Abstract
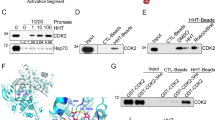
The cellular level of the CDC25A phosphatase is tightly regulated during both the normal and genotoxic-perturbed cell cycle. Here, we describe a caspase-dependent cleavage of this protein at residue D223 in non-genotoxic apoptotic conditions. This specific proteolysis generates a catalytically active C-terminal fragment that localizes to the nuclear compartment. Accumulation of this active CDC25A fragment leads to reduced inhibitory phosphorylation of the CDC25A substrate cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) on Tyr15. Moreover, CDK2 was found stably associated with this fragment, as well as with an ectopically expressed CDC25A224–525 truncation mutant that mimicks the cleavage product. Ectopic expression of this mutant induced CDK2 Tyr15 dephosphorylation, whereas its catalytically inactive version did not. Finally, this 224–525 mutant initiated apoptosis when transfected into HeLa cells, whereas its catalytic inactive form did not. Altogether, this study demonstrates for the first time that caspase-dependent cleavage of CDC25A is a central step linking CDK2 activation with non-genotoxic apoptotic induction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
acute myeloid leukemia
- CDK2:
-
cyclin-dependent kinase 2
- FACS:
-
fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- FDP:
-
fluorescein diphosphate
- NES:
-
nuclear export sequence
- NLS:
-
nuclear localization sequence
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- STS:
-
staurosporin
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha
References
Jinno S, Suto K, Nagata A, Igarashi M, Kanaoka Y, Nojima H et al. Cdc25A is a novel phosphatase functioning early in the cell cycle. EMBO J 1994; 13: 1549–1556.
Blomberg I, Hoffmann I . Ectopic expression of cdc25A accelerates the G1/S transition and leads to premature activation of cyclin E- and cyclin A-dependent kinases. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 6183–6194.
Mailand N, Podtelejnikov AV, Groth A, Mann M, Bartek J, Lukas J . Regulation of G2/M events by CDC25A through phosphorylation dependent modulation of its stability. EMBO J 2002; 21: 5911–5920.
Boutros R, Lobjois V, Ducommun B . CDC25 phosphatases in cancer cells: key players? Good targets? Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 1–12.
Busino L, Chiesa M, Draetta GF, Donzelli M . CDC25A phosphatase: combinatorial phosphorylation, ubiquitylation and proteolysis. Oncogene 2004; 23: 2050–2056.
Chen X, Prywes R . Serum-induced expression of the CDC25A gene by relief of E2F mediated repression. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 4695–4702.
Khaled AR, Bulavin DV, Kittipatarin C, Li WQ, Alvarez M, Kim K et al. Cytokine-driven cell cycling is mediated through CDC25A. J Cell Biol 2005; 169: 755–763.
Fernandez-Vidal A, Ysebaert L, Didier C, Betous R, De Toni F, Prade-Houdellier N et al. Cell adhesion regulates CDC25A expression and proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 7128–7135.
Galaktionov K, Chen X, Beach D . CDC25A cell-cycle phosphatase as a target of cmyc. Nature 1996; 382: 511–517.
Fuhrmann G, Leisser C, Rosenberger G, Grusch M, Huettenbrenner S, Halama T et al. Cdc25A phosphatase suppresses apoptosis induced by serum deprivation. Oncogene 2001; 20: 4542–4553.
Zou X, Tsutsui T, Ray D, Blomquist JF, Ichijo H, Ucker DS et al. The cell cycle-regulatory CDC25A phosphatase inhibits apoptosis signal regulating kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 4818–4828.
Xue D, Horvitz HR . Inhibition of the Caenorhabditis elegans cell-death protease CED-3 by a CED-3 cleavage site in baculovirus p35 protein. Nature 1995; 377: 248–251.
Xu G, Cirilli M, Huang Y, Rich RL, Myszka DG, Wu H . Covalent inhibition revealed by the crystal structure of the caspase-8/p35 complex. Nature 2001; 410: 494–497.
Kallstrom H, Lindqvist A, Pospisil V, Lundgren A, Rosenthal CK . Cdc25A localisation and shuttling: characterisation of sequences mediating nuclear export and import. Exp Cell Res 2005; 303: 89–100.
Eymin B, Haugg M, Droin N, Sordet O, Dimanche-Boitrel MT, Solary E . Caspase-induced proteolysis of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 mediates its anti-apoptotic activity. Oncogene 1999; 18: 4839–4847.
Levkau B, Koyama H, Raines EW, Clurman BE, Herren B, Orth K et al. Cleavage of p21Cip1/Waf1 and p27Kip1 mediates apoptosis in endothelial cells through activation of Cdk2: role of a caspase cascade. Mol Cell 1998; 4: 553–563.
Zha J, Weiler S, Oh KJ, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ . Post-translational N-myristoylation of BID as a molecular switch for targeting mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 2000; 290: 1761–1765.
Yim H, Jin YH, Park BD, Choi HJ, Lee SK . Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of Cdc6 induces nuclear localization of p49-truncated Cdc6 and apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 2003; 14: 4250–4259.
Yim H, Hwang IS, Choi JS, Chun KH, Jin YH, Ham YM et al. Cleavage of Cdc6 by caspase-3 promotes ATM/ATR kinase-mediated apoptosis of HeLa cells. J Cell Biol 2006; 174: 77–88.
Petersen B, Lukas J, Sorensen C, Bartek J, Helin K . Phosphorylation of mammalian cdc6 by cyclin A/CDK2 regulates its subcellular localization. EMBO J 1999; 18: 396–410.
Guo M, Hay BA . Cell proliferation and apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1999; 11: 745–752.
Hakem A, Sasaki T, Kozieradzki I, Penninger J . The cyclin-dependent kinase 2 regulates thymocyte apoptosis. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 957–968.
Turowski P, Franckhauser C, Morris MC, Vaglio P, Fernandez A, Lamb NJ . Functional cdc25C dual-specificity phosphatase is required for S phase entry in human cells. Mol Biol Cell 2003; 14: 2984–2998.
Deb-Basu D, Aleem E, Kaldis P, Felsher DW . CDK2 is required by MYC to induce apoptosis. Cell Cycle 2006; 5: 1342–1347.
Cathelin S, Rebe C, Haddaoui L, Simioni N, Verdier F, Fontenay M et al. Identification of proteins cleaved downstream of caspase activation in monocytes undergoing macrophage differentiation. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 17779–17788.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Professor E Solary (Dijon, France) for providing us with the U937-p35 cell line. We also thank Fatima L'Faqihi-Olive for expert assistance with the FACS experiments. This study was supported by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, by the Association Laurette Fugain (Grant no. R05027BB), by the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC, Grant no. 3638) by the ‘Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer’ (Equipe labellisée 2005 to BD) and by the Institut National du Cancer (INCA, Grant no. PL103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by B Zhivotovsky
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazars, A., Fernandez-Vidal, A., Mondesert, O. et al. A caspase-dependent cleavage of CDC25A generates an active fragment activating cyclin-dependent kinase 2 during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 16, 208–218 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.142
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.142
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Age-dependent differential expression of death-associated protein 6 (Daxx) in various peripheral tissues and different brain regions of C57BL/6 male mice
Biogerontology (2016)
-
Radio-sensitization of human leukaemic MOLT-4 cells by DNA-dependent protein kinase inhibitor, NU7441
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics (2014)
-
CDC25A targeting by miR-483-3p decreases CCND–CDK4/6 assembly and contributes to cell cycle arrest
Cell Death & Differentiation (2013)
-
The regulatory crosstalk between kinases and proteases in cancer
Nature Reviews Cancer (2010)