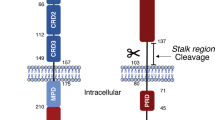
Abstract
CD95 (APO-1/Fas) is a member of the death receptor (DR) family. Stimulation of CD95 leads to induction of apoptotic and non-apoptotic signaling pathways. The formation of the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) is the initial step of CD95 signaling. Activation of procaspase-8 at the DISC leads to the induction of DR-mediated apoptosis. The activation of procaspase-8 is blocked by cellular FLICE-inhibitory proteins (c-FLIP). This review is focused on the role in the CD95-mediated signaling of the death effector domain-containing proteins procaspase-8 and c-FLIP. We discuss how dynamic cross-talk between procaspase-8 and c-FLIP at the DISC regulates life/death decisions at CD95.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- DISC:
-
death-inducing signaling complex
- c-FLIP:
-
cellular FLICE-inhibitory proteins
- cyt C:
-
cytochrome C
References
Krammer PH . CD95's deadly mission in the immune system. Nature 2000; 407: 789–795.
Tartaglia LA, Ayres TM, Wong GH, Goeddel DV . A novel domain within the 55 kd TNF receptor signals cell death. Cell 1993; 74: 845–853.
Weber CH, Vincenz C . The death domain superfamily: A tale of two interfaces? Trends Biochem Sci 2001; 26: 475–481.
Suda T, Takahashi T, Golstein P, Nagata S . Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell 1993; 75: 1169–1178.
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AM, Matzku S, Moller P, Falk W et al. Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 1989; 245: 301–305.
Peter ME, Budd RC, Desbarats J, Hedrick SM, Hueber AO, Newell MK et al. The CD95 receptor: apoptosis revisited. Cell 2007; 129: 447–450.
Desbarats J, Birge RB, Mimouni-Rongy M, Weinstein DE, Palerme JS, Newell MK . Fas engagement induces neurite growth through ERK activation and p35 upregulation. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5: 118–125.
Neumann L, Pforr C, Beaudouin J, Pappa A, Fricker N, Krammer PH et al. Dynamics within the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex decide life and death of cells. Mol Syst Biol 2010; 6: 352.
Lavrik IN, Golks A, Riess D, Bentele M, Eils R, Krammer PH . Analysis of CD95 threshold signaling: triggering of CD95 (FAS/APO-1) at low concentrations primarily results in survival signaling. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 13664–13671.
Demjen D, Klussmann S, Kleber S, Zuliani C, Stieltjes B, Metzger C et al. Neutralization of CD95 ligand promotes regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nat Med 2004; 10: 389–395.
Kleber S, Sancho-Martinez I, Wiestler B, Beisel A, Gieffers C, Hill O et al. Yes and PI3K bind CD95 to signal invasion of glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 235–248.
Zuliani C, Kleber S, Klussmann S, Wenger T, Kenzelmann M, Schreglmann N et al. Control of neuronal branching by the death receptor CD95 (Fas/Apo-1). Cell Death Differ 2006; 13: 31–40.
O'Reilly LA, Tai L, Lee L, Kruse EA, Grabow S, Fairlie WD et al. Membrane-bound Fas ligand only is essential for Fas-induced apoptosis. Nature 2009; 461: 659–663.
Krammer PH, Arnold R, Lavrik IN . Life and death in peripheral T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 532–542.
Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC, O'Rourke K, Shevchenko A, Ni J et al. FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death--inducing signaling complex. Cell 1996; 85: 817–827.
Sprick M, Rieser E, Stahl H, Grosse-Wilde A, Weigand M, Walczak H . Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally substitute caspase-8. EMBO J 2002; 21: 4520–4530.
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH, Peter ME . The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 1541–1548.
Siegel RM, Frederiksen JK, Zacharias DA, Chan FK, Johnson M, Lynch D et al. Fas preassociation required for apoptosis signaling and dominant inhibition by pathogenic mutations [see comments]. Science 2000; 288: 2354–2357.
Scott FL, Stec B, Pop C, Dobaczewska MK, Lee JJ, Monosov E et al. The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure unravels signalling by receptor clustering. Nature 2009; 457: 1019–1022.
Wang L, Yang JK, Kabaleeswaran V, Rice AJ, Cruz AC, Park AY et al. The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure reveals the basis of DISC assembly and disease mutations. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2010; 17: 1324–1329.
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ et al. Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J 1998; 17: 1675–1687.
