Abstract
Aim:
The dried tuber root of Ophiopogon japonicus has been used in the traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of myocardial ischemia and thrombosis. In this study we investigated the effects of methylophiopogonanone A (MO-A), a major homoisoflavonoid in Ophiopogon japonicus, on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury.
Methods:
Mice were pretreated with MO-A (10 mg·kg-1·d-1, po) for 2 weeks and then subjected to transient occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Cardiac function was evaluated, and the infarct size and apoptosis index were assessed. The mechanisms underlying the cardio-protection of MO-A were analyzed in H9C2 rat cardiomyocytes subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R). The cell viability and apoptosis were evaluated; apoptotic and relevant signaling proteins were analyzed. NO levels in the culture medium were assessed.
Results:
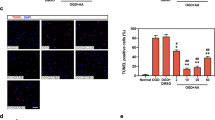
In I/R mice, pretreatment with MO-A significantly reduced the infarct size (by 60.7%) and myocardial apoptosis (by 56.8%), and improved cardiac function. In H9C2 cells subjected to H/R, pretreatment with MO-A (10 μmol/L) significantly decreased apoptosis and cleaved caspase-3 expression, elevated the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and restored NO production. Furthermore, pretreatment with MO-A markedly increased the activation of PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in H9C2 cells subjected to H/R, and the protective effects of MO-A were abolished in the presence of the PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (100 nmol/L).
Conclusion:
MO-A attenuates I/R-induced myocardial apoptosis in mice via activating the PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ibanez B, Heusch G, Ovize M, Van de Werf F . Evolving therapies for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 65: 1454–71.
Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ . Mechanisms of disease: myocardial reperfusion injury. New Engl J Med 2007; 357: 1121–35.
Heusch G . Molecular basis of cardioprotection: signal transduction in ischemic pre-, post-, and remote conditioning. Circ Res 2015; 116: 674–99.
Hernandez-Resendiz S, Palma-Flores C, De Los Santos S, Roman-Anguiano NG, Flores M, de la Pena A, et al. Reduction of no-reflow and reperfusion injury with the synthetic 17beta-aminoestrogen compound Prolame is associated with PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling cascade. Basic Res Cardiol 2015; 110: 1.
Ma CJ, Li G, Zhang J, Zheng QS, Fan X, Wang ZH . An efficient combination of supercritical fluid extraction and high-speed counter-current chromatography to extract and purify homoisoflavonoids from Ophiopogon japonicus (Thunb) Ker-Gawler. J Sep Sci 2009; 32: 1949–56.
Zhu YZ, Huang SH, Tan BKH, Sun J, Whiteman M, Zhu YC . Antioxidants in Chinese herbal medicines: a biochemical perspective. Nat Prod Rep 2004; 21: 478–89.
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM . New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: targeting the reperfusion injury Salvage kinase (RISK)-pathway. Cardiovasc Res 2004; 61: 448–60.
Tsang A, Hausenloy DJ, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM . Postconditioning: A form of “modified reperfusion” protects the myocardium by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway. Circ Res 2004; 95: 230–2.
Zhao MM, Yang JY, Wang XB, Tang CS, Du JB, Jin HF . The PI3K/Akt pathway mediates the protection of SO(2) preconditioning against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2013; 34: 501–6.
Oyama J, Blais C, Liu XL, Pu MY, Kobzik L, Kelly RA, et al. Reduced myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in toll-like receptor 4-deficient mice. Circulation 2004; 109: 784–9.
Ren BH, Shen Y, Shao HT, Qian JJ, Wu HW, Jing H . Brain natriuretic peptide limits myocardial infarct size dependent of nitric oxide synthase in rats. Clin Chim Acta 2007; 377: 83–7.
Salas MA, Valverde CA, Sanchez G, Said M, Rodriguez JS, Portiansky EL, et al. The signalling pathway of CaMKII-mediated apoptosis and necrosis in the ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2010; 48: 1298–306.
Elrod JW, Calvert JW, Morrison J, Doeller JE, Kraus DW, Tao L, et al. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by preservation of mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007; 104: 15560–5.
Zhou SS, He F, Chen AH, Hao PY, Song XD . Suppression of rat Frizzled-2 attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced Ca2+ accumulation in rat H9c2 cells. Exp Cell Res 2012; 318: 1480–91.
Lee S, Kim K, Kim YH, Chung MH, Kang I, Ha J, et al. Preventive role of propofol in hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptotic H9c2 rat cardiac myoblast cell death. Mol Med Rep 2011; 4: 351–6.
