Abstract
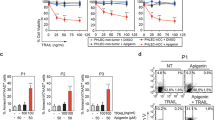
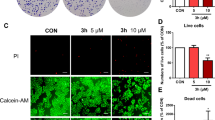
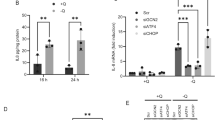
The tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/APO2L) is a member of the TNF gene superfamily that induces apoptosis upon engagement of cognate death receptors. While TRAIL is relatively non-toxic to normal cells, it selectively induces apoptosis in many transformed cells. Nevertheless, breast tumor cells are particularly resistant to the effects of TRAIL. Here we report that, in combination with the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor roscovitine, exposure to TRAIL induced marked apoptosis in the majority of TRAIL-resistant breast cancer cell lines examined. Roscovitine facilitated TRAIL death-inducing signaling complex formation and the activation of caspase-8. The cFLIPL and cFLIPS FLICE-inhibitory proteins were significantly down-regulated following exposure to roscovitine and, indeed, the knockdown of cFLIP isoforms by siRNA sensitized breast tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In addition, we demonstrate that roscovitine strongly suppressed Mcl-1 expression and up-regulated E2F1 protein levels in breast tumor cells. Significantly, the silencing of Mcl-1 by siRNA sensitized breast tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, the knockdown of E2F1 protein by siRNA reduced the sensitizing effect of roscovitine in TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In summary, our results reveal a pleitropic mechanism for the pro-apoptotic influence of roscovitine, highlighting its potential as an antitumor agent in breast cancer in combination with TRAIL.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- (TRAIL):
-
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- (TNF):
-
tumor necrosis factor
- (DISC):
-
death-inducing signaling complex
- (FADD):
-
Fas-associated death domain
- (CDK):
-
cyclin-dependent kinase
- (FLIP):
-
FLICE-inhibitory protein
- (OMe):
-
benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-
- (z-VAD.FMK):
-
fluoromethyl ketone
- (PARP):
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
References
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM . Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 1998; 281:1305–1308.
Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM, et al. Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 1997; 277:818–821.
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 1999; 104:155–162.
Reed JC . Drug insight: cancer therapy strategies based on restoration of endogenous cell death mechanisms. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2006; 3:388–398.
El-Zawahry A, McKillop J, Voelkel-Johnson C . Doxorubicin increases the effectiveness of Apo2L/TRAIL for tumor growth inhibition of prostate cancer xenografts. BMC Cancer 2005; 7:2–5.
Kim EH, Kim SU, Shin DY, Choi KS . Roscovitine sensitizes glioma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by downregulation of survivin and XIAP. Oncogene 2004; 23:446–456.
Lashinger LM, Zhu K, Williams SA, Shrader M, Dinney CP, McConkey DJ . Bortezomib abolishes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance via a p21-dependent mechanism in human bladder and prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65:4902–4908.
Chinnaiyan AM, Prasad U, Shankar S, et al. Combined effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and ionizing radiation in breast cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97:1754–1759.
Ohtsuka T, Buchsbaum D, Oliver P, Makhija S, Kimberly R, Zhou T . Synergistic induction of tumor cell apoptosis by death receptor antibody and chemotherapy agent through JNK/p38 and mitochondrial death pathway. Oncogene 2003; 22:2034–2044.
Ruiz-Ruiz C, Lopez-Rivas A . Mitochondria-dependent and -independent mechanisms in tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis are both regulated by interferon-gamma in human breast tumour cells. Biochem J 2002; 365:825–832.
Sprick MR, Weigand MA, Rieser E, et al. FADD/MORT1 and caspase-8 are recruited to TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 and are essential for apoptosis mediated by TRAIL receptor 2. Immunity 2000; 12:599–609.
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, et al. Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 1997; 388:190–195.
Krueger A, Schmitz I, Baumann S, Krammer PH, Kirchhoff S . Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein splice variants inhibit different steps of caspase-8 activation at the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:20633–20640.
Sharp DA, Lawrence DA, Ashkenazi A . Selective knockdown of the long variant of cellular FLICE inhibitory protein augments death receptor-mediated caspase-8 activation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:19401–19409.
Yeh WC, Itie A, Elia AJ, et al. Requirement for Casper (c-FLIP) in regulation of death receptor-induced apoptosis and embryonic development. Immunity 2000; 12:633–642.
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Scheurich P, Wajant H . NF-κB inducers upregulate cFLIP, a cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signaling. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21:3964–3973.
Fukazawa T, Fujiwara T, Uno F, et al. Accelerated degradation of cellular FLIP protein through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in p53-mediated apoptosis of human cancer cells. Oncogene 2001; 20:5225–5231.
Grana X, Reddy EP . Cell cycle control in mammalian cells: role of cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs), growth suppressor genes and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs). Oncogene 1995; 11:211–219.
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, et al. Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and cdk5. Eur J Biochem 1997; 243:527–536.
McClue SJ, Blake D, Clarke R, et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor properties of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine). Int J Cancer 2002; 102:463–468.
