Abstract
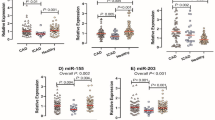
miRNAs have shown promise as potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction (AMI). However, the current used quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) allows solely for relative expression of nucleic acids and it is susceptible to day-to-day variability, which has limited the validity of using the miRNAs as biomarkers. In this study we explored the technical qualities and diagnostic potential of a new technique, chip-based digital PCR, in quantifying the miRNAs in patients with AMI and ischaemia-reperfusion injury (I/R). In a dilution series of synthetic C.elegans-miR-39, chip-based digital PCR displayed a lower coefficient of variation (8.9% vs 46.3%) and a lower limit of detection (0.2 copies/μL vs 1.1 copies/μL) compared with qRT-PCR. In the serum collected from 24 patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and 20 patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) patients after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), we used qRT-PCR and multiplexed chip-based digital PCR to quantify the serum levels of miRNA-21 and miRNA-499 as they have been validated in AMI in prior studies. In STEMI, I/R injury was assessed via measurement of ST-segment resolution (ST-R). Chip-based digital PCR revealed a statistical significance in the difference of miR-21 levels between stable CAD and STEMI groups (118.8 copies/μL vs 59 copies/μL; P=0.0300), whereas qRT-PCR was unable to reach significance (136.4 copies/μL vs 122.8 copies/μL; P=0.2273). For miR-499 levels, both chip-based digital PCR and qRT-PCR revealed statistically significant differences between stable CAD and STEMI groups (2 copies/μL vs 8.5 copies/μL, P=0.0011; 0 copies/μL vs 19.4 copies/μL; P<0.0001). There was no association between miR-21/499 levels and ST-R post-PCI. Our results show that the chip-based digital PCR exhibits superior technical qualities and promises to be a superior method for quantifying miRNA levels in the circulation, which may become a more accurate and reproducible method for directly quantifying miRNAs, particularly for use in large multi-centre clinical trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Mohr AM, Justin LM. Overview of microRNA biology. Seminars in Liver Disease 2014; 35: 3–11.
Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM. Circulating microRNAs: novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases? Eur Heart J 2010; 31: 2705–7.
D'Alessandra Y, Devanna P, Limana F, Straino S, Di Carlo A, Brambilla PG, et al. Circulating microRNAs are new and sensitive biomarkers of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 2010; 31: 2765–73.
Fichtlscherer S, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. Circulating microRNAs biomarkers or mediators of cardiovascular diseases? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2011; 11: 2383–90.
Ji R, Cheng Y, Yue J, Yang J, Liu X, Chen H, et al. MicroRNA expression signature and antisense-mediated depletion reveal an essential role of microRNA in vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ Res 2007; 100: 1579–88.
Hu S, Huang M, Nguyen PK, Gong Y, Li Z, Jia F, et al. Novel MicroRNA prosurvival cocktail for improving engraftment and function of cardiac progenitor cell transplantation. Circulation 2011; 124: 27–34.
Thum T, Gross C, Fiedler J, Fischer T, Kissler S, Bussen M, et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature 2008; 456: 980–4.
van Rooij E, Quiat D, Johnson BA, Sutherland LB, Qi X, Richardson JA, et al. A family of microRNAs encoded by myosin genes governs myosin expression and muscle performance. Dev Cell 2009; 17: 662–73.
Heinrich EM, Dimmeler S. MicroRNAs and stem cells control of pluripotency reprogramming and lineage commitment. Circ Res 2012; 110: 1014–22.
Wang JX, Jiao JQ, Li Q, Long B, Wang K, Liu JP, et al. miR-499 regulated mitochondrial dynamics by targeting calcineurin and dynamin-related protein-1. Nat Med 2011; 17: 71–8.
Wang F, Long G, Zhao C, Li H, Chaugai S, Wang Y, et al. Atherosclerosis-related circulating miRNAs as novel and sensitive predictors for acute myocardial infarction. PLoS One 2014; 9: 9
Olivieri F, Antonicelli R, Lorenzi M, D'Alessandra Y, Lazzarini R, Santini G, et al. Diagnostic potential of circulating miR-499-5p in elderly patients with acute non ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 2013; 167: 531–6.
Wang GK, Zhu JQ, Zhang JT, Li Q, Li Y, He J, et al. Circulating microRNA: a novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Eur Heart J 2010; 31: 659–66.
Xi C, Zhang L, Su T, Li H, Huang Q, Wu D, et al. Kinetics of plasma microRNA-499 expression in acute myocardial infarction. J Thorac Dis 2015; 7: 890–6.
Wei Y, Shao J, Bai X, Zhang G. Expression of plasma microRNA-1/21/ 208a/499 in myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury. Cardiology 2015; 130: 237–41.
Devaux Y, Vausort M, Goretti E, Nazarov PV, Azuaje F, Gilson G, et al. Use of circulating microRNAs to diagnose acute myocardial infarction. Clin Chem 2012; 58: 559–67.
Schulte C, Zeller T. microRNA-based diagnostics and therapy in cardiovascular disease - Summing up the facts. Cardiovasc Diagnost Ther 2015; 5: 17–36.
Koshiol J, Wang E, Zhao Y, Marincola F, Landi MT. Strengths and limitations of laboratory procedures for microRNA detection. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prevent 2010; 19: 907–11.
Kanagal-Shamanna R. Digital PCR: principles and applications. Methods Mol Biol 2016; 1392: 43–50.
Hindson BJ, Ness KD, Masquelier DA, Belgrader P, Heredia NJ, Makarewicz AJ, et al. High-throughput Droplet digital PCR system for absolute quantitation of DNA copy number. Anal Chem 2011; 83: 8604–10.
Hindson CM, Chevillet JR, Briggs HA, Gallichotte E, Ruf IK, Hindson BJ, et al. Absolute quantification by Droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat Methods 2013; 10: 1003–5.
Bosman KJ, Nijhuis M, van Ham PM, Wensing AMJ, Vervisch K, Vandekerckhove L, et al. Comparison of digital PCR platfroms and semi nested qPCR as a tool to detemine the size of the HIV reservoir. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 13811.
Conte D, Verri C, Borzi C, Suatoni P, Pastorino U, Sozzi G, Fortunato O. Novel method to detect microRNAs using chip-based QuantStudio 3D digital PCR. BMC Genomics 2015; 16: 849.
Lee H, Park Y, We Y, Han DJ, Seo JW, Moon H, et al. Evaluation of digital PCR as a technique for monitoring acute rejection in kidney transplantation. Genomics Inform 2017; 15: 2–10.
Kinz E, Leiherer A, Lang AH, Drexel H, Muendlein A. Accurate quantitation of JAK2 V617F allele burden by array-based digital PCR. Int Jnl Lab Hem 2015; 37: 217–24.
Pfaffl MW. Quantification strategies in real-time PCR. A-Z of quantitative PCR [serial on the Internet]. 2004 Jun [cited 2016 Aug 4]; Chapter 3. Available from: http://gene-quantification.org/chapter-3-pfaffl.pdf. (4 August 2016).
Massart DL. Data Handling in Science and Technology.In: Massart DL, Vandeginste BGM, Buydens LMC, De Jong S, Lewi PJ, Smereys-Verbeke J, editors. Handbook of Chemometrics and Qualimetrics. Amsterdam:Elsevier Science B.V.; 1998. Part A.
Shrivastava A, Gupta VB. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantification of the analytical methods. Chron Young Sci 2011; 2: 21–5.
Schröder R, Wegscheider K, Schroder K, Dissmann R, Meyer-Sabellek W, for the INJECT Trial Group. SExtent of early ST segment elevation resolution: a strong predictor of outcome in patients with acute myocardial infarction and a sensitive measure to compare thrombolytic regimens. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995; 26: 1657–64
de Lemos JA, Braunwald E. ST segment resolution as a tool for assessing the efficacy of reperfusion therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001; 38: 1283–94.
de Roeck L, Vandamme S, Everaert BR, Hoymans V, Haine S, Vandendriessche T, et al. Adiponectin and ischemia-reperfusion injury in ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care 2016; 5: 71–6.
Dong S, Cheng Y, Yang J, Li J, Liu X, Wang X, et al. MicroRNA expression signature and the role of microRNA-21 in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 29514–25.
Gu GL, Xu XL, Sun XT, Zhang J, Guo CG, Wang CS, et al. Cardioprotective effect of microRNA-21 in murine myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Ther 2015; 33: 109–17.
Liu X, Dong Y, Chen S, Zhang G, Zhang M, Gong Y, Li X. Circulating micro-RNA-146a and microRNA-21 predict left ventricular remodeling after ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Cardiology 2015; 132: 233–41.
Ma J, Li N, Jiang F. Quantification of plasma miRNAs by digital PCR for cancer diagnosis. Biomarker Insights 2013; 8: 127–36.
Di CA, Plewka M, Werren M, Badano LP, Fresco C, Fioretti PM. Estimation of infarct size by single measurements of creatine kinase levels in patients with a first myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Med 2006; 7: 340–6.
Savonitto S, Granger CB, Ardissino D, Gardner L, Cavallini C, Galvani M, et al. The prognostic value of creatine kinase elevations extends across the whole spectrum of acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002; 39: 22–9
Dohi T, Maehara A, Brener SJ, Genereux P, Gershlick AH, Mehran R, et al. Utility of peak creatine kinase-MB measurements in predicting myocardial infarct size, left ventricular dysfunction, and outcome after first anterior wall acute myocardial infarction (from the INFUSE-AMI trial). Am J Cardiol 2015; 115: 563–70.
Nienhuis MB, Ottervanger JP, de Boer MJ, Dambrink JE, Hoorntje JCA, Gosselink M, et al. Prognostic importance of creatine kinase and creatine Kinase-MB after primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 2008; 155: 673–9.
Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ, Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Bueno H, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J 2017; 00: 1–66.
Acknowledgements
The authors declare that discounted consumables related to the use of the QuantStudio® 3D Digital PCR system were offered by ThermoFisher.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, S., Follo, M., Haenel, D. et al. Chip-based digital PCR as a novel detection method for quantifying microRNAs in acute myocardial infarction patients. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39, 1217–1227 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.136
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.136
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
miRNA biomarkers: advancing early detection of acute myocardial infarction
Microchimica Acta (2025)
-
A systematic review of miRNAs as biomarkers for chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients reveals potentially clinically informative panels as well as key challenges in miRNA research
Cardio-Oncology (2022)
-
miRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets and challenges
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)
-
Circulating biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases: the beats never stop
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)