Li LH, Wang JS, Kong LY . Protective effects of Shengmai San and its three fractions on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin J Nat Med 2013; 11: 222–30.
Li N, Zhang JY, Zeng KW, Zhang L, Che YY, Tu PF . Anti-inflammatory homoisoflavonoids from the tuberous roots of Ophiopogon japonicus. Fitoterapia 2012; 83: 1042–5.
Chiong M, Wang ZV, Pedrozo Z, Cao DJ, Troncoso R, Ibacache M, et al. Cardiomyocyte death: mechanisms and translational implications. Cell Death Disease 2011; 2: 11.
Cheng Y, Zhu P, Yang J, Liu X, Dong S, Wang X, et al. Ischaemic preconditioning-regulated miR-21 protects heart against ischaemia/reperfusion injury via anti-apoptosis through its target PDCD4. Cardiovasc Res 2010; 87: 431–9.
Wagner C, Tillack D, Simonis G, Strasser RH, Weinbrenner C . Ischemic post-conditioning reduces infarct size of the in vivo rat heart: role of PI3-K, mTOR, GSK-3beta, and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 2010; 339: 135–47.
Aurora AB, Mahmoud AI, Luo X, Johnson BA, van Rooij E, Matsuzaki S, et al. MicroRNA-214 protects the mouse heart from ischemic injury by controlling Ca2+ overload and cell death. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 1222–32.
Hullinger TG, Montgomery RL, Seto AG, Dickinson BA, Semus HM, Lynch JM, et al. Inhibition of miR-15 protects against cardiac ischemic injury. Circ Res 2012; 110: 71–81.
Arslan F, Lai RC, Smeets MB, Akeroyd L, Choo A, Aguor ENE, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res 2013; 10: 301–12.
Breivik L, Helgeland E, Aarnes EK, Mrdalj J, Jonassen AK . Remote postconditioning by humoral factors in effluent from ischemic preconditioned rat hearts is mediated via PI3K/Akt-dependent cell-survival signaling at reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol 2011; 106: 135–45.
Takada Y, Hashimoto M, Kasahara J, Aihara K, Fukunaga K . Cytoprotective effect of sodium orthovanadate on ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in the rat heart involves Akt activation and inhibition of fodrin breakdown and apoptosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004; 311: 1249–55.
Wu H, Ye M, Yang J, Ding J, Yang J, Dong W, et al. Nicorandil protects the heart from Ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum response-induced apoptosis through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015; 35: 2320–32.
Uchiyama T, Engelman RM, Maulik N, Das DK . Role of Akt signaling in mitochondrial survival pathway triggered by hypoxic preconditioning. Circulation 2004; 109: 3042–9.
Bharti S, Golechha M, Kumari S, Siddiqui KM, Arya DS . Akt/GSK-3beta/eNOS phosphorylation arbitrates safranal-induced myocardial protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Eur J Nutr 2012; 51: 719–27.
Wang T, Mao X, Li H, Qiao S, Xu A, Wang J, et al. N-Acetylcysteine and allopurinol up-regulated the Jak/STAT3 and PI3K/Akt pathways via adiponectin and attenuated myocardial postischemic injury in diabetes. Free Radical Biol Med 2013; 63: 291–303.
Gao F, Gao E, Yue TL, Ohlstein EH, Lopez BL, Christopher TA, et al. Nitric oxide mediates the antiapoptotic effect of insulin in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion: the roles of PI3-kinase, Akt, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation. Circulation 2002; 105: 1497–502.
Peng X, Chen R, Wu Y, Huang B, Tang C, Chen J, et al. PPARgamma-PI3K/AKT-NO signal pathway is involved in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by high glucose and insulin. J Diabetes Complication 2015; 29: 755–60.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a clinical research fund from Anhui Medical University (2015×kj112) and the foundation of basic research program of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (2016qn018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, F., Xu, Bl., Chen, C. et al. Methylophiopogonanone A suppresses ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial apoptosis in mice via activating PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37, 763–771 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.14
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.14
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular Mechanism of Yangshen Maidong Decoction in the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure based on Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2024)
-
Cordycepin alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by enhancing autophagy via AMPK-mTOR pathway
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2022)
-
Resveratrol pretreatment alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting STIM1-mediated intracellular calcium accumulation
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2019)
-
Hypoxia induces universal but differential drug resistance and impairs anticancer mechanisms of 5-fluorouracil in hepatoma cells
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2017)