Whittaker SR, Walton MI, Garrett MD, Workman P . The Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CYC202 (R-roscovitine) inhibits retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation, causes loss of Cyclin D1, and activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cancer Res 2004; 64:262–272.
Mgbonyebi OP, Russo J, Russo IH . Roscovitine induces cell death and morphological changes indicative of apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 1999; 59:1903–1910.
MacCallum DE, Melville J, Frame S, et al. Seliciclib (CYC202, R-Roscovitine) induces cell death in multiple myeloma cells by inhibition of RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription and down-regulation of Mcl-1. Cancer Res 2005; 65:5399–5407.
Palacios C, Yerbes R, Lopez-Rivas A . Flavopiridol induces cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein degradation by the proteasome and promotes TRAIL-induced early signaling and apoptosis in breast tumor cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66:8858–8869.
Rosato RR, Dai Y, Almenara JA, Maggio SC, Grant S . Potent antileukemic interactions between flavopiridol and TRAIL/Apo2L involve flavopiridol-mediated XIAP downregulation. Leukemia 2004; 18:1780–1788.
Taniai M, Grambihler A, Higuchi H, et al. Mcl-1 mediates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2004; 64:3517–3524.
Ma Y, Cress WD, Haura EB . Flavopiridol-induced apoptosis is mediated through up-regulation of E2F1 and repression of Mcl-1. Mol Cancer Ther 2003; 2:73–81.
Hahntow IN, Schneller F, Oelsner M, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Roscovitine induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2004; 18:747–755.
Bodmer JL, Holler N, Reynard S, et al. TRAIL receptor-2 signals apoptosis through FADD and caspase-8. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2:241–243.
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ, Ashkenazi A . Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity 2000; 12:611–620.
Gibson SB, Oyer R, Spalding AC, Anderson SM, Johnson GL . Increased expression of death receptors 4 and 5 synergizes the apoptosis response to combined treatment with etoposide and TRAIL. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20:205–212.
MacFarlane M, Harper N, Snowden RT, et al. Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primary B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Oncogene 2002; 21:6809–6818.
Delmas D, Rebe C, Micheau O, et al. Redistribution of CD95, DR4 and DR5 in rafts accounts for the synergistic toxicity of resveratrol and death receptor ligands in colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2004; 23:8979–8986.
Vanoosten RL, Moore JM, Ludwig AT, Griffith TS . Depsipeptide (FR901228) enhances the cytotoxic activity of TRAIL by redistributing TRAIL receptor to membrane lipid rafts. Mol Ther 2005; 11:542–552.
Chang DW, Xing Z, Pan Y, et al. c-FLIP(L) is a dual function regulator for caspase-8 activation and CD95-mediated apoptosis. EMBO J 2002; 21:3704–3714.
Kim Y, Suh N, Sporn M, Reed JC . An inducible pathway for degradation of FLIP protein sensitizes tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277:22320–22329.
Michels J, O'Neill JW, Dallman CL, et al. Mcl-1 is required for Akata6 B-lymphoma cell survival and is converted to a cell death molecule by efficient caspase-mediated cleavage. Oncogene 2004; 23:4818–4827.
Zhou P, Levy NB, Xie H, et al. MCL1 transgenic mice exhibit a high incidence of B-cell lymphoma manifested as a spectrum of histologic subtypes. Blood 2001; 97:3902–3909.
Zhang B, Gojo I, Fenton RG . Myeloid cell factor-1 is a critical survival factor for multiple myeloma. Blood 2002; 99:1885–1893.
Clohessy JG, Zhuang J, de Boer J, Gil-Gomez G, Brady HJ . Mcl-1 interacts with truncated Bid and inhibits its induction of cytochrome c release and its role in receptor-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2006; 281:5750–5759.
Han J, Goldstein LA, Gastman BR, Rabinowich H . Interrelated roles for Mcl-1 and BIM in regulation of TRAIL-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2006; 281:10153–10163.
Wirth T, Kuhnel F, Fleischmann-Mundt B, et al. Telomerase-dependent virotherapy overcomes resistance of hepatocellular carcinomas against chemotherapy and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand by elimination of Mcl-1. Cancer Res 2005; 65:7393–7402.
Nip J, Strom DK, Fee BE, Zambetti G, Cleveland JL, Hiebert SW . E2F-1 cooperates with topoisomerase II inhibition and DNA damage to selectively augment p53-independent apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17:1049–1056.
Salon C, Eymin B, Micheau O, et al. E2F1 induces apoptosis and sensitizes human lung adenocarcinoma cells to death-receptor-mediated apoptosis through specific downregulation of c-FLIP(short). Cell Death Differ 2006; 13:260–272.
Croxton R, Ma Y, Song L, Haura EB, Cress WD . Direct repression of the Mcl-1 promoter by E2F1. Oncogene 2002; 21:1359–1369.
Fesik SW . Promoting apoptosis as a strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5:876–885.
Trauzold A, Siegmund D, Schniewind B, et al. TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2006; 25:7434–7439.
