Abstract
Aim:
Neferine is an isoquinoline alkaloid isolated from seed embryos of Nelumbo nucifera (Gaertn), which has a variety of biological activities. In this study we examined the effects of neferine on Kv4.3 channels, a major contributor to the transient outward current (Ito) in rabbit heart, and on ex vivo electrophysiology of rabbit hearts.
Methods:
Whole-cell Kv4.3 currents were recorded in HEK293 cells expressing human cardiac Kv4.3 channels using patch-clamp technique. Arterially perfused wedges of rabbit left ventricles (LV) were prepared, and transmembrane action potentials were simultaneously recorded from epicardial (Epi) and endocardial (Endo) sites with floating microelectrodes together with transmural electrocardiography (ECG).
Results:
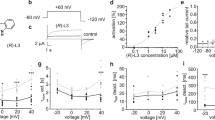
Neferine (0.1–100 μmol/L) dose-dependently and reversibly inhibited Kv4.3 currents (the IC50 value was 8.437 μmol/L, and the maximal inhibition at 100 μmol/L was 44.12%). Neferine (10 μmol/L) caused a positive shift of the steady-state activation curve of Kv4.3 currents, and a negative shift of the steady-state inactivation curve. Furthermore, neferine (10 μmol/L) accelerated the inactivation but not the activation of Kv4.3 currents, and markedly slowed the recovery of Kv4.3 currents from inactivation. Neferine-induced blocking of Kv4.3 currents was frequency-dependent. In arterially perfused wedges of rabbit LV, neferine (1, 3, and 10 μmol/L) dose-dependently prolonged the QT intervals and action potential durations (APD) at both Epi and Endo sites, and caused dramatic increase of APD10 at Epi sites.
Conclusion:
Neferine inhibits Kv4.3 channels likely by blocking the open state and inactivating state channels, which contributes to neferine-induced dramatic increase of APD10 at Epi sites of rabbit heart.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hatano N, Ohya S, Muraki K, Giles W, Imaizumi Y . Dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel antagonists and agonists block Kv4.2, Kv4.3 and Kv1.4 K+ channels expressed in hek293 cells. Br J Pharmacol 2003; 139: 533–44.
Yan GX, Antzelevitch C . Cellular basis for the brugada syndrome and other mechanisms of arrhythmogenesis associated with st-segment elevation. Circulation 1999; 100: 1660–6.
Yan GX, Antzelevitch C . Cellular basis for the electrocardiographic J wave. Circulation 1996; 93: 372–9.
Di Diego JM, Antzelevitch C . Pinacidil-induced electrical heterogeneity and extrasystolic activity in canine ventricular tissues. Does activation of atp-regulated potassium current promote phase 2 reentry? Circulation 1993; 88: 1177–89.
Krishnan SC, Antzelevitch C . Flecainide-induced arrhythmia in canine ventricular epicardium. Phase 2 reentry? Circulation 1993; 87: 562–72.
Lukas A, Antzelevitch C . Phase 2 reentry as a mechanism of initiation of circus movement reentry in canine epicardium exposed to simulated ischemia. Cardiovasc Res 1996; 32: 593–603.
Wang Z, Feng J, Shi H, Pond A, Nerbonne JM, Nattel S . Potential molecular basis of different physiological properties of the transient outward K+ current in rabbit and human atrial myocytes. Circ Res 1999; 84: 551–61.
Fiset C, Clark RB, Shimoni Y, Giles WR . Shal-type channels contribute to the Ca2+-independent transient outward K+ current in rat ventricle. J Physiol 1997; 500: 51–64.
Dixon JE, Shi W, Wang HS, McDonald C, Yu H, Wymore RS, et al. Role of the kv4.3 K+ channel in ventricular muscle. A molecular correlate for the transient outward current. Circ Res 1996; 79: 659–68.
Kong W, Po S, Yamagishi T, Ashen MD, Stetten G, Tomaselli GF . Isolation and characterization of the human gene encoding Ito: Further diversity by alternative mrna splicing. Am J Physiol 1998; 275: H1963–70.
Huang HL, Rao MR . Effects of neferine and its combination with taurine on platelet aggregation and experimental thrombosis in rats. Acta Pharm Sin 1995; 30: 486–90.
Guo Z . Electrophysiological effects of neferine against ischemic ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 1992; 20: 119–122, 134.
Pan Y, Cai B, Wang K, Wang S, Zhou S, Yu X, et al. Neferine enhances insulin sensitivity in insulin resistant rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2009; 124: 98–102.
Yoon JS, Kim HM, Yadunandam AK, Kim NH, Jung HA, Choi JS, et al. Neferine isolated from nelumbo nucifera enhances anti-cancer activities in hep3b cells: Molecular mechanisms of cell cycle arrest, er stress induced apoptosis and anti-angiogenic response. Phytomedicine 2013; 20: 1013–22.
