Abstract
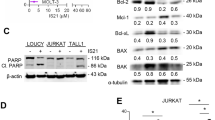
p27BBP/eIF6 (β4-binding protein/eukaryotic initiation factor 6) regulates the joining of 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits, on receptor for activated C kinase 1 binding and protein kinase C phosphorylation in serine 235. In Xenopus, p27BBP/eIF6 is abundantly expressed in the majority of the embryonic anlagen. Although p27BBP/eIF6 abundance may be required for a general regulation of protein synthesis, our data suggest that p27BBP/eIF6 may target the translation of specific mRNAs. We injected Xp27BBP/eIF6 mRNA in one blastomere of two-cell-stage embryos and obtained a bent phenotype, the curvature being lateral with respect to the embryo antero-posterior axis. The injected side had fewer apoptotic cells than the uninjected side, whereas cell proliferation appeared unaffected. Accordingly, in Xp27BBP/eIF6 morphants, endogenous apoptosis increased. Injection of Xp27BBP/eIF6 point mutants indicated that the anti-apoptotic action of Xp27BBP/eIF6 requires the conserved S235. The bent phenotype was also obtained with B-cell lymphoma gene-2 (Bcl-2) overexpression and was rescued by Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax)/Xp27BBP/eIF6 co-injection. In addition, embryos overexpressing Xp27BBP/eIF6 had a higher amount of Bcl-2 and an unchanged amount of Bax with respect to controls. In Xp27BBP/eIF6 morphants, Bcl-2 levels were unaffected and Bax levels were higher than in the controls. Thus, we propose that Xp27BBP/eIF6 is part of a mechanism acting on the specific translation of messengers regulating cell survival. In particular, we suggest that Xp27BBP/eIF6 may regulate the translation of factors upstream of Bcl-2/Bax.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
Abbreviations
- A-P:
-
antero-posterior axis
- Bax:
-
Bcl-2-associated X protein
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma gene-2
- BrdU:
-
5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- D-V:
-
dorsoventral axis
- DAPI:
-
4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DTT:
-
dithiothreitol
- e:
-
eye
- EGTA:
-
ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid
- enc:
-
encephalon
- end.:
-
endoderm
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- H:
-
head
- HEPES:
-
N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid
- HUA:
-
hydroxyurea and aphidicolin
- i.s:
-
injected side
- m:
-
miotome
- mo:
-
morpholino
- nc:
-
notochord
- ot.v:
-
otic vesicle
- p27BBP/eIF6:
-
β4-binding protein/eukaryotic initiation factor 6
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- ph:
-
pharynx
- pH3:
-
phospho histone 3
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- RACK1:
-
receptor for activated C kinase 1
- SBTI:
-
soybean trypsin inhibitor
- SDS-PAGE:
-
SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- sp.c.:
-
spinal cord
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcriptase-PCR
- T:
-
tail
- TAME:
-
Nα-(p-toluene sulfonyl)-L-arginine methyl ester
- Tris:
-
hydroxymethyl aminomethane
References
Biffo S, Sanvito F, Costa S, Preve L, Pignatelli R, Spinardi L et al. Isolation of a novel β4 integrin binding protein (p27BBP) highly expressed in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 30314–30321.
Basu U, Si K, Warner JR, Maitra U . The Saccharomyces cerevisiae TIF6 gene encoding translation initiation factor 6 is required for 60S ribosomal subunit biogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 1453–1462.
Senger B, Lafontaine DL, Graindorge JS, Gadal O, Camasses A, Sanni A et al. The nucleolar Tif6p and Efl1p are required for a late cytoplasmic step of ribosome synthesis. Mol Cell 2001; 8: 1363–1373.
Sanvito F, Piatti S, Villa A, Bossi M, Lucchini G, Marchisio PC et al. The beta4 integrin interactor p27(BBP/elF6) is an essential nuclear matrix protein involved in 60S ribosomal subunit assembly. J Cell Biol 1999; 144: 823–837.
Gandin V, Miluzio A, Barbieri A, Magri L, Kiyokawa H, Marchisio PC . eIF6 is rate limiting for translation, growth and transformation. Nature 2008; 455: 684–688.
Ceci M, Gaviraghi C, Gorrini C, Sala LA, Offenhauser N, Marchisio PC et al. Release of elF6 (p27BBP) from the 6OS subunit allows 80S ribosome assembly. Nature 2003; 426: 579–584.
Carotenuto R, De Marco N, Biffo S, Wilding M, Vaccaro MC, Marchisio PC et al. Phosphorylation of p27BBP/elF6 and its association with the cytoskeleton are developmentally regulated in Xenopus oogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2005; 62: 1641–1652.
Vaccaro MC, Cuccaro M, De Marco N, Campanella C . Isolation and expression pattern of p27 BBP/eIF6 cDNA in Xenopus laevis embryos. Mol Reprod Dev 2006a; 73: 485–490.
Vaccaro MC, Cuccaro M, De Marco N, Campanella C . Isolation and expression pattern of p27 BBP/eIF6 cDNA in Xenopus laevis embryos ERRATUM Mol Reprod Dev 2006b; 73:1612.