Held J, Schulze-Osthoff K . Potential and caveats of TRAIL in cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat 2001; 4:243–252.
Munoz-Pinedo C, Ruiz-Ruiz C, Ruiz de Almodovar C, Palacios C, Lopez-Rivas A . Inhibition of glucose metabolism sensitizes tumor cells to death receptor-triggered apoptosis through enhancement of death-inducing signaling complex formation and apical procaspase-8 processing. J Biol Chem 2003; 278:12759–12768.
Mihara M, Shintani S, Kiyota A, Matsumura T, Wong DT . Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (roscovitine) suppresses growth and induces apoptosis by regulating Bcl-x in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 2002; 21:95–101.
Harper N, Hughes MA, Farrow SN, Cohen GM, MacFarlane M . Protein kinase C modulates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by targeting the apical events of death receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 2003; 278:44338–44347.
Inoue S, MacFarlane M, Harper N, Wheat LM, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM . Histone deacetylase inhibitors potentiate TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in lymphoid malignancies. Cell Death Differ 2004; 11(Suppl 2):S193–206.
Gajate C, Mollinedo F . Edelfosine and perifosine induce selective apoptosis in multiple myeloma by recruitment of death receptors and downstream signaling molecules into lipid rafts. Blood 2007; 109:711–719.
Lin T, Genestier L, Pinkoski MJ, et al. Role of acidic sphingomyelinase in Fas/CD95-mediated cell death. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:8657–8663.
Nijhawan D, Fang M, Traer E, et al. Elimination of Mcl-1 is required for the initiation of apoptosis following ultraviolet irradiation. Genes Dev 2003; 17:1475–1486.
Poukkula M, Kaunisto A, Hietakangas V, et al. Rapid turnover of c-FLIPshort is determined by its unique C-terminal tail. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:27345–27355.
Yang Y, Fang S, Jensen JP, Weissman AM, Ashwell JD . Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteasomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science 2000; 288:874–877.
Chao SH, Price DH . Flavopiridol inactivates P-TEFb and blocks most RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:31793–31799.
Lam LT, Pickeral OK, Peng AC, et al. Genomic-scale measurement of mRNA turnover and the mechanisms of action of the anti-cancer drug flavopiridol. Genome Biol 2001; 2:RESEARCH0041.
Alvi AJ, Austen B, Weston VJ, et al. A novel CDK inhibitor, CYC202 (R-roscovitine), overcomes the defect in p53-dependent apoptosis in B-CLL by down-regulation of genes involved in transcription regulation and survival. Blood 2005; 105:4484–4491.
Jin TG, Kurakin A, Benhaga N, et al. Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD)-independent recruitment of c-FLIPL to death receptor 5. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:55594–55601.
de Almodovar C, Ruiz, Ruiz-Ruiz C, Munoz-Pinedo C, Robledo G, Lopez-Rivas A . The differential sensitivity of Bc1-2-overexpressing human breast tumor cells to TRAIL or doxorubicin-induced apoptosis is dependent on Bc1-2 protein levels. Oncogene 2001; 20:7128–7133.
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, et al. Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 2006; 9:351–365.
Dai Y, Grant S . Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2003; 3:362–370.
Edamatsu H, Gau CL, Nemoto T, Guo L, Tamanoi F . Cdk inhibitors, roscovitine and olomoucine, synergize with farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) to induce efficient apoptosis of human cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2000; 19:3059–3068.
Harper N, Farrow SN, Kaptein A, Cohen GM, MacFarlane M . Modulation of tumor necrosis factor apoptosis-inducing ligand- induced NF-κ B activation by inhibition of apical caspases. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:34743–34752.
De Maria R, Lenti L, Malisan F, et al. Requirement for GD3 ganglioside in CD95- and ceramide-induced apoptosis. Science 1997; 277:1652–1655.
Parolini I, Sargiacomo M, Lisanti MP, Peschle C . Signal transduction and glycophosphatidylinositol-linked proteins (lyn, lck, CD4, CD45, G proteins, and CD55) selectively localize in Triton-insoluble plasma membrane domains of human leukemic cell lines and normal granulocytes. Blood 1996; 87:3783–3794.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortiz-Ferrón, G., Yerbes, R., Eramo, A. et al. Roscovitine sensitizes breast cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through a pleiotropic mechanism. Cell Res 18, 664–676 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.54
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.54
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Overcoming chemotherapy drug resistance by targeting inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs)
Apoptosis (2017)
-
Guiding TRAIL to cancer cells through Kv10.1 potassium channel overcomes resistance to doxorubicin
European Biophysics Journal (2016)
-
A phase 1 study with dose expansion of the CDK inhibitor dinaciclib (SCH 727965) in combination with epirubicin in patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer
Investigational New Drugs (2015)
-
Reduction of phosphorylated Thr-161 Cdk1 level participates in roscovitine-induced Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis in rat eggs cultured in vitro
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2015)
-
Selective CDK9 inhibition overcomes TRAIL resistance by concomitant suppression of cFlip and Mcl-1
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)