Abstract
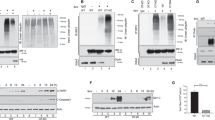
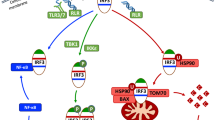
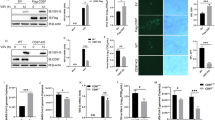
Viral infection causes host cells to produce type I interferons (IFNs), which are critically involved in viral clearance. Previous studies have demonstrated that activation of the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor (IRF)3 is essential for virus-triggered induction of type I IFNs. Here we show that the E3 ubiquitin ligase RBCC protein interacting with PKC1 (RBCK1) catalyzes the ubiquitination and degradation of IRF3. Overexpression of RBCK1 negatively regulates Sendai virus-triggered induction of type I IFNs, while knockdown of RBCK1 has the opposite effect. Plaque assays consistently demonstrate that RBCK1 negatively regulates the cellular antiviral response. Furthermore, viral infection leads to induction of RBCK1 and subsequent degradation of IRF3. These findings suggest that the cellular antiviral response is controlled by a negative feedback regulatory mechanism involving RBCK1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of IRF3.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- NF-κB:
-
(nuclear factor kappa B)
- IRF:
-
(interferon regulatory factor)
- ISRE:
-
(IFN-stimulated response elements)
- CARD:
-
(caspase recruitment domain)
- TBK1:
-
(TANK-binding kinase 1)
- IKKɛ:
-
(inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase subunit epsilon)
- RIG-I:
-
(retinoic acid-inducible gene I)
- MDA5:
-
(melanoma differentiation associated protein-5)
- SeV:
-
(Sendai virus)
- RBCK1:
-
(RBCC protein interacting with PKC1)
References
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR . Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994; 264:1415–1421.
Siegal FP, Kadowaki N, Shodell M, et al. The nature of the principal type 1 interferon-producing cells in human blood. Science 1999; 284:1835–1837.
Levy DE, Garcia-Sastre A . The virus battles: IFN induction of the antiviral state and mechanisms of viral evasion. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2001; 12:143–156.
Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH . Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23:307–336.
Au WC, Moore PA, Lowther W, Juang YT, Pitha PM . Identification of a member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds to the interferon-stimulated response element and activates expression of interferon-induced genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92:11657–11661.
Wathelet MG, Lin CH, Parekh BS, et al. Virus infection induces the assembly of coordinately activated transcription factors on the IFN-beta enhancer in vivo. Mol Cell 1998; 1:507–518.
Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T, et al. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat Immunol 2004; 5:730–737.
Meylan E, Curran J, Hofmann K, et al. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 2005; 437:1167–1172.
Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Chen ZJ . Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. Cell 2005; 122:669–682.
Kawai T, Takahashi K, Sato S, et al. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat Immunol 2005; 6:981–988.
Xu LG, Wang YY, Han KJ, et al. VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. Mol Cell 2005; 19:727–740.
Kawai T, Akira S . Innate immune recognition of viral infection. Nat Immunol 2006; 7:131–137.
Sun Q, Sun L, Liu HH, et al. The specific and essential role of MAVS in antiviral innate immune responses. Immunity 2006; 24:633–642.
Lin R, Heylbroeck C, Pitha PM, Hiscott J . Virus-dependent phosphorylation of the IRF-3 transcription factor regulates nuclear translocation, transactivation potential, and proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18:2986–2996.
Hiscott J, Pitha P, Genin P, et al. Triggering the interferon response: the role of IRF-3 transcription factor. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1999; 19:1–13.
Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM, Faia KL, et al. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2003; 4:491–496.
Sharma S, tenOever BR, Grandvaux N, et al. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 2003; 300:1148–1151.
Rothenfusser S, Goutagny N, DiPerna G, et al. The RNA helicase Lgp2 inhibits TLR-independent sensing of viral replication by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I. J Immunol 2005; 175:5260–5268.
Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Matsumoto K, et al. Shared and unique functions of the DExD/H-box helicases RIG-I, MDA5, and LGP2 in antiviral innate immunity. J Immunol 2005; 175:2851–2858.
Komuro A, Horvath CM . RNA- and virus-independent inhibition of antiviral signaling by RNA helicase LGP2. J Virol 2006; 80:12332–12342.
Saito T, Hirai R, Loo YM, et al. Regulation of innate antiviral defenses through a shared repressor domain in RIG-I and LGP2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104:582–587.
Diao F, Li S, Tian Y, et al. Negative regulation of MDA5- but not RIG-I-mediated innate antiviral signaling by the dihydroxyacetone kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104:11706–11711.
Huang J, Liu T, Xu LG, et al. SIKE is an IKK epsilon/TBK1-associated suppressor of TLR3- and virus-triggered IRF-3 activation pathways. EMBO J 2005; 24:4018–4028.
Lin R, Yang L, Nakhaei P, et al. Negative regulation of the retinoic acid-inducible gene I-induced antiviral state by the ubiquitin-editing protein A20. J Biol Chem 2006; 281:2095–2103.
