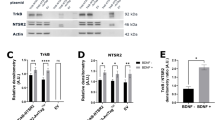
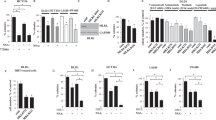
Abstract
Glucocorticoids are used as part of front-line therapy to treat lymphoid malignancy because of their remarkable ability to induce apoptosis. Yet, in T cells, glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis is readily inhibited by lymphocyte activation and signaling. We have previously shown that the Src family kinase, Lck (lymphocyte cell-specific tyrosine kinase), which is predominantly expressed in T cells, interacts with IP3 receptors to facilitate calcium signaling. Here, we discovered that dexamethasone downregulates Lck, which, in turn, suppresses lymphocyte activation by inhibiting pro-survival calcium oscillations. Moreover, stable expression of shRNAs that selectively targeted Lck or treatment with the Src inhibitor dasatinib (BMS-354825) enhanced apoptosis induction by dexamethasone. To investigate the effect of Lck inhibition in a primary leukemia model, we employed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells that aberrantly expressed Lck and were relatively insensitive to dexamethasone. Lck expression was correlated with resistance to dexamethasone in CLL cells, and its inhibition by dasatinib or other inhibitors markedly enhanced glucocorticoid sensitivity. Collectively, these data indicate that Lck protects cells from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and its inhibition enhances sensitivity to dexamethasone. Small-molecule inhibitors of Lck, such as dasatinib, may function to reverse glucocorticoid resistance in some lymphoid malignancies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CLL:
-
chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Lck:
-
lymphocyte cell-specific tyrosine kinase
References
Gaynon PS, Carrel AL . Glucocorticosteroid therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Adv Exp Med Biol 1999; 457: 593–605.
Smets LA, Salomons G, van den Berg J . Glucocorticoid induced apoptosis in leukemia. Adv Exp Med Biol 1999; 457: 607–614.
Kofler R . The molecular basis of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Histochem Cell Biol 2000; 114: 1–7.
Herold MJ, McPherson KG, Reichardt HM . Glucocorticoids in T cell apoptosis and function. Cell Mol Life Sci 2006; 63: 60–72.
Schmidt S, Rainer J, Ploner C, Presul E, Riml S, Kofler R . Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and glucocorticoid resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Cell Death Differ 2004; 11 (Suppl 1): S45–S55.
Cidlowski JA, King KL, Evans-Storms RB, Montague JW, Bortner CD, Hughes Jr FM . The biochemistry and molecular biology of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in the immune system. Recent Prog Horm Res 1996; 51: 457–490; discussion 490–1.
Necela BM, Cidlowski JA . Mechanisms of glucocorticoid receptor action in noninflammatory and inflammatory cells. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2004; 1: 239–246.
Distelhorst CW . Recent insights into the mechanism of glucocorticosteroid-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2002; 9: 6–19.
Tolosa E, Ashwell JD . Thymus-derived glucocorticoids and the regulation of antigen-specific T-cell development. Neuroimmunomodulation 1999; 6: 90–96.
Iwata M, Hanaoka S, Sato K . Rescue of thymocytes and T cell hybridomas from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis by stimulation via the T cell receptor/CD3 complex: a possible in vitro model for positive selection of the T cell repertoire. Eur J Immunol 1991; 21: 643–648.
Jamieson CA, Yamamoto KR . Crosstalk pathway for inhibition of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis by T cell receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 7319–7324.
Tsitoura DC, Rothman PB . Enhancement of MEK/ERK signaling promotes glucocorticoid resistance in CD4+ T cells. J Clin Invest 2004; 113: 619–627.
Palacios EH, Weiss A . Function of the Src-family kinases, Lck and Fyn, in T-cell development and activation. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7990–8000.
Mustelin T, Tasken K . Positive and negative regulation of T-cell activation through kinases and phosphatases. Biochem J 2003; 371: 15–27.
Lewis RS . Calcium signaling mechanisms in T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol 2001; 19: 497–521.
Harr MW, Rong Y, Bootman MD, Roderick HL, Distelhorst CW . Glucocorticoid-mediated inhibition of Lck modulates the pattern of T cell receptor-induced calcium signals by down-regulating inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 31860–31871.
Crabtree GR . Generic signals and specific outcomes: signaling through Ca2+, calcineurin, and NF-AT. Cell 1999; 96: 611–614.
