Abstract
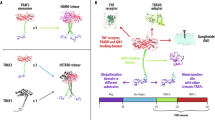
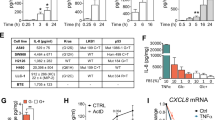
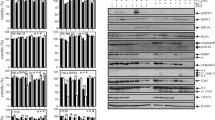
In the present article, we report that DR4 or DR5 overexpression dramatically activates the release of the inflammatory cytokines IL-8, TNF-α, CCL20, MIP-2 and MIP-1β in an NF-κB-dependent manner in 293T, MDA-MB-231 and HCT-116 cells. We showed that death receptor-mediated signals were extracellular domain-independent, whereas the effect of overexpression of the DR4 intracellular domain was much less potent. The TRADD-TRAF2-NIK-IKKα/β signaling cascade, which plays an essential role in TNF-induced NF-κB activation, was found to be involved in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor-mediated signal transduction. The FADD-caspase signaling pathway, which has been reported to be mostly related to apoptosis, was identified as being essential for DR4 or DR5 overexpression-mediated NF-κB activation and cytokine secretion and crosstalks with the TRADD-TRAF2-NIK-IKKα/β signaling cascade. Furthermore, a DR5 agonistic antibody (AD5-10) triggered the inflammatory cytokine release. These data, together with previous reports, provide strong evidence that TRAIL and TRAIL receptors play an important role in inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- TRAIL:
-
(tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand)
- DR:
-
(death receptor)
- DcR:
-
(decoy receptor)
- DISC:
-
(death-inducing signaling complex)
- DN:
-
(dominant negative)
References
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med 1999; 5:157–163.
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 1999; 104:155–162.
Pan G, O'Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, et al. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science 1997; 276:111–113.
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS, et al. TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J 1997; 16:5386–5397.
Chaudhary PM, Eby M, Jasmin A, Bookwalter A, Murray J, Hood L . Death receptor 5, a new member of the TNFR family, and DR4 induce FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate the NF-kappaB pathway. Immunity 1997; 7:821–830.
Sprick MR, Weigand MA, Rieser E, et al. FADD/MORT1 and caspase-8 are recruited to TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 and are essential for apoptosis mediated by TRAIL receptor 2. Immunity 2000; 12:599–609.
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ, Ashkenazi A . Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity 2000; 12:611–620.
Bodmer JL, Holler N, Reynard S, et al. TRAIL receptor-2 signals apoptosis through FADD and caspase-8. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2:241–243.
Anel A, Bosque A, Naval J, et al. Apo2L/TRAIL and immune regulation. Front Biosci 2007; 12:2074–2084.
Grosse-Wilde A, Voloshanenko O, Bailey SL, et al. TRAIL-R deficiency in mice enhances lymph node metastasis without affecting primary tumor development. J Clin Invest 2008; 118:100–110.
Zerafa N, Westwood JA, Cretney E, et al. Cutting edge: TRAIL deficiency accelerates hematological malignancies. J Immunol 2005; 175:5586–5590.
Cretney E, Uldrich AP, Berzins SP, Strasser A, Godfrey DI, Smyth MJ . Normal thymocyte negative selection in TRAIL-deficient mice. J Exp Med 2003; 198:491–496.
Lamhamedi-Cherradi SE, Zheng SJ, Maguschak KA, Peschon J, Chen YH . Defective thymocyte apoptosis and accelerated autoimmune diseases in TRAIL−/− mice. Nat Immunol 2003; 4:255–260.
Janssen EM, Droin NM, Lemmens EE, et al. CD4+ T-cell help controls CD8+ T-cell memory via TRAIL-mediated activation-induced cell death. Nature 2005; 434:88–93.
Li JH, Kirkiles-Smith NC, McNiff JM, Pober JS . TRAIL induces apoptosis and inflammatory gene expression in human endothelial cells. J Immunol 2003; 171:1526–1533.
Secchiero P, Corallini F, di Iasio MG, Gonelli A, Barbarotto E, Zauli G . TRAIL counteracts the proadhesive activity of inflammatory cytokines in endothelial cells by down-modulating CCL8 and CXCL10 chemokine expression and release. Blood 2005; 105:3413–3419.
Secchiero P, Gonelli A, Carnevale E, et al. TRAIL promotes the survival and proliferation of primary human vascular endothelial cells by activating the Akt and ERK pathways. Circulation 2003; 107:2250–2256.
