Abstract
Aim:
Blockade of EGFR by EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as erlotinib is insufficient for effective treatment of human pancreatic cancer due to independent activation of the Akt pathway, while amiloride, a potassium-sparing diuretic, has been found as a potential Akt inhibitor. The aim of this study was to investigate the anticancer effects of combined amiloride with erlotinib against human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro.
Methods:
Cell proliferation, colony formation, cell cycle and apoptosis were analyzed in 4 human pancreatic cancer cell lines Bxpc-3, PANC-1, Aspc-1 and CFPAC-1 treated with erlotinib or amiloride alone, or in their combination. The synergistic analysis for the effects of combinations of amiloride and erlotinib was performed using Chou-Talalay's combination index isobolographic method.
Results:
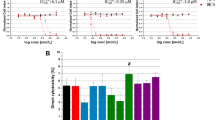
Amiloride (10, 30, and 100 μmol/L) concentration-dependently potentiated erlotinib-induced inhibition of cell proliferation and colony formation in the 4 pancreatic cancer cell lines. Isobolographic analysis confirmed that combinations of amiloride and erlotinib produced synergistic cytotoxic effects. Amiloride significantly potentiated erlotinib-induced G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in Bxpc-3 and PANC-1 cells. Amiloride inhibited EGF-stimulated phorsphorylation of AKT, and significantly enhanced erlotinib-induced downregulation of phorsphorylation of EGFR, AKT, PI3K P85 and GSK 3β in Bxpc-3 and PANC-1 cells.
Conclusion:
Amiloride sensitizes human pancreatic cancer cells to erlotinib in vitro through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Treatment of pancreatic cancer patients with combination of erlotinib and amiloride merits further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11–30.
Werner J, Combs SE, Springfeld C, Harteig W, Hackert T, Büchler MW . Advanced-stage pancreatic cancer: therapy options. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2013; 10: 323–33.
Burris H. 3rd, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 2403–13.
Heinemann V, Quietzsch D, Gieseler F, Gonnermann M, Schönekäs H, Rost A, et al. Randomized phase III trial of gemcitabine plus cisplatin compared with gemcitabine alone in advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 3946–52.
Miyabayashi K, Ijichi H, Mohri D, Tada M, Yamamoto K, Asaoka Y, et al. Erlotinib prolongs survival in pancreatic cancer by blocking gemcitabine-induced MAPK signals. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 2221–34.
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S, et al. National cancer institute of canada clinical trials group. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 1960–6.
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Haridas D, Jain M, Ganti AK, Batra SK . Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert opin Ther Targets 2012; 16: 15–31.
Prior IA, Lewis PD, Mattos C . A comprehensive survey of Ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 2457–67.
Donev IS, Wang W, Yamada T, Li Q, Takeuchi S, Matsumoto K, et al. Transient PI3K inhibition induces apoptosis and overcomes HGF-mediated resistance to EGFR-TKIs in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 2260–9.
Wang W, Li Q, Takeuchi S, Yamada T, Koizumi H, Nakamura T, et al. Met kinase inhibitor E7050 reverses three different mechanisms of hepatocyte growth factor-induced tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 1663–71.
Li P, Torossian A, Zhang Q, Xu WC, Fu S . Inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase enhances the cytotoxicity of AG1478, an epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, in breast cancer cells. Med Oncol 2012; 29: 3258–64.
Yi YW, Hong W, Kang HJ, Kim HJ, Zhao W, Wang A, et al. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway potentiates cytotoxicity of EGFR kinase inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med 2013; 17: 648–56.
Tatsuta M, Iishi H, Baba M, Uehara H, Nakaizumi A . Chemoprevention by amiloride of experimental carcinogenesis in rat colon induced by azoxymethane. Carcinogenesis 1995; 16: 941–2.
Tatsuta M, Iishi H, Baba M, Yano H, Iseki K, Uehara H, et al. Inhibition by amiloride of experimental carcinogenesis induced by azaserine in rat pancreas. Cancer Lett 1996; 106: 23–8.
Kim KM, Lee YJ . Amiloride augments TRAIL-induced apoptotic death by inhibiting phosphorylation of kinases and phosphatases associated with the PI3K-Akt pathway. Oncogene 2005; 24: 355–66.
Chou TC, Talalay P . Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 1984; 22: 27–55.
Baynes RD, Gansert J . KRAS mutational status as a predictor of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor efficacy in colorectal cancer. Am J Ther 2009; 16: 554–61.
Ludovini V, Bianconi F, Pistola L, Chiari R, Minotti V, Colella R, et al. Phosphoinositide-3-kinase catalytic alpha and KRAS mutations are important predictors of resistance to therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2011; 6: 707–15.
Linardou H, Dahabreh IJ, Kanaloupiti D, Siannis F, Bafaloukos D, Kosmidis P, et al. Assessment of somatic k-RAS mutations as a mechanism associated with resistance to EGFR-targeted agents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol 2008; 9: 962–72.
Lièvre A, Bachet JB, Le Corre D, Boige V, Landi B, Emile JF, et al. KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 3992–5.
Prior IA, Lewis PD, Mattos C . A comprehensive survey of ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 2457–67.
Davis RJ, Czech MP . Amiloride directly inhibits growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem 1985; 260: 2543–51.
Gadgeel SM, Wozniak A . Preclinical rationale for PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors as therapy for epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 2013; 14: 322–32.
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J . Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science 2004; 305: 1163–7.
Amann J, Kalyankrishna S, Massion PP, Ohm JE, Girard L, Shigematsu H, et al. Aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and enhanced sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 226–35.
Tracy S, Mukohara T, Hansen M, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Jänne PA . Gefitinib induces apoptosis in the EGFRL858R non-small-cell lung cancer cell line H3255. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 7241–4.
Diep CH, Munoz RM, Choudhary A, VonHoff DD, Han H . Synergistic effects between erlotinib and MEK inhibitors in KRAS wild-type human pancreatic cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 2744–56.
Marshall J . Clinical implications of the mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Cancer 2006; 107: 1207–18.
Kobayashi S, Shimamura T, Monti S, Steidl U, Hetherington CJ, Lowell AM, et al. Transcriptional profiling identifies cyclin D1 as a critical downstream effector of mutant epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 11389–98.
Helfrich BA, Raben D, Varella-Garcia M, Gustafson D, Chan DC, Bemis L, et al. Antitumor activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib (ZD1839, Iressa) in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines correlates with gene copy number and EGFR mutations but not EGFR protein levels. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 7117–25.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely appreciate Dr Li-xin Wu (Fudan-Zhangjiang New Drug R&D Joint Platform, Shanghai, China) for assistance with cell cycle analysis. The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81102459) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Yt., Yang, Hy., Li, T. et al. Amiloride sensitizes human pancreatic cancer cells to erlotinib in vitro through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36, 614–626 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The abscopal effect of anti-CD95 and radiotherapy in melanoma
Discover Oncology (2023)
-
An updated, computable MEDication-Indication resource for biomedical research
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Kaempferol potentiates the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to erlotinib via inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and epidermal growth factor receptor
Inflammopharmacology (2021)
-
The epithelial sodium channel has a role in breast cancer cell proliferation
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2021)
-
Hypoxia-induced exosome secretion promotes survival of African-American and Caucasian prostate cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2018)