Iwata M, Ohoka Y, Kuwata T, Asada A . Regulation of T cell apoptosis via T cell receptors and steroid receptors. Stem Cells 1996; 14: 632–641.
Van Laethem F, Baus E, Smyth LA, Andris F, Bex F, Urbain J et al. Glucocorticoids attenuate T cell receptor signaling. J Exp Med 2001; 193: 803–814.
Baus E, Andris F, Dubois PM, Urbain J, Leo O . Dexamethasone inhibits the early steps of antigen receptor signaling in activated T lymphocytes. J Immunol 1996; 156: 4555–4561.
Northrop JP, Crabtree GR, Mattila PS . Negative regulation of interleukin 2 transcription by the glucocorticoid receptor. J Exp Med 1992; 175: 1235–1245.
Lowenberg M, Tuynman J, Bilderbeek J, Gaber T, Buttgereit F, van Deventer S et al. Rapid immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids mediated through Lck and Fyn. Blood 2005; 106: 1703–1710.
Lowenberg M, Verhaar AP, Bilderbeek J, Marle J, Buttgereit F, Peppelenbosch MP et al. Glucocorticoids cause rapid dissociation of a T-cell-receptor-associated protein complex containing LCK and FYN. EMBO Rep 2006; 7: 1023–1029.
Abraham KM, Levin SD, Marth JD, Forbush KA, Perlmutter RM . Thymic tumorigenesis induced by overexpression of p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 3977–3981.
Jucker M, Abts H, Eick D, Lenoir GM, Tesch H . Over-expression of lck in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. Leukemia 1991; 5: 528–530.
Von Knethen A, Abts H, Kube D, Diehl V, Tesch H . Expression of p56lck in B-cell neoplasias. Leuk Lymphoma 1997; 26: 551–562.
Abts H, Jucker M, Diehl V, Tesch H . Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells regularly express mRNAs of the protooncogenes lck and c-fgr. Leuk Res 1991; 15: 987–997.
Rouer E, Dreyfus F, Melle J, Ribrag V, Benarous R . Selective increase of alternatively spliced Lck transcripts from the proximal promotor in hematopoietic malignancies. Leukemia 1993; 7: 246–250.
Majolini MB, D'Elios MM, Galieni P, Boncristiano M, Lauria F, Del Prete G et al. Expression of the T-cell-specific tyrosine kinase Lck in normal B-1 cells and in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 1998; 91: 3390–3396.
al-Ramadi BK, Zhang H, Bothwell AL . Cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis hypersusceptibility as a consequence of Lck deficiency in nontransformed T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 12498–12503.
Wang Z, Rong YP, Malone MH, Davis MC, Zhong F, Distelhorst CW . Thioredoxin-interacting protein (txnip) is a glucocorticoid-regulated primary response gene involved in mediating glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2006; 25: 1903–1913.
Wang Z, Malone MH, He H, McColl KS, Distelhorst CW . Microarray analysis uncovers the induction of the proapoptotic BH3-only protein Bim in multiple models of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 23861–23867.
Schade AE, Schieven GL, Townsend R, Jankowska AM, Susulic V, Zhang R et al. Dasatinib, a small-molecule protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, inhibits T-cell activation and proliferation. Blood 2008; 111: 1366–1377.
Faderl S, Ferrajoli A, Frankfurt O, Pettitt A . Treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia with nonchemotherapeutic agents: experience with single-agent and combination therapy. Leukemia 2009; 23: 457–466.
Efremov DG, Gobessi S, Longo PG . Signaling pathways activated by antigen-receptor engagement in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells. Autoimmun Rev 2007; 7: 102–108.
Contri A, Brunati AM, Trentin L, Cabrelle A, Miorin M, Cesaro L et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells contain anomalous Lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 369–378.
Eck MJ, Shoelson SE, Harrison SC . Recognition of a high-affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide by the Src homology-2 domain of p56lck. Nature 1993; 362: 87–91.
Cousins-Wasti RC, Ingraham RH, Morelock MM, Grygon CA . Determination of affinities for lck SH2 binding peptides using a sensitive fluorescence assay: comparison between the pYEEIP and pYQPQP consensus sequences reveals context-dependent binding specificity. Biochemistry 1996; 35: 16746–16752.
