Abstract
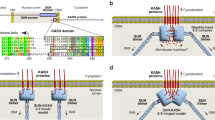
Linker of the nucleoskeleton and the cytoskeleton (LINC) complexes are composed of SUN and KASH domain-containing proteins and bridge the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope. LINC complexes play critical roles in nuclear positioning, cell polarization and cellular stiffness. Previously, we reported the homotrimeric structure of human SUN2. We have now determined the crystal structure of the human SUN2-KASH complex. In the complex structure, the SUN domain homotrimer binds to three independent “hook”-like KASH peptides. The overall conformation of the SUN domain in the complex closely resembles the SUN domain in its apo state. A major conformational change involves the AA'-loop of KASH-bound SUN domain, which rearranges to form a mini β-sheet that interacts with the KASH peptide. The PPPT motif of the KASH domain fits tightly into a hydrophobic pocket on the homotrimeric interface of the SUN domain, which we termed the BI-pocket. Moreover, two adjacent protomers of the SUN domain homotrimer sandwich the KASH domain by hydrophobic interaction and hydrogen bonding. Mutations of these binding sites disrupt or reduce the association between the SUN and KASH domains in vitro. In addition, transfection of wild-type, but not mutant, SUN2 promotes cell migration in Ovcar-3 cells. These results provide a structural model of the LINC complex, which is essential for additional study of the physical and functional coupling between the cytoplasm and the nucleoplasm.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Crisp M, Liu Q, Roux K, et al. Coupling of the nucleus and cytoplasm: role of the LINC complex. J Cell Bio 2006; 172:41–53.
Ostlund C, Folker ES, Choi JC, et al. Dynamics and molecular interactions of linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex proteins. J Cell Sci 2009; 122:4099–4108.
Lombardi ML, Lammerding J . Keeping the LINC: the importance of nucleocytoskeletal coupling in intracellular force transmission and cellular function. Biochem Soc Trans 2011; 39:1729–1734.
Goldman RD, Gruenbaum Y, Moir RD, Shumaker DK, Spann TP . Nuclear lamins: building blocks of nuclear architecture. Genes Dev 2002; 16:533–547.
Tzur YB, Margalit A, Melamed-Book N, Gruenbaum Y . Matefin/SUN-1 is a nuclear envelope receptor for CED-4 during Caenorhabditis elegans apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103:13397–13402.
Gob E, Schmitt J, Benavente R, Alsheimer M . Mammalian sperm head formation involves different polarization of two novel LINC complexes. PloS One 2010; 5:e12072.
Hale CM, Shrestha AL, Khatau SB, et al. Dysfunctional connections between the nucleus and the actin and microtubule networks in laminopathic models. Biophys J 2008; 95:5462–5475.
Worman HJ, Bonne G . “Laminopathies”: a wide spectrum of human diseases. Exp Cell Res 2007; 313:2121–2133.
Mounkes L, Kozlov S, Burke B, Stewart CL . The laminopathies: nuclear structure meets disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2003; 13:223–230.
Wang Q, Du X, Cai Z, Greene MI . Characterization of the structures involved in localization of the SUN proteins to the nuclear envelope and the centrosome. DNA Cell Biol 2006; 25:554–562.
Hodzic DM, Yeater DB, Bengtsson L, Otto H, Stahl PD . Sun2 is a novel mammalian inner nuclear membrane protein. J Bio Chem 2004; 279:25805–25812.
Zhou Z, Du X, Cai Z, et al. Structure of Sad1-UNC84 homology (SUN) domain defines features of molecular bridge in nuclear envelope. J Bio Chem 2012; 287:5317–5326.
Liang Y, Chiu PH, Yip KY, Chan SY . Subcellular localization of SUN2 is regulated by Lamin A and Rab5. PloS One 2011; 6:e 20507.
Turgay Y, Ungricht R, Rothballer A, et al. A classical NLS and the SUN domain contribute to the targeting of SUN2 to the inner nuclear membrane. EMBO J 2010; 29:2262–2275.
Lu W, Gotzmann J, Sironi L, et al. Sun1 forms immobile macromolecular assemblies at the nuclear envelope. BBA-Mol Cell Res 2008; 1783:2415–2426.
Lei K, Zhang X, Ding X, et al. SUN1 and SUN2 play critical but partially redundant roles in anchoring nuclei in skeletal muscle cells in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106