Abstract
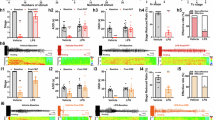
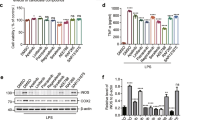
Major depressive disorder is a common but devastating mental disorder, and recent evidence shows that neuroinflammation may play a pivotal role in the etiology of depression. Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is an active component purifed from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch) Bge, which has shown anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic effects. In this study, we explored whether AS-IV produced antidepressant effects via its inhibition of neuroinflammation in mouse models of depression. Depressive-like behaviors including decreased sucrose consumption, reduced locomotor activity and increased immobility time were induced in mice using repeated restraint stress (RRS). We found that administration of AS-IV (16, 32 and 64 mg·kg-1·d-1, ig) significantly attenuated RRS-induced depressive-like behaviors. Furthermore, AS-IV administration significantly reduced the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β, increased PPARγ expression and GSK3β phosphorylation, decreased NF-κB phosphorylation, and reduced NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containingprotein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and caspase-1 p20 generation in the hippocampus of the mice. LPS-induced depression-like behaviors were induced by LPS injection (1 mg·kg-1·d-1, ip), which were ameliorated by administration of AS-IV (20, 40 mg·kg-1·d-1, ig). The results of the LPS-induced mouse model were in accordance with those acquired from the RRS-induced mouse model: LPS injection significantly increased TNF-α and IL-1β expression in the mouse hippocampus, which was reversed by administration of AS-IV. Moreover, administration of AS-IV significantly increased PPARγ expression and GSK3β phosphorylation, and decreased NF-κB phosphorylation and NLRP3 inflammasome. These results suggest that AS-IV is a potential drug against depression, and its antidepressant effects are partially mediated by inhibition of neuroinflammation via the upregulation of PPARγ expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Duman RS, Aghajanian GK, Sanacora G, Krystal JH. Synaptic plasticity and depression: new insights from stress and rapid-acting antidepressants. Nat Med 2016; 22: 238–49.
Ferrari AJ, Norman RE, Freedman G, Baxter AJ, Pirkis JE, Harris MG, et al. The burden attributable to mental and substance use disorders as risk factors for suicide: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. PLos One 2014; 9: e91936.
Murray CJ, Atkinson C, Bhalla K, Birbeck G, Burstein R, Chou D, et al. The state of US health, 1990–2010: burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA 2013; 310: 591–608.
Miller AH, Raison CL. The role of inflammation in depression: from evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat Rev Immunol 2015; 16: 22–34.
Glaser R, Kiecolt-Glaser JK. Stress-induced immune dysfunction: implications for health. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 243–51.
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW. From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2008; 9: 46–56.
Janssen DG, Caniato RN, Verster JC, Baune BT. A psychoneuro-immunological review on cytokines involved in antidepressant treat-ment response. Hum Psychopharmacol 2010; 25: 201–15.
Miller AH, Maletic V, Raison CL. Inflammation and its discontents: the role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2009; 65: 732–41.
Hannestad J, DellaGioia N, Bloch M. The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacol 2011; 36: 2452–9.
Wang Y, Xu Y, Sheng H, Ni X, Lu J. Exercise amelioration of depression-like behavior in OVX mice is associated with suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 2016; 307: 18–24.
de Timary P, Starkel P, Delzenne NM, Leclercq S. A role for the peripheral immune system in the development of alcohol use disorders? Neuropharmacology 2017; 122: 148–60.
Allison DJ, Ditor DS. The common inflammatory etiology of depression and cognitive impairment: a therapeutic target. J Neuroinflamm 2014; 11: 151.
Hodes GE, Kana V, Menard C, Merad M, Russo SJ. Neuroimmune mechanisms of depression. Nat Neurosci 2015; 18: 1386–93.
