Abstract
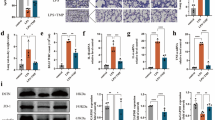
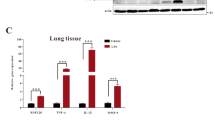
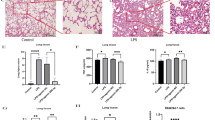
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated signaling plays a critical role in sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI). LYRM03 (3-amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-valyl-isoleucine) is a novel derivative of ubenimex, a widely used antineoplastic medicine. We previously found that LYRM03 has anti-inflammatory effects in cecal ligation puncture mouse model. In this study we determined whether LYRM03 attenuated LPS-induced ALI in mice. LPS-induced ALI mouse model was established by challenging the mice with intratracheal injection of LPS (5 mg/kg), which was subsequently treated with LYRM03 (10 mg/kg, ip). LYRM03 administration significantly alleviated LPS-induced lung edema, inflammatory cell (neutrophils and macrophages) infiltration and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, decreased pro-inflammatory and chemotactic cytokine (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, MIP-2) generation and reduced iNOS and COX-2 expression in the lung tissues. In cultured mouse alveolar macrophages in vitro, pretreatment with LYRM03 (100 μmol/L) suppressed LPS-induced macrophage activation by reducing Myd88 expression, increasing IκB stability and inhibiting p38 phosphorylation. These results suggest that LYRM03 effectively attenuates LPS-induced ALI by inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and Myd88-dependent TLR4 signaling pathways in alveolar macrophages. LYRM03 may serve as a potential treatment for sepsis-mediated lung injuries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ware LB, Matthay MA . The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 1334–49.
Gordon DR, Ellen C, Eve P, Jim W, Diane PM, Margaret N, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1685–93.
Abraham E . Neutrophils and acute lung injury. Crit Care Med 2003; 31: S195–9.
Lee WL, Gregory PD . Neutrophil activation and acute lung injury. Curr Opin Crit Care 2001; 7: 1–7.
Corteling R, Wyss D, Trifilieff A . In vivo models of lung neutrophil activation. Comparison of mice and hamsters. BMC Pharmacol 2002; 2: 1.
Moraes TJ, Joanna HZ, Gregory PD . Neutrophil granule contents in the pathogenesis of lung injury. Curr Opin Hematol 2006; 13: 21–7.
George CL, Jin H, Christine LW . Marsha EO', John CP, Patrick O'S, et al. Endotoxin responsiveness and subchronic grain dust-induced airway disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2001; 280: L203–13.
Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S . Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 2003; 21: 335–76.
Andonegui G, Zhou H, Bullard D, Kelly MM, Mullaly SC, McDonald B, et al. Mice that exclusively express TLR4 on endothelial cells can efficiently clear a lethal systemic Gram-negative bacterial infection. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 1921–30.
Fitzgerald KA, Palsson-McDermott EM, Bowie AG, Jefferies CA, Mansell AS, Brady G, Brint E, Dunne A, Gray P, Harte MT, McMurray D, Smith DE, Sims JE, Bird TA, O'Neill LA . Mal (MyD88-adapter-like) is required for Toll-like receptor-4 signal transduction. Nature 2001; 413 (6851): 78–83.
Palsson-McDermott, Eva M, O'Neill, Luke AJ . Signal transduction by the lipopolysaccharide receptor, Toll-like receptor-4. Immunology 2004; 113: 153–62.
Herlaar E, Brown Z . P38 MAPK signaling cascades in inflammatory disease. Mol Med Today 1999; 5: 439–46.
Pearson G, Robinson F, Gibson TB, Xu BE, Karadikar M, Berman K, Cobb ME . Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocrinol Rev 2001; 22: 153–83.
Arancibia SA, Beltrán CJ, Aguirre IM, Silva P, Peralta AL, Malinarich F, Hermoso MA . Toll-like receptors are key participants in innate immune responses. Biol Res 2007; 40: 97–112.
Standiford TJ, Peter AW . Therapeutic targeting of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Transl Res 2016; 167: 183–91.
Umezawa H, Aoyagi T, Suda H, Hamada M, Takeuchi T . Bestatin, an inhibitor of aminopeptidase B, produced by actinomycetes. J Antibiot 1976; 29: 97–9.
Muskardin DT, Voelkel NF, Fitzpatrick FA . Modulation of pulmonary leukotriene formation and perfusion pressure by Bestatin, an inhibitor of leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Biochem Pharmacol 1994; 48: 131–7.
Sekine K, Fujii H, Abe F . Induction of apoptosis by Bestatin (ubenimex) in human leukemic cell lines. Leukemia 1999; 13: 729–34.
Bauvois B, Dauzonne D . Aminopeptidase-N/CD13 (EC 3.4.11.2) inhibitors: chemistry, biological evaluations, and therapeutic prospects. Med Res Rev 2006; 26: 88–130.
Hirayama Y, Sakamaki S, Takayanagi N, Tsuji Y, Sagawa T, Chiba H, et al. Chemotherapy with ubenimex corresponding to patient age and organ disorder for 18 cases of acute myelogeneous leukemia in elderly patients-effects, complications and long-term survival. Cancer Chemother 2003; 30: 1113–8.
Lkhagvaa B, Tani K, Sato K, Toyoda Y, Suzuka C, Sone S . Bestatin, an inhibitor for aminopeptidases, modulates the production of cytokines and chemokines by activated monocytes and macrophages. Cytokine 2008; 44: 386–91.
Qian F, Deng J, Gantner BN, Flavell RA, Dong C, Christman JW, et al. MAP kinase phosphatase 5 protects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2012; 302: L866–74.
Matthay MA, Zimmerman GA, Esmon C, Bhattacharya J, Coller B, Doerschuk CM, et al. Future research directions in acute lung injury: summary of a national heart, lung, and blood institute working group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 167: 1027–35.
Marshall HE, Potts EN, Kelleher ZT, Stamler JS, Foster WM, Auten RL . Protection from lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by augmentation of airway S-nitrosothiols. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009; 180: 11–8.
Faurschou M, Niels B . Neutrophil granules and secretory vesicles in inflammation. Microbes Infect 2003; 5: 1317–27.
Corteling R, Wyss D, Trifilieff A . In vivo models of lung neutrophil activation. Comparison of mice and hamsters. BMC Pharmacol 2002; 2: 1.
Moraes TJ, Joanna HZ, Gregory PD . Neutrophil granule contents in the pathogenesis of lung injury. Curr Opin Hematol 2006; 13: 21–7.
Qian F, Deng J, Lee YG, Zhu J, Karpurapu M, Chung S, et al. The transcription factor PU.1 promotes alternative macrophage polarization and asthmatic airway inflammation. J Mol Cell Biol 2015; 7: 557–67.
Sanbongi C, Takano H, Osakabe N, Sasa N, Natsume M, Yanagisawa R, et al. Rosmarinic acid inhibits lung injury induced by diesel exhaust particles. Free Radical Bio Med 2003; 34: 1060–9.
Hinder F, Stubbe HD, Van Aken H, Waurick R, Booke M, Meyer J . Role of nitric oxide in sepsis-associated pulmonary edema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 159: 252–7.
Kristof AS, Goldberg P, Laubach V, Hussain SN . Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 158: 1883–9.
Gust R, Kozlowski JK, Stephenson AH, Schuster DP . Schuster role of cyclooxygenase-2 in oleic acid-induced acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 160: 1165–70.
Morrison DC, Ryan JL . Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol 1979; 28: 293–450.
Jeyaseelan S, Chu HW, Young SK, Freeman MW, Worthen GS . Distinct roles of pattern recognition receptors CD14 and Toll-like receptor 4 in acute lung injury. Infect Immun 2005; 73: 1754–63.
Wu F, Liu Y, Lv X, Miao X, Sun Y, Yu W . Small interference RNA targeting TLR4 gene effectively attenuates pulmonary inflammation in a rat model. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012; 2012: 406435.
Ghosh M, Subramani J, Rahman MM, Shapiro LH . CD13 restricts TLR4 endocytic signal transduction in inflammation. J Immunol 2015; 194: 4466–76.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81373424, 81573438, and 81401302), and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No 20130073120108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Hq., Wu, Yx., Nie, Yj. et al. LYRM03, an ubenimex derivative, attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by suppressing the TLR4 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38, 342–350 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.141
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.141
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Rubusoside relieves lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via modulating inflammatory responses: in vitro and in vivo studies
Applied Nanoscience (2023)
-
Fisetin alleviates sepsis-induced multiple organ dysfunction in mice via inhibiting p38 MAPK/MK2 signaling
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2020)
-
HDAC2 hyperexpression alters hippocampal neuronal transcription and microglial activity in neuroinflammation-induced cognitive dysfunction
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2019)
-
Costunolide alleviates HKSA-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of macrophage activation
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2019)
-
Protostemonine effectively attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)