Abstract
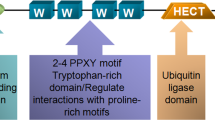
POU transcription factor OCT4 not only plays an essential role in maintaining the pluripotent and self-renewing state of embryonic stem (ES) cells but also acts as a cell fate determinant through a gene dosage effect. However, the molecular mechanisms that control the intracellular OCT4 protein level remain elusive. Here, we report that human WWP2, an E3 ubiquitin (Ub)-protein ligase, interacts with OCT4 specifically through its WW domain and enhances Ub modification of OCT4 both in vitro and in vivo. We first demonstrated that endogenous OCT4 in human ES cells can be post-translationally modified by Ub. Furthermore, we found that WWP2 promoted degradation of OCT4 through the 26S proteasome in a dosage-dependent manner, and the active site cysteine residue of WWP2 was required for both its enzymatic activity and proteolytic effect on OCT4. Remarkably, our data show that the endogenous OCT4 protein level was significantly elevated when WWP2 expression was downregulated by specific RNA interference (RNAi), suggesting that WWP2 is an important regulator for maintaining a proper OCT4 protein level in human ES cells. Moreover, northern blot analysis showed that the WWP2 transcript was widely present in diverse human tissues/organs and highly expressed in undifferentiated human ES cells. However, its expression level was quickly decreased after human ES cells differentiated, indicating that WWP2 expression might be developmentally regulated. Our findings demonstrate that WWP2 is an important regulator of the OCT4 protein level in human ES cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Sinawat S. Potential applications of human embryonic stem cells. J Med Assoc Thai 2007; 90:1253–1258.
Niwa H . How is pluripotency determined and maintained? Development 2007; 134:635–646.
Scholer HR, Dressler GR, Balling R, et al. Oct-4: a germline-specific transcription factor mapping to the mouse t-complex. EMBO J 1990; 9:2185–2195.
Rosner MH, Vigano MA, Ozato K, et al. A POU-domain transcription factor in early stem cells and germ cells of the mammalian embryo. Nature 1990; 345:686–692.
Okamoto K, Okazawa H, Okuda A, et al. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell 1990; 60:461–472.
Hansis C, Grifo JA, Krey LC . Oct-4 expression in inner cell mass and trophectoderm of human blastocysts. Mol Hum Reprod 2000; 6:999–1004.
Ginis I, Luo Y, Miura T, et al. Differences between human and mouse embryonic stem cells. Dev Biol 2004; 269:360–380.
Gidekel S, Pizov G, Bergman Y, et al. Oct-3/4 is a dose-dependent oncogenic fate determinant. Cancer Cell 2003; 4:361–370.
Nichols J, Zevnik B, Anastassiadis K, et al. Formation of pluripotent stem cells in the mammalian embryo depends on the POU transcription factor Oct4. Cell 1998; 95:379–391.
Niwa H, Miyazaki J, Smith AG . Quantitative expression of Oct-3/4 defines differentiation, dedifferentiation or self-renewal of ES cells. Nat Genet 2000; 24:372–376.
Boiani M, Eckardt S, Scholer HR, et al. Oct4 distribution and level in mouse clones: consequences for pluripotency. Genes Dev 2002; 16:1209–1219.
Donovan PJ . High Oct-ane fuel powers the stem cell. Nat Genet 2001; 29:246–247.
Xu HM, Liao B, Zhang QJ, et al. Wwp2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets transcription factor Oct-4 for ubiquitination. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:23495–23503.
Conaway RC, Brower CS, Conaway JW . Emerging roles of ubiquitin in transcription regulation. Science 2002; 296:1254–1258.
Ciechanover A . The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway: on protein death and cell life. EMBO J 1998; 17:7151–7160.
Naujokat C, Hoffmann S . Role and function of the 26S proteasome in proliferation and apoptosis. Lab Invest 2002; 82:965–980.
Mayer RJ . The meteoric rise of regulated intracellular proteolysis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2000; 1:145–148.
Weissman AM . Themes and variations on ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2:169–178.
Joazeiro CA, Weissman AM . RING finger proteins: mediators of ubiquitin ligase activity. Cell 2000; 102:549–552.
Huibregtse JM, Scheffner M, Beaudenon S, et al. A family of proteins structurally and functionally related to the E6-AP ubiquitin-protein ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92:5249.
Harvey KF, Kumar S . Nedd4-like proteins: an emerging family of ubiquitin-protein ligases implicated in diverse cellular functions. Trends Cell Biol 1999; 9:166–169.
Kato Y, Nagata K, Takahashi M, et al. Common mechanism of ligand recognition by group II/III WW domains: redefining their functional classification. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:31833–31841.
Murillas R, Simms KS, Hatakeyama S, et al. Identification of developmentally expressed proteins that functionally interact with Nedd4 ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem 2002; 277:2897–2907.
