Abstract
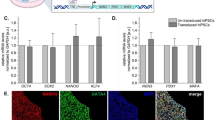
Human pluripotent stem cells represent a potentially unlimited source of functional pancreatic endocrine lineage cells. Here we report a highly efficient approach to induce human embryonic stem (ES) cells and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells to differentiate into mature insulin-producing cells in a chemical-defined culture system. The differentiated human ES cells obtained by this approach comprised nearly 25% insulin-positive cells as assayed by flow cytometry analysis, which released insulin/C-peptide in response to glucose stimuli in a manner comparable to that of adult human islets. Most of these insulin-producing cells co-expressed mature β cell-specific markers such as NKX6-1 and PDX1, indicating a similar gene expression pattern to adult islet β cells in vivo. In this study, we also demonstrated that EGF facilitates the expansion of PDX1-positive pancreatic progenitors. Moreover, our protocol also succeeded in efficiently inducing human iPS cells to differentiate into insulin-producing cells. Therefore, this work not only provides a new model to study the mechanism of human pancreatic specialization and maturation in vitro, but also enhances the possibility of utilizing patient-specific iPS cells for the treatment of diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Stanley EG, Elefanty AG . Building better beta cells. Cell Stem Cell 2008; 2:300–301.
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007; 131:861–872.
Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 2007; 318:1917–1920.
Park IH, Arora N, Huo H, et al. Disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell 2008; 134:877–886.
Dimos JT, Rodolfa KT, Niakan KK, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells generated from patients with ALS can be differentiated into motor neurons. Science 2008; 321:1218–1221.
D'Amour KA, Bang AG, Eliazer S, et al. Production of pancreatic hormone-expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 2006; 24:1392–1401.
Jiang J, Au M, Lu K, et al. Generation of insulin-producing islet-like clusters from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2007; 25:1940–1953.
Jiang W, Shi Y, Zhao D, et al. In vitro derivation of functional insulin-producing cells from human embryonic stem cells. Cell Res 2007; 17:333–344.
Phillips BW, Hentze H, Rust WL, et al. Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into the pancreatic endocrine lineage. Stem Cells Dev 2007; 16:561–578.
Oliver-Krasinski JM, Stoffers DA . On the origin of the beta cell. Genes Dev 2008; 22:1998–2021.
Murtaugh LC . Pancreas and beta-cell development: from the actual to the possible. Development 2007; 134:427–438.
Seymour PA, Freude KK, Tran MN, et al. SOX9 is required for maintenance of the pancreatic progenitor cell pool. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104:1865–1870.
Lynn FC, Smith SB, Wilson ME, et al. Sox9 coordinates a transcriptional network in pancreatic progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104:10500–10505.
Jiang W, Bai Z, Zhang D, et al. Differentiation of mouse nuclear transfer embryonic stem cells into functional pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2008; 51:1671–1679.
Zhao Y, Yin X, Qin H, et al. Two supporting factors greatly improve the efficiency of human iPS cell generation. Cell Stem Cell 2008; 3:475–479.
Nakagawa M, Koyanagi M, Tanabe K, et al. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:101–106.
Miettinen PJ, Huotari M, Koivisto T, et al. Impaired migration and delayed differentiation of pancreatic islet cells in mice lacking EGF-receptors. Development 2000; 127:2617–2627.
Kroon E, Martinson LA, Kadoya K, et al. Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:443–452.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant 2006AA02A113), Science and Technology Plan of Beijing Municipal Government (D07050701350705), Gongjian Project of Beijing Municipal Education Commission, National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2007CB947900, 2009CB941200 and 2009CB941100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30830061) and a 111 Project to H Deng. We thank Dr Jinning Lou (China-Japan Friendship Hospital) for providing adult human islets and Yizhe Zhang for technical support on real-time PCR. We also thank Yang Zhao, Han Qin, Fangfang Zhu, Zhihua Song, Jiefang You, Yuhua Han and other colleagues in our laboratory for providing technical assistance during the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary information Figure S1
The comparable differentiation efficiency of insulin-producing cells from human ES cell line H1 and H9. (PDF 243 kb)
Supplementary information Figure S2
The pluripotency assay of human iPS cell lines. (PDF 180 kb)
Supplementary information Table S1
Reverse-transcription PCR primers (PDF 62 kb)
Supplementary information Table S2
Quantitive PCR primers (PDF 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Jiang, W., Liu, M. et al. Highly efficient differentiation of human ES cells and iPS cells into mature pancreatic insulin-producing cells. Cell Res 19, 429–438 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.28
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.28
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Single-cell analyses reveal distinct expression patterns and roles of long non-coding RNAs during hESC differentiation into pancreatic progenitors
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2023)
-
Comparative Study of Two Common In Vitro Models for the Pancreatic Islet with MIN6
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2023)
-
Urine-derived stem cell therapy for diabetes mellitus and its complications: progress and challenges
Endocrine (2023)
-
Stepwise differentiation of functional pancreatic β cells from human pluripotent stem cells
Cell Regeneration (2022)
-
Stem cells differentiation into insulin-producing cells (IPCs): recent advances and current challenges
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)