Abstract
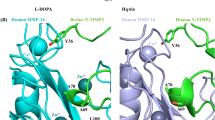
Gelatinase A (MMP-2) is considered to play a critical role in cell migration and invasion. The proteinase is secreted from the cell as an inactive zymogen. In vivo it is postulated that activation of progelationase A (proMMP-2) takes place on the cell surface mediated by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases (MT-MMPs). Recent studies have demonstrated that proMMP-2 is recruited to the cell surface by interacting with tissue in- hibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) bound to MT1-MMP by forming a ternary complex. Free MT1-MMP closely located to the ternary complex then activates proMMP-2 on the cell surface. MT1-MMP is found in cultured invasive cancer cells at the invadopodia. The MT-MMP/TIMP-2/MMP-2 system thus provides localized expression of proteolysis of the extracellular matrix required for cell migration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Woessner JF, Jr . The family of matrix metalloproteinases. Ann NY Acad Sci 1994; 732:11–21.
Nagase H . Matrix metalloproteinases. In: Hooper, N. M.ed. Zinc Metalloproteases in Health and Disease. Taylor & Francis: London 1996:153–204.
Nagase H . Activation mechanisms of matrix metalloproteinases. Biol Chem 1997; 378:151–60.
Sato H, Takino T, Okada Y et al. A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumor cells. Nature 1994; 370:61–5.
Overall CM, Sodek J . Concanavalin A produces a matrix-degradative phenotype in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 1990; 265: 21141–21151.
Brown PD, Levy AT, Margulies IMK, Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG . Independent expression and cellular processing of Mr 72,000 type IV collagenase and interstitial collagenase in human tumorigenic cell lines. Cancer Res 1990; 50:6184–91.
Strongin AY, Marmer BL, Grant GA, Goldberg, GI . Plasma membrane-dependent activation of the 72-kDa type IV collagenase is prevented by complex formation with TIMP-2. J Biol Chem 1993; 268:14033–9.
Murphy G, Willenbrock F, Ward RV, Cockett MI, Eaton D, Docherty AJP . The C-terminal domain of 72 kDa gelatinase A is not required for catalysis, but is essential for membrane activation and modulates interactions with tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Biochem J 1992; 283:637–41.
Strongin AY, Collier I, Bannikov G, Marmer BL, Grant GA, Goldberg GI . Mechanism of cell surface activation of 72-kDa type IV collagenase. J Biol Chem 1995; 270:5331–8.
Butler GS, Butler MJ, Atkinson SJ et al. The TIMP2 membrane type 1 metalloproteinase “receptor” regulates the concentration and efficient activation of progelatinase A. J Biol Chem 1998; 273:871–80.
Pei D, Weiss SJ . Transmembrane-deletion mutants of the membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 process progelatinase A and express intrinsic matrix-degrading activity. J Biol Chem 1996; 271:9135–40.
Cao J, Rehemtulla A, Bahou W, Zucker S . Membrane type matrix metalloproteinase 1 activates pro-gelatinase A without furin cleavage of the N-terminal domain. J Biol Chem 1996; 271:30174–80.
Lee AY, Akers KT, Collier M, Li L, Eisen AZ, Seltzer JL . Intracellular activation of gelatinase A (72-kDa type IV collagenase) by normal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94:4424–9.
Poulsom R, Pignatelli M, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Liotta LA, Wright PA, Jeffrey RE . Stromal expression of 72 kDa type IV collagenase (MMP-2) and TIMP-2 mRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Am J Pathol 1992; 141:389–96.
Emmert-Buck MR, Emonard HP, Corcoran ML, Krutzsch HC, Foidart JM, Stetler-Stevenson WG . Cell surface binding of TIMP-2 and pro-MMP-2/TIMP-2 complex. FEBS Lett 1995; 364:28–32.
Brooks PC, Ströblad S, Sanders LC et al. Localization of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2 to the surface of invasive cells by interaction with integrin αvβ3. Cell 1997; 85:683–93.
Brooks PC, Silletti S, von Schalscha TL, Friedlander M, Cheresh DA . Disruption of angiogenesis by PEX, a noncatalytic metalloproteinase fragment with integrin binding activity. Cell 1998; 92:391–400.
Haas TL, Davis SJ, Madri JA . Three-dimensional type I collagen lattices induce coordinate expression of matrix metalloproteinases MT1-MMP and MMP-2 in microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273:3604–10.
Nakahara H, Howard L, Thompson EW et al. Transmembrane/cytoplasmic domain-mediated membrane type 1-matrix metalloprotease docking to invadopodia is required for cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94:7959–64.
Giannelli G, Falk-Marzillier J, Schiraldi O, Stetler-Stevenson, WG, Quaranta V . Induction of cell migration by matrix metalloprotease-2 cleavage of laminin-5. Science 1997; 277:225–8.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by NIH grants AR39189 and AR40994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagase, H. Cell surface activation of progelatinase A (proMMP-2) and cell migration. Cell Res 8, 179–186 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.1998.18
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.1998.18
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of metal nanoparticles on tight junction-associated proteins via HIF-1α/miR-29b/MMPs pathway in human epidermal keratinocytes
Particle and Fibre Toxicology (2021)
-
RECK and TIMP-2 mediate inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 by Annona muricata
Journal of Biosciences (2020)
-
Differential TIMP3 expression affects tumor progression and angiogenesis in melanomas through regulation of directionally persistent endothelial cell migration
Angiogenesis (2014)
-
Thyroid hormone-induced cell-cell interactions are required for the development of adult intestinal stem cells
Cell & Bioscience (2013)
-
Quantitative proteomics reveals altered expression of extracellular matrix related proteins of human primary dermal fibroblasts in response to sulfated hyaluronan and collagen applied as artificial extracellular matrix
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine (2012)