Pirozzi G, McConnell SJ, Uveges AJ, et al. Identification of novel human WW domain-containing proteins by cloning of ligand targets. J Biol Chem 1997; 272:14611–14616.
Wood JD, Yuan J, Margolis RL, et al. Atrophin-1, the DRPLA gene product, interacts with two families of WW domain-containing proteins. Mol Cell Neurosci 1998; 11:149–160.
McDonald FJ, Western AH, McNeil JD, et al. Ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP2 binds to and downregulates the epithelial Na(+) channel. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2002; 283:F431–F436.
Flores SY, Debonneville C, Staub O . The role of Nedd4/Nedd4-like dependant ubiquitylation in epithelial transport processes. Pflugers Arch 2003; 446:334–338.
Cowan CA, Klimanskaya I, McMahon J, et al. Derivation of embryonic stem-cell lines from human blastocysts. N Engl J Med 2004; 350:1353–1356.
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 1998; 282:1145–1147.
Gropp M, Itsykson P, Singer O, et al. Stable genetic modification of human embryonic stem cells by lentiviral vectors. Mol Ther 2003; 7:281–287.
Huibregtse JM, Scheffner M, Beaudenon S, et al. A family of proteins structurally and functionally related to the E6-AP ubiquitin-protein ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92:2563–2567.
Huang L, Kinnucan E, Wang G, et al. Structure of an E6AP-UbcH7 complex: insights into ubiquitination by the E2-E3 enzyme cascade. Science 1999; 286:1321–1326.
Przyborski SA, Christie VB, Hayman MW, et al. Human embryonal carcinoma stem cells: models of embryonic development in humans. Stem Cells Dev 2004; 13:400–408.
Horrocks GM, Lauder L, Stewart R, et al. Formation of neurospheres from human embryonal carcinoma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 304:411–416.
Josephson R, Ording CJ, Liu Y, et al. Qualification of embryonal carcinoma 2102Ep as a reference for human embryonic stem cell research. Stem Cells 2007; 25:437–446.
Sun BW, Yang AC, Feng Y, et al. Temporal and parental-specific expression of imprinted genes in a newly derived Chinese human embryonic stem cell line and embryoid bodies. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15:65–75.
van de Wetering M, Oving I, Muncan V, et al. Specific inhibition of gene expression using a stably integrated, inducible small-interfering-RNA vector. EMBO Rep 2003; 4:609–615.
Zangrossi S, Marabese M, Broggini M, et al. Oct-4 expression in adult human differentiated cells challenges its role as a pure stem cell marker. Stem Cells 2007; 25:1675–1680.
Roche S, Richard MJ, Favrot MC . Oct-4, Rex-1, and Gata-4 expression in human MSC increase the differentiation efficiency but not hTERT expression. J Cell Biochem 2007; 101:271–280.
Trosko JE . From adult stem cells to cancer stem cells: Oct-4 Gene, cell-cell communication, and hormones during tumor promotion. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006; 1089:36–58.
Suo G, Han J, Wang X, et al. Oct4 pseudogenes are transcribed in cancers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 337:1047–1051.
Hay DC, Sutherland L, Clark J, et al. Oct-4 knockdown induces similar patterns of endoderm and trophoblast differentiation markers in human and mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2004; 22:225–235.
Atlasi Y, Mowla SJ, Ziaee SA, et al. OCT-4, an embryonic stem cell marker, is highly expressed in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer 2007; 120:1598–1602.
Zaehres H, Lensch MW, Daheron L, et al. High-efficiency RNA interference in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2005; 23:299–305.
Rubinson DA, Dillon CP, Kwiatkowski AV, et al. A lentivirus-based system to functionally silence genes in primary mammalian cells, stem cells and transgenic mice by RNA interference. Nat Genet 2003; 33:401–406.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr DA Melton (Harvard University) for sharing his human ES cells with us. The study was supported by grants from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2006CB943900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program, 30500088), the Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, and the Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The study was also supported by the Shanghai Leading Academic Deciline Project (S30201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Wang, W., Li, C. et al. WWP2 promotes degradation of transcription factor OCT4 in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Res 19, 561–573 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.31
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.31
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP2 and the regulation of PARP1 by ubiquitinated degradation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
Kap1 regulates the self-renewal of embryonic stem cells and cellular reprogramming by modulating Oct4 protein stability
Cell Death & Differentiation (2021)
-
LSD1-mediated demethylation of OCT4 safeguards pluripotent stem cells by maintaining the transcription of PORE-motif-containing genes
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Posttranscriptional regulation of maternal Pou5f1/Oct4 during mouse oogenesis and early embryogenesis
Histochemistry and Cell Biology (2020)
-
The oncogene Gankyrin is expressed in testicular cancer and contributes to cisplatin sensitivity in embryonal carcinoma cells
BMC Cancer (2019)