Goshen I, Kreisel T, Ben-Menachem-Zidon O, Licht T, Weidenfeld J, Ben-Hur T, et al. Brain interleukin-1 mediates chronic stress-induced depression in mice via adrenocortical activation and hippocampal neurogenesis suppression. Mol Psychiatry 2008; 13: 717–28.
Colle R, de Larminat D, Rotenberg S, Hozer F, Hardy P, Verstuyft C, et al. PPAR-gamma agonists for the treatment of major depression: a review. Pharmacopsychiatry 2017; 50: 49–55.
Sun K, Park J, Kim M, Scherer PE. Endotrophin, a multifaceted player in metabolic dysregulation and cancer progression, is a predictive biomarker for the response to PPARγ agonist treatment. Diabetologia 2017; 60: 24–9.
Wang X, Wang Y, Hu J, Yu S, Li B, Cui Y, et al. Astragaloside IV, a natural PPARγ agonist, reduces Aβ production in Alzheimer's disease through inhibition of BACE1. Mol Neurobiol 2017; 54: 2939–49.
Martin M, Rehani K, Jope RS, Michalek SM. Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production is differentially regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 777–84.
Beurel E, Grieco SF, Jope RS. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol Therapeut 2015; 148: 114–31.
Cheng Y, Pardo M, Armini RDS, Martinez A, Mouhsine H, Zagury J, et al. Stress-induced neuroinflammation is mediated by GSK3-dependent TLR4 signaling that promotes susceptibility to depression-like behavior. Brain Behavior Immunity 2016; 53: 207–22.
Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A, Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, et al. Cutting edge: NF-κB activating pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol 2009; 183: 787–91.
Gui D, Guo Y, Wang F, Liu W, Chen J, Chen Y, et al. Astragaloside IV, a novel antioxidant, prevents glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. PLos One 2012; 7: e39824.
Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Natteru PA, Selvakumar GP, Saeed D, Zahoor H, et al. Neuroinflammation induces neurodegeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Spine 2016; 1. pii: 1003.
Zhang W, Frei B. Astragaloside IV inhibits NF-κB activation and inflammatory gene expression in LPS-treated mice. Mediat Inflamm 2015; 2015: 1–11.
Abe-Higuchi N, Uchida S, Yamagata H, Higuchi F, Hobara T, Hara K, et al. Hippocampal sirtuin 1 signaling mediates depression-like behavior. Biol Psychiatry 2016; 80: 815–26.
Liu XL, Luo L, Mu RH, Liu BB, Geng D, Liu Q, et al. Fluoxetine regulates mTOR signalling in a region-dependent manner in depression-like mice. Sci Rep 2015; 5: 16024.
Liu L, Zhang Q, Cai Y, Sun D, He X, Wang L, et al. Resveratrol counteracts lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviors via enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 56045–59.
Qin T, Fang F, Song M, Li R, Ma Z, Ma S. Umbelliferone reverses depression-like behavior in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced rats by attenuating neuronal apoptosis via regulating ROCK/Akt pathway. Behav Brain Res 2017; 317: 147–56.
Rodrigues AL, Da SG, Mateussi AS, Fernandes ES, Miguel OG, Yunes RA, et al. Involvement of monoaminergic system in the antidepressant-like effect of the hydroalcoholic extract of Siphocampylus verticillatus. Life Sci 2002; 70: 1347–58.
Liu X, Peprah D, Gershenfeld HK. Tail-suspension induced hyperthermia: a new measure of stress reactivity. J Psychiatr Res 2003; 37: 249–59.
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M. Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 1977; 229: 327–36.
Vyas A, Mitra R, Shankaranarayana RB, Chattarji S. Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 6810–8.
Mokler DJ, Torres OI, Galler JR, Morgane PJ. Stress-induced changes in extracellular dopamine and serotonin in the medial prefrontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus of prenatally malnourished rats. Brain Res 2007; 1148: 226–33.
Xu Y, Ku BS, Yao HY, Lin YH, Ma X, Zhang YH, et al. Antidepressant effects of curcumin in the forced swim test and olfactory bulbectomy models of depression in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005; 82: 200–6.