Kayagaki N, Phung Q, Chan S, et al. DUBA: a deubiquitinase that regulates type I interferon production. Science 2007; 318:1628–1632.
Arimoto K, Takahashi H, Hishiki T, et al. Negative regulation of the RIG-I signaling by the ubiquitin ligase RNF125. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104:7500–7505.
Gack MU, Shin YC, Joo CH, et al. TRIM25 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for RIG-I-mediated antiviral activity. Nature 2007; 446:916–920.
Yamanaka K, Ishikawa H, Megumi Y, et al. Identification of the ubiquitin-protein ligase that recognizes oxidized IRP2. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5:336–340.
Ishikawa H, Kato M, Hori H, et al. Involvement of heme regulatory motif in heme-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of IRP2. Mol Cell 2005; 19:171–181.
Iwai K, Ishikawa H, Kirisako T . Identification, expression, and assay of an oxidation-specific ubiquitin ligase, HOIL-1. Methods Enzymol 2005; 398:256–271.
Cong YS, Yao YL, Yang WM, Kuzhandaivelu N, Seto E . The hepatitis B virus X-associated protein, XAP3, is a protein kinase C-binding protein. J Biol Chem 1997; 272:16482–16489.
Marin I, Ferrus A . Comparative genomics of the RBR family, including the Parkinson's disease-related gene parkin and the genes of the ariadne subfamily. Mol Biol Evol 2002; 19:2039–2050.
Bayle J, Lopez S, Iwai K, Dubreuil P, De Sepulveda P . The E3 ubiquitin ligase HOIL-1 induces the polyubiquitination and degradation of SOCS6 associated proteins. FEBS Lett 2006; 580:2609–2614.
Tian Y, Zhang Y, Zhong B, et al. RBCK1 negatively regulates tumor necrosis factor- and interleukin-1-triggered NF-kappaB activation by targeting TAB2/3 for degradation. J Biol Chem 2007; 282:16776–16782.
Kothapalli R, Nyland SB, Kusmartseva I, et al. Constitutive production of proinflammatory cytokines RANTES, MIP-1beta and IL-18 characterizes LGL leukemia. Int J Oncol 2005; 26:529–535.
Bach JF . Infections and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 2005; 25 Suppl:74–80.
Rotondi M, Chiovato L, Romagnani S, Serio M, Romagnani P . Role of chemokines in endocrine autoimmune diseases. Endocr Rev 2007; 28:492–520.
Mondini M, Vidali M, Airo P, et al. Role of the interferon-inducible gene IFI16 in the etiopathogenesis of systemic autoimmune disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2007; 1110:47–56.
Lin R, Noyce RS, Collins SE, Everett RD, Mossman KL . The herpes simplex virus ICP0 RING finger domain inhibits IRF3- and IRF7-mediated activation of interferon-stimulated genes. J Virol 2004; 78:1675–1684.
Henderson G, Zhang Y, Jones C . The Bovine herpesvirus 1 gene encoding infected cell protein 0 (bICP0) can inhibit interferon-dependent transcription in the absence of other viral genes. J Gen Virol 2005; 86:2697–2702.
Bibeau-Poirier A, Gravel SP, Clement JF, et al. Involvement of the IkappaB kinase (IKK)-related kinases tank-binding kinase 1/IKKi and cullin-based ubiquitin ligases in IFN regulatory factor-3 degradation. J Immunol 2006; 177:5059–5067.
Saitoh T, Tun-Kyi A, Ryo A, et al. Negative regulation of interferon-regulatory factor 3-dependent innate antiviral response by the prolyl isomerase Pin1. Nat Immunol 2006; 7:598–605.
Saira K, Zhou Y, Jones C . The infected cell protein 0 encoded by bovine herpesvirus 1 (bICP0) induces degradation of interferon response factor 3 and, consequently, inhibits beta interferon promoter activity. J Virol 2007; 81:3077–3086.
Graff JW, Ewen J, Ettayebi K, Hardy ME . Zinc-binding domain of rotavirus NSP1 is required for proteasome-dependent degradation of IRF3 and autoregulatory NSP1 stability. J Gen Virol 2007; 88:613–620.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of our laboratory for technical help and stimulating discussion. This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2006CB504301) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30630019 and No. 30570959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Tian, Y., Wang, RP. et al. Negative feedback regulation of cellular antiviral signaling by RBCK1-mediated degradation of IRF3. Cell Res 18, 1096–1104 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.277
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.277
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Early innate immune response triggered by the human respiratory syncytial virus and its regulation by ubiquitination/deubiquitination processes
Journal of Biomedical Science (2022)
-
Ubiquitination modification: critical regulation of IRF family stability and activity
Science China Life Sciences (2021)
-
IFITM3 inhibits virus-triggered induction of type I interferon by mediating autophagosome-dependent degradation of IRF3
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)
-
Identification of RBCK1 as a novel regulator of FKBPL: implications for tumor growth and response to tamoxifen
Oncogene (2014)
-
IRF7: activation, regulation, modification and function
Genes & Immunity (2011)