Donadini A, Giodini A, Sanvito F, Marchisio PC, Biffo S . The human ITGB4BP gene is constitutively expressed in vitro, but highly modulated in vivo. Gene 2001; 266: 35–43.
Sanvito F, Vivoli F, Gambini S, Santambrogio G, Catena M, Viale E et al. Expression of a highly conserved protein, p27BBP, during the progression of human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 510–516.
Vreugde S, Ferrai C, Miluzio A, Hauben E, Marchisio PC, Crippa M et al. Nuclear myosin VI enhances RNA polymerase II dependent transcription. Mol Cell 2006; 23: 749–755.
Ji Y, Shah S, Soanes K, Islam MN, Hoxter B, Biffo S et al. Eukaryotic initiation factors 6 selectively regulates Wnt signalling and β-catenin protein synthesis. Oncogene 2008; 27: 755–762.
Chendrimada TP, Finn KJ, Ji X, Baillat D, Gregory RI, Liebhaber SA et al. MicroRNA silencing through RISC recruitment of eIF6. Nature 2007; 447: 823–829.
Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E . GW182 interaction with Argonaute is essential for miRNA-mediated translation repression and mRNA decay. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2008; 15: 346–353.
Hensey C, Gautier J . A developmental timer that regulates apoptosis at the onset of gastrulation. Mech Dev 1997; 69: 183–195.
Yeo W, Gautier J . A role for programmed cell death during early neurogenesis in Xenopus. Dev Biol 2003; 260: 31–45.
Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC . Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell 1997; 88: 347–354.
Viczian AS, Vignali R, Zuber ME, Barsacchi G, Harris WA . Xotx5b and Xotx2 regulate photoreceptor and bipolar fates in the Xenopus retina. Development 2003; 130: 1281–1294.
Hensey C, Gautier J . Programmed cell death during xenopus development: a spatio-temporal analysis. Dev Biol 1998; 238: 36–48.
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA . Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 1992; 119: 493–501.
Kaufmann SH, Lee SH, Meng XW, Loegering DA, Kottke TJ, Henzing AJ et al. Apoptosis-associated caspase activation assays. Methods 2008; 44: 262–272.
Yuan J, Shaham S, Ledoux S, Ellis HM, Horvitz HR . The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell 1993; 75: 641–652.
Harris WA, Hartenstein V . Neuronal determination without cell division in Xenopus embryos. Neuron 1991; 6: 499–515.
Zorn AM, Mason J . Gene expression in the embryonic Xenopus liver. Mech Dev 2001; 103: 153–157.
Rot-Nikcevic I, Wassersug RJ . Arrested development in Xenopus laevis tadpoles: how size constrains metamorphosis. J Exp Biol 2004; 207: 2133–2144.
Adams JM, Cory S . Life-or-death decisions by the Bcl-2 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci 2001; 26: 61–66.
Cory S, Adams JM . The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 647–656.
Tríbulo C, Aybar MJ, Sánchez SS, Mayor R . A balance between the anti-apoptotic activity of Slug and the apoptotic activity of msx1 is required for the proper development of the neural crest. Dev Biol 2004; 275: 325–342.
Coles HS, Burne JF, Raff MC . Large-scale normal cell death in the developing rat kidney and its reduction by epidermal growth factor. Development 1993; 118: 777–784.
Burek MJ, Oppenheim RW . Programmed cell death in the developing nervous system. Brain Pathos 1996; 6: 427–446.
Finkielstein CV, Lewellyn AL, Maller JL . The midblastula transition in Xenopus embryos activates multiple pathways to prevent apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 1006–1011.
Nieuwkoop PD, Faber J . Normal Table of Xenopus laevis. Daudin, Amsterdam: North Holland, 1967.
De Marco N, Buono M, Troise F, Diez-Roux G . Optineurin increases cell survival and translocates to the nucleus in a Rab8-dependent manner upon an apoptotic stimulus. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 16147–16156.
Maturi G, Infante V, Carotenuto R, Focarelli R, Caputo M, Campanella C . Specific glycoconjugates are present at the oolemma of the fertilization site in the egg of Discoglossus pictus (Anurans) and bind spermatozoa in an in vitro assay. Dev Biol 1998; 204: 210–223.
Harland RM . In situ hybridisation: an improved whole mount method for Xenopus embryos. Meth Cell Biol 1991; 36: 675–685.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Professor PG Marchisio for reading the paper and to Drs Amalia De Angelis and Margherita Tussellino for assistance. Special thanks go to Dr Graciana Diez Roux for carefully reading the paper and contributing with critical suggestions. This work was partially funded by AMRA Scarl, by a Grant of the Italian Ministry of University and Research (P.R.I.N. 1997) to CC and by a Grant of the ‘Compagnia di San Paolo’ (‘Integration of spatial and biochemical clues during brain development’ Project) to CC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by P Bouillet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Marco, N., Iannone, L., Carotenuto, R. et al. p27BBP/eIF6 acts as an anti-apoptotic factor upstream of Bcl-2 during Xenopus laevis development. Cell Death Differ 17, 360–372 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.128
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.128