Lee B, Sur B, Park J, Kim SH, Kwon S, Yeom M, et al. Chronic administration of baicalein decreases depression-like behavior induced by repeated restraint stress in rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 2013; 17: 393–403.
Uchida S, Hara K, Kobayashi A, Funato H, Hobara T, Otsuki K, et al. Early life stress enhances behavioral vulnerability to stress through the activation of REST4-mediated gene transcription in the medial prefrontal cortex of rodents. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 15007–18.
Nakatomi Y, Mizuno K, Ishii A, Wada Y, Tanaka M, Tazawa S, et al. Neuroinflammation in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome/myalgic encephalomyelitis: An 11C-(R)-PK11195 PET study. J Nucl Med 2014; 55: 945–50.
Busse M, Busse S, Myint AM, Gos T, Dobrowolny H, Muller UJ, et al. Decreased quinolinic acid in the hippocampus of depressive patients: evidence for local anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective responses? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2015; 265: 321–9.
Dang R, Zhou X, Tang M, Xu P, Gong X, Liu Y, et al. Fish oil supple-mentation attenuates neuroinflammation and alleviates depressive-like behavior in rats submitted to repeated lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Nutr 2018; 57: 893–906.
Li M, Ma RN, Li LH, Qu YZ, Gao GD. Astragaloside IV reduces cerebral edema post-ischemia/reperfusion correlating the suppression of MMP-9 and AQP4. Eur J Pharmacol 2013; 715: 189–95.
Han Q, Yuan Q, Meng X, Huo J, Bao Y, Xie G. 6-Shogaol attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in BV2 microglia cells by activating PPAR-γ. Oncotarget 2017; 8: 42001–6.
Bordet R, Ouk T, Petrault O, Gele P, Gautier S, Laprais M, et al. PPAR: a new pharmacological target for neuroprotection in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem Soc Trans 2006; 34: 1341–6.
Aoun P, Watson DG, Simpkins JW. Neuroprotective effects of PPARgamma agonists against oxidative insults in HT-22 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2003; 472: 65–71.
Zhu R, Zheng J, Chen L, Gu B, Huang S. Astragaloside IV facilitates glucose transport in C2C12 myotubes through the IRS1/AKT pathway and suppresses the palmitate-induced activation of the IKK/IkappaBalpha pathway. Int J Mol Med 2016; 37: 1697–705.
Gárate I, Garcia-Bueno B, Madrigal JLM, Caso JR, Alou L, Gomez-Lus ML, et al. Stress-induced neuroinflammation: role of the Toll-Like receptor-4 pathway. Biol Psychiat 2013; 73: 32–43.
Zhu W, Cao FS, Feng J, Chen HW, Wan JR, Lu Q, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to long-term behavioral alterations in mice injected with lipopolysaccharide. Neuroscience 2017; 343: 77–84.
Raison CL, Miller AH. Anti-inflammatory agents as antidepressants: truth or dare. Psychiatric Annals 2015; 45: 255–61.
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81573701), the College Students Innovation Project for the R&D of Novel Drugs (J1310032) and National Fund for Fostering Talents of Basic Science (NFFTBS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Mt., Ruan, J., Zhang, Ry. et al. Astragaloside IV ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice via the PPARγ/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39, 1559–1570 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.208
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.208
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ferroptosis-induced immune modulation: a new frontier in glioblastoma therapy
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2026)
-
Luteolin ameliorates chronic stress-induced depressive-like behaviors in mice by promoting the Arginase-1+ microglial phenotype via a PPARγ-dependent mechanism
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2025)
-
Astragaloside IV ameliorates cardiomyocyte injury and heart failure through hif/rho/rock pathway regulation: In vitro and in vivo insights
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (2025)
-
Anti-depressant effect of Naringenin-loaded hybridized nanoparticles in diabetic rats via PPARγ/NLRP3 pathway
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Saponins as potential novel NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors for inflammatory disorders
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2024)