Couture C, Songyang Z, Jascur T, Williams S, Tailor P, Cantley LC et al. Regulation of the Lck SH2 domain by tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 24880–24884.
Caron L, Abraham N, Pawson T, Veillette A . Structural requirements for enhancement of T-cell responsiveness by the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12: 2720–2729.
Hilberg F, Roth GJ, Krssak M, Kautschitsch S, Sommergruber W, Tontsch-Grunt U et al. BIBF 1120: triple angiokinase inhibitor with sustained receptor blockade and good antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 4774–4782.
Norman MR, Thompson EB . Characterization of a glucocorticoid-sensitive human lymphoid cell line. Cancer Res 1977; 37: 3785–3791.
Tissing WJ, den Boer ML, Meijerink JP, Menezes RX, Swagemakers S, van der Spek PJ et al. Genomewide identification of prednisolone-responsive genes in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Blood 2007; 109: 3929–3935.
Schmidt S, Rainer J, Riml S, Ploner C, Jesacher S, Achmuller C et al. Identification of glucocorticoid-response genes in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 2061–2069.
Sosinowski T, Pandey A, Dixit VM, Weiss A . Src-like adaptor protein (SLAP) is a negative regulator of T cell receptor signaling. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 463–474.
Mansha M, Carlet M, Ploner C, Gruber G, Wasim M, Wiegers GJ et al. Functional analyses of Src-like adaptor (SLA), a glucocorticoid-regulated gene in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Res 2009; 34: 529–534.
Rambal AA, Panaguiton ZL, Kramer L, Grant S, Harada H . MEK inhibitors potentiate dexamethasone lethality in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells through the pro-apoptotic molecule BIM. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1744–1754.
Amrein L, Hernandez TA, Ferrario C, Johnston J, Gibson SB, Panasci L et al. Dasatinib sensitizes primary chronic lymphocytic leukaemia lymphocytes to chlorambucil and fludarabine in vitro. Br J Haematol 2008; 143: 698–706.
Kipps TJ . The B-cell receptor and ZAP-70 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2007; 20: 415–424.
Veldurthy A, Patz M, Hagist S, Pallasch CP, Wendtner CM, Hallek M et al. The kinase inhibitor dasatinib induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in vitro with preference for a subgroup of patients with unmutated IgVH genes. Blood 2008; 112: 1443–1452.
Nam NH, Pitts RL, Sun G, Sardari S, Tiemo A, Xie M et al. Design of tetrapeptide ligands as inhibitors of the Src SH2 domain. Bioorg Med Chem 2004; 12: 779–787.
Dungarwalla M, Evans SO, Riley U, Catovsky D, Dearden CE, Matutes E . High dose methylprednisolone and rituximab is an effective therapy in advanced refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia resistant to fludarabine therapy. Haematologica 2008; 93: 475–476.
Alexanian R, Dimopoulos MA, Delasalle K, Barlogie B . Primary dexamethasone treatment of multiple myeloma. Blood 1992; 80: 887–890.
Zhong F, Davis MC, McColl KS, Distelhorst CW . Bcl-2 differentially regulates Ca2+ signals according to the strength of T cell receptor activation. J Cell Biol 2006; 172: 127–137.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Michael Sramkoski of the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center flow cytometry core facility for providing us with technical expertise and advice. We would also like to acknowledge that this work was supported by NCI research grants 5R01 CA042755 (C.W.D.) and by T32 CA059366 (M.W.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by M Federici
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harr, M., Caimi, P., McColl, K. et al. Inhibition of Lck enhances glucocorticoid sensitivity and apoptosis in lymphoid cell lines and in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cell Death Differ 17, 1381–1391 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.25
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.25
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Combination efficacy of ruxolitinib with standard-of-care drugs in CRLF2-rearranged Ph-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Leukemia (2021)
-
Lck is a relevant target in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells whose expression variance is unrelated to disease outcome
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Transcriptional regulation of kinases downstream of the T cell receptor: another immunomodulatory mechanism of glucocorticoids
BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology (2014)
-
Recurrent mutations in epigenetic regulators, RHOA and FYN kinase in peripheral T cell lymphomas
Nature Genetics (2014)
-
Reconstructing targetable pathways in lung cancer by integrating diverse omics data
Nature Communications (2013)