011; 112: 2106–14.
Brideau G, Makinen MJ, Elamaa H, Tu H, Nilsson G, Alitalo K, et al. Endostatin overexpression inhibits lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in mice. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 11528–35.
Zhuo W, Luo C, Wang X, Song X, Fu Y, Luo Y . Endostatin inhibits tumour lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis via cell surface nucleolin on lymphangiogenic endothelial cells. J Pathol 2010; 222: 249–60.
Zhuo W, Chen Y, Song X, Luo Y . Endostatin specifically targets both tumor blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. Front Med 2011; 5: 336–40.
Folkman J . Antiangiogenesis in cancer therapy — endostatin and its mechanisms of action. Exp Cell Res 2006; 312: 594–607.
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O'Reilly MS . Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 1997; 390: 404–7.
Dhanabal M, Ramchandran R, Volk R, Stillman IE, Lombardo M, Iruela-Arispe ML, et al. Endostatin: yeast production, mutants, and antitumor effect in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 189–97.
Whitworth A . Endostatin: are we waiting for Godot? J Natl Cancer Inst 2006; 98: 731–3.
Rong B, Yang S, Li W, Zhang W, Ming Z . Systematic review and meta-analysis of Endostar (rh-endostatin) combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treating advanced non-small cell lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol 2012; 10: 170.
Fu Y, Luo Y . The N-terminal integrity is critical for the stability and biological functions of endostatin. Biochemistry 2010; 49: 6420–9.
Fu Y, Tang H, Huang Y, Song N, Luo Y . Unraveling the mysteries of endostatin. IUBMB Life 2009; 61: 613–26.
Yang L, Wang JW, Tang ZM, Liu XW, Huang J, Li ST, et al. A phase I clinical trial for recombinant human endostatin. Chin J New Drugs 2004; 13: 548–53.
Yang L, Wang JW, Sun Y, Zhu YZ, Liu XQ, Li WL, et al. Randomized phase II trial on escalated doses of Rh-endostatin (YH-16) for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za zhi 2006; 28: 138–41.
Wang J, Sun Y, Liu Y, Yu Q, Zhang Y, Li K, et al. Results of randomized, multicenter, double-blind phase III trial of rh-endostatin (YH-16) in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Chin J Lung Cancer 2005; 8: 283–90.
Li Y, Huang XE, Yan PW, Jiang Y, Xiang J . Efficacy and safety of endostar combined with chemotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2010; 11: 1119–23.
Han B, Xiu Q, Wang H, Shen J, Gu A, Luo Y, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy of paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with endostar for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2011; 6: 1104–9.
Cui C, Mao L, Chi Z, Si L, Sheng X, Kong Y, et al. A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter trial of Endostar in patients with metastatic melanoma. Mol Ther 2013; 21: 1456–63.
Guo L, Geng X, Chen Y, Qi F, Liu L, Miao Y, et al. Pre-clinical toxicokinetics and safety study of M2ES, a PEGylated recombinant human endostatin, in rhesus monkeys. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 2014; 69: 512–23.
Harris JM, Chess RB . Effect of pegylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003; 2: 214–21.
Glue P, Fang JW, Rouzier-Panis R, Raffanel C, Sabo R, Gupta SK, et al. Pegylated interferon-alpha2b: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and preliminary efficacy data. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2000; 68: 556–67.
He XL, Yin HL, Wu J, Zhang K, Liu Y, Yuan T, et al. A multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of polyethylene glycol recombinant human interleukin-6 (PEG-rhIL-6) in rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2011; 12: 32–9.
Tanaka H, Satake-Ishikawa R, Ishikawa M, Matsuki S, Asano K . Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor conjugated to polyethylene glycol in rats. Cancer Res 1991; 51: 3710–4.
Bai H, Jing D, Jiang H, Yin S . Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion of recombinant human parathyroid hormone 1–84 in animals. Cell Biochem Biophys 2013; 66: 379–87.
Song HF, Liu XW, Zhang HN, Zhu BZ, Yuan SJ, Liu SY, et al. Pharmacokinetics of His-tag recombinant human endostatin in Rhesus monkeys. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005; 26: 124–8.
Yang XX, Hu ZP, Chan E, Duan W, Zhou S . Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human endostatin in rats. Curr Drug Metab 2006; 7: 565–76.
Molema G, van Veen-Hof I, van Loenen-Weemaes AM, Proost JH, de Leij LF, Meijer DK . Pharmacokinetics and whole body distribution of elastase derived angiostatin (K1-3) in rats. Int J Cancer 2001; 91: 1–7.
Xie Y, Zhong G, He H, Fan G, Wu Y . Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion of porcine fibrinogen after intraperitoneal injection of a porcine-derived fibrin glue to rats. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2011; 54: 148–53.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project 2009ZX09306-002; Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for “Significant New Drug Creation” 2009ZX09102-243; and Protgen Ltd (Beijing, China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Zg., Jia, L., Guo, Lf. et al. Pharmacokinetics of PEGylated recombinant human endostatin (M2ES) in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36, 847–854 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.16
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.16