Yin XM, Wang K, Gross A, Zhao Y, Zinkel S, Klocke B et al. Bid-deficient mice are resistant to Fas-induced hepatocellular apoptosis. Nature 1999; 400: 886–891.
Kaufmann T, Tai L, Ekert PG, Huang DC, Norris F, Lindemann RK et al. The BH3-only protein bid is dispensable for DNA damage- and replicative stress-induced apoptosis or cell-cycle arrest. Cell 2007; 129: 423–433.
Jost PJ, Grabow S, Gray D, McKenzie MD, Nachbur U, Huang DC et al. XIAP discriminates between type I and type II FAS-induced apoptosis. Nature 2009; 460: 1035–1039.
Lavrik IN, Mock T, Golks A, Hoffmann JC, Baumann S, Krammer PH . CD95 stimulation results in the formation of a novel death effector domain protein-containing complex. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 26401–26408.
Geserick P, Hupe M, Moulin M, Wong WW, Feoktistova M, Kellert B et al. Cellular IAPs inhibit a cryptic CD95-induced cell death by limiting RIP1 kinase recruitment. J Cell Biol 2009; 187: 1037–1054.
Micheau O, Tschopp J . Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 2003; 114: 181–190.
Varfolomeev E, Maecker H, Sharp D, Lawrence D, Renz M, Vucic D et al. Molecular determinants of kinase pathway activation by Apo2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 40599–40608.
Medema JP, Scaffidi C, Kischkel FC, Shevchenko A, Mann M, Krammer PH et al. FLICE is activated by association with the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). EMBO J 1997; 16: 2794–2804.
Scaffidi C, Medema JP, Krammer PH, Peter ME . FLICE is predominantly expressed as two functionally active isoforms, caspase-8/a and caspase-8/b. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 26953–26958.
Muzio M, Stockwell BR, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM . An induced proximity model for caspase-8 activation. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 2926–2930.
Pop C, Fitzgerald P, Green DR, Salvesen GS . Role of proteolysis in caspase-8 activation and stabilization. Biochemistry 2007; 46: 4398–4407.
Chang DW, Xing Z, Capacio VL, Peter ME, Yang X . Interdimer processing mechanism of procaspase-8 activation. EMBO J 2003; 22: 4132–4142.
Golks A, Brenner D, Schmitz I, Watzl C, Krueger A, Krammer PH et al. The role of CAP3 in CD95 signaling: new insights into the mechanism of procaspase-8 activation. Cell Death Differ 2006; 13: 489–498.
Hoffmann JC, Pappa A, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN . A new C-terminal cleavage product of procaspase-8, p30, defines an alternative pathway of procaspase-8 activation. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 4431–4440.
Lavrik IN, Golks A, Krammer PH . Caspases: pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2665–2672.
Hughes MA, Harper N, Butterworth M, Cain K, Cohen GM, MacFarlane M . Reconstitution of the death-inducing signaling complex reveals a substrate switch that determines CD95-mediated death or survival. Mol Cell 2009; 35: 265–279.
Lavrik I, Krueger A, Schmitz I, Baumann S, Weyd H, Krammer PH et al. The active caspase-8 heterotetramer is formed at the CD95 DISC. Cell Death Differ 2003; 10: 144–145.
Kang TB, Oh GS, Scandella E, Bolinger B, Ludewig B, Kovalenko A et al. Mutation of a self-processing site in caspase-8 compromises its apoptotic but not its nonapoptotic functions in bacterial artificial chromosome-transgenic mice. J Immunol 2008; 181: 2522–2532.
Matthess Y, Raab M, Sanhaji M, Lavrik IN, Strebhardt K . Cdk1/cyclin B1 controls Fas-mediated apoptosis by regulating caspase-8 activity. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 5726–5740.
Cursi S, Rufini A, Stagni V, Condo I, Matafora V, Bachi A et al. Src kinase phosphorylates Caspase-8 on Tyr380: a novel mechanism of apoptosis suppression. EMBO J 2006; 25: 1895–1905.
Jin Z, Li Y, Pitti R, Lawrence D, Pham VC, Lill JR et al. Cullin3-based polyubiquitination and p62-dependent aggregation of caspase-8 mediate extrinsic apoptosis signaling. Cell 2009; 137: 721–735.
Varfolomeev EE, Schuchmann M, Luria V, Chiannilkulchai N, Beckmann JS, Mett IL et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse Caspase 8 gene ablates cell death induction by the TNF receptors, Fas/Apo1, and DR3 and is lethal prenatally. Immunity 1998; 9: 267–276.
Kaiser WJ, Upton JW, Long AB, Livingston-Rosanoff D, Daley-Bauer LP, Hakem R et al. RIP3 mediates the embryonic lethality of caspase-8-deficient mice. Nature 2011; 471: 368–372.
Su H, Bidere N, Zheng L, Cubre A, Sakai K, Dale J et al. Requirement for caspase-8 in NF-kappaB activation by antigen receptor. Science 2005; 307: 1465–1468.
Budd RC, Yeh WC, Tschopp J . cFLIP regulation of lymphocyte activation and development. Nat Rev Immunol 2006; 6: 196–204.
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V et al. Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 1997; 388: 190–195.
Micheau O, Thome M, Schneider P, Holler N, Tschopp J, Nicholson DW et al. The long form of FLIP is an activator of caspase-8 at the Fas death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 45162–45171.
Tschopp J, Irmler M, Thome M . Inhibition of fas death signals by FLIPs. Curr Opin Immunol 1998; 10: 552–558.
Dohrman A, Kataoka T, Cuenin S, Russell JQ, Tschopp J, Budd RC . Cellular FLIP (long form) regulates CD8(+) T cell activation through caspase-8-dependent NF-kappa B activation. J Immunol 2005; 174: 5270–5278.
Kataoka T, Budd RC, Holler N, Thome M, Martinon F, Irmler M et al. (2000 The caspase-8 inhibitor FLIP promotes activation of NF-kappaB and Erk signaling pathways. Curr Biol 10: 640–648.
Fricker N, Beaudouin J, Richter P, Eils R, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN . Model-based dissection of CD95 signaling dynamics reveals both a pro- and antiapoptotic role of c-FLIPL. J Cell Biol 2010; 190: 377–389.
Thome M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Fickenscher H, Meinl E, Neipel F et al. Viral FLICE-inhibitory proteins (FLIPs) prevent apoptosis induced by death receptors. Nature 1997; 386: 517–521.
Krueger A, Baumann S, Krammer PH, Kirchhoff S . FLICE-inhibitory proteins: regulators of death receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 8247–8254.
Golks A, Brenner D, Fritsch C, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN . c-FLIPR, a new regulator of death receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 14507–14513.
Golks A, Brenner D, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN . The c-FLIP-NH2 terminus (p22-FLIP) induces NF-kappa B activation. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1295–1305.
Krueger A, Schmitz I, Baumann S, Krammer PH, Kirchhoff S (2001 Cellular flice-inhibitory protein splice variants inhibit different steps of caspase-8 activation at the cd95 death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 276: 20633–20640.
Kataoka T, Tschopp J . N-terminal fragment of c-FLIP(L) processed by caspase 8 specifically interacts with TRAF2 and induces activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 2627–2636.
Bentele M, Lavrik I, Ulrich M, Stosser S, Heermann DW, Kalthoff H et al. Mathematical modeling reveals threshold mechanism in CD95-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol 2004; 166: 839–851.
Lavrik IN, Eils R, Fricker N, Pforr C, Krammer PH . Understanding apoptosis by systems biology approaches. Mol Biosyst 2009; 5: 1105–1111.
Lavrik IN . Systems biology of apoptosis signaling networks. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2010; 21: 551–555.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Helmholtz Alliance on Systems Biology (NW1SBCancer/UniHD) and the Helmholtz-Russia Joint Research Groups-2008-2 for supporting our work. We thank Nicolai Fricker, Selcen Öztürk, Kolja Schleich and Claudia Weber for their critical comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article is dedicated to Jürg Tschopp.
Edited by G Melino
Rights and permissions
About this article
This article is cited by
-
Caspase 8 deletion causes infection/inflammation-induced bone marrow failure and MDS-like disease in mice
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
A metal-free salalen ligand with anti-tumor and synergistic activity in resistant leukemia and solid tumor cells via mitochondrial pathway
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2021)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Atrazine-induced cell-mediated immunotoxicity in rabbits and the ameliorating role of glycyrrhizic acid
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2021)
-
Proteomic analysis revealed T cell hyporesponsiveness induced by Haemonchus contortus excretory and secretory proteins
Veterinary Research (2020)
-
Role of mesenchymal stem cells and their culture medium in alleviating kidney injury in rats diabetic nephropathy
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2020)