Li GR, Li XG, Lu FH . Effects of neferine on transmembrane potential in rabbit sinoatrial nodes and clusters of cultured myocardial cells from neonatal rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 1989; 10: 328–31.
Gu DF, Li XL, Qi ZP, Shi SS, Hu MQ, Liu DM, et al. Blockade of herg K+ channel by isoquinoline alkaloid neferine in the stable transfected hek293 cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 2009; 380: 143–51.
Dong ZX, Zhao X, Gu DF, Shi YQ, Zhang J, Hu XX, et al. Comparative effects of liensinine and neferine on the human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channel and pharmacological activity analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem 2012; 29: 431–42.
Huang Y, Zhao L, Bai Y, Liu P, Wang J, Xiang J . Simultaneous determination of liensinine, isoliensinine and neferine from seed embryo of nelumbo nucifera gaertn. In rat plasma by a rapid hplc method and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. Arzneimittelforschung 2011; 61: 347–52.
Liu T, Brown BS, Wu Y, Antzelevitch C, Kowey PR, Yan GX . Blinded validation of the isolated arterially perfused rabbit ventricular wedge in preclinical assessment of drug-induced proarrhythmias. Heart Rhythm 2006; 3: 948–56.
Yan GX, Shimizu W, Antzelevitch C . Characteristics and distribution of m cells in arterially perfused canine left ventricular wedge preparations. Circulation 1998; 98: 1921–7.
Singarayar S, Bursill J, Wyse K, Bauskin A, Wu W, Vandenberg J, et al. Extracellular acidosis modulates drug block of Kv4.3 currents by flecainide and quinidine. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2003; 14: 641–50.
Wang H, Shi H, Zhang L, Pourrier M, Yang B, Nattel S, et al. Nicotine is a potent blocker of the cardiac a-type K+ channels. Effects on cloned Kv4.3 channels and native transient outward current. Circulation 2000; 102: 1165–71.
Sah R, Ramirez RJ, Oudit GY, Gidrewicz D, Trivieri MG, Zobel C, et al. Regulation of cardiac excitation-contraction coupling by action potential repolarization: Role of the transient outward potassium current Ito . J Physiol 2003; 546: 5–18.
Fischer F, Vonderlin N, Zitron E, Seyler C, Scherer D, Becker R, et al. Inhibition of cardiac Kv1.5 and Kv4.3 potassium channels by the class Ia anti-arrhythmic ajmaline: Mode of action. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2013; 386: 991–9.
Delpon E, Cordeiro JM, Nunez L, Thomsen PE, Guerchicoff A, Pollevick GD, et al. Functional effects of kcne3 mutation and its role in the development of brugada syndrome. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2008; 1: 209–18.
Lee HJ, Sung KW, Hahn SJ . Effects of haloperidol on kv4.3 potassium channels. Eur J Pharmacol 2014; 740: 1–8.
Wang Z, Fermini B, Nattel S . Effects of flecainide, quinidine, and 4-aminopyridine on transient outward and ultrarapid delayed rectifier currents in human atrial myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1995; 272: 184–96.
Jeong I, Kim SW, Yoon SH, Hahn SJ . Block of cloned kv4.3 potassium channels by dapoxetine. Neuropharmacology 2012; 62: 2261–6.
Choi JS, Hahn SJ . Duloxetine blocks cloned kv4.3 potassium channels. Brain Res 2012; 1466: 15–23.
Jeong I, Choi BH, Hahn SJ . Pergolide block of the cloned kv1.5 potassium channels. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 2013; 386: 125–33.
Tang Q, Li ZQ, Li W, Guo J, Sun HY, Zhang XH, et al. The 5-HT2 antagonist ketanserin is an open channel blocker of human cardiac ether-a-go-go-related gene (herg) potassium channels. Br J Pharmacol 2008; 155: 365–73.
Tang Q, Jin MW, Xiang JZ, Dong MQ, Sun HY, Lau CP, et al. The membrane permeable calcium chelator bapta-am directly blocks human ether a-go-go-related gene potassium channels stably expressed in HEK293 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 2007; 74: 1596–607.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Gui-rong LI (University of Hong Kong) for providing the HEK293 cells that stably expressed Kv4.3 potassium channels.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Chen, Yf., Quan, Xq. et al. Effects of neferine on Kv4.3 channels expressed in HEK293 cells and ex vivo electrophysiology of rabbit hearts. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36, 1451–1461 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.83
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.83
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibitory effects of hesperetin on Nav1.5 channels stably expressed in HEK 293 cells and on the voltage-gated cardiac sodium current in human atrial myocytes
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2016)
-
Neferine increase in vitro anticancer effect of dehydroepiandrosterone on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
Applied Biological Chemistry (2016)
-
Inhibitory effects of neferine on Nav1.5 channels expressed in HEK293 cells
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology [Medical Sciences] (2016)