Zauli G, Pandolfi A, Gonelli A, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) sequentially upregulates nitric oxide and prostanoid production in primary human endothelial cells. Circ Res 2003; 92:732–740.
Harper N, Farrow SN, Kaptein A, Cohen GM, MacFarlane M . Modulation of tumor necrosis factor apoptosis-inducing ligand- induced NF-kappa B activation by inhibition of apical caspases. J Biol Chem 2001; 276:34743–34752.
Varfolomeev E, Maecker H, Sharp D, et al. Molecular determinants of kinase pathway activation by Apo2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:40599–40608.
Choi C, Kutsch O, Park J, Zhou T, Seol DW, Benveniste EN . Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand induces caspase-dependent interleukin-8 expression and apoptosis in human astroglioma cells. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22:724–736.
Guo Y, Chen C, Zheng Y, et al. A novel anti-human DR5 monoclonal antibody with tumoricidal activity induces caspase-dependent and caspase-independent cell death. J Biol Chem 2005; 280:41940–41952.
Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Beyaert R, Fiers W . Two tumour necrosis factor receptors: structure and function. Trends Cell Biol 1995; 5:392–399.
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS Jr. NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 1998; 281:1680–1683.
Zong WX, Edelstein LC, Chen C, Bash J, Gelinas C . The prosurvival Bcl-2 homolog Bfl-1/A1 is a direct transcriptional target of NF-kappaB that blocks TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999; 13:382–387.
Wang CY, Guttridge DC, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS Jr. NF-kappaB induces expression of the Bcl-2 homologue A1/Bfl-1 to preferentially suppress chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19:5923–5929.
Chen C, Edelstein LC, Gelinas C . The Rel/NF-kappaB family directly activates expression of the apoptosis inhibitor Bcl-x(L). Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20:2687–2695.
Mitsiades CS, Treon SP, Mitsiades N, et al. TRAIL/Apo2L ligand selectively induces apoptosis and overcomes drug resistance in multiple myeloma: therapeutic applications. Blood 2001; 98:795–804.
Trauzold A, Wermann H, Arlt A, et al. CD95 and TRAIL receptor-mediated activation of protein kinase C and NF-kappaB contributes to apoptosis resistance in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene 2001; 20:4258–4269.
Oya M, Ohtsubo M, Takayanagi A, Tachibana M, Shimizu N, Murai M . Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappaB prevents TRAIL-induced apoptosis in renal cancer cells. Oncogene 2001; 20:3888–3896.
Wuchter C, Krappmann D, Cai Z, et al. In vitro susceptibility to TRAIL-induced apoptosis of acute leukemia cells in the context of TRAIL receptor gene expression and constitutive NF-kappa B activity. Leukemia 2001; 15:921–928.
Kurbanov BM, Fecker LF, Geilen CC, Sterry W, Eberle J . Resistance of melanoma cells to TRAIL does not result from upregulation of antiapoptotic proteins by NF-kappaB but is related to downregulation of initiator caspases and DR4. Oncogene 2007; 26:3364–3377.
Weckmann M, Collison A, Simpson JL, et al. Critical link between TRAIL and CCL20 for the activation of T(H)2 cells and the expression of allergic airway disease. Nat Med 2007; 13:1308–1315.
Pan G, Ni J, Yu G, Wei YF, Dixit VM . TRUNDD, a new member of the TRAIL receptor family that antagonizes TRAIL signaling. FEBS Lett 1998; 424:41–45.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Hongbing Shu (Wuhan University, China), Jiandong Li (University of Rochester Medical Center, USA), Andrew Thorburn (University of Colorado Comprehensive Cancer Center, USA) and Andreas Strasser (The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Australia) for the generous gifts of the constructs. This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 30571687 and 30721063) and the State Key Basic Research Program of China (Grant 2007CB507404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, W., Wang, W., Zhang, Y. et al. TRAIL receptor mediates inflammatory cytokine release in an NF-κB-dependent manner. Cell Res 19, 758–767 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.57
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.57
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) deletion in myeloid cells augments cholestatic liver injury
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Kaempferol sensitizes tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-resistance chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to apoptosis
Molecular Biology Reports (2022)
-
Biliary tract instillation of a SMAC mimetic induces TRAIL-dependent acute sclerosing cholangitis-like injury in mice
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
TRAF2 inhibits TRAIL- and CD95L-induced apoptosis and necroptosis
Cell Death & Disease (2014)
-
Adeno-associated virus-mediated doxycycline-regulatable TRAIL expression suppresses growth of human breast carcinoma in nude mice
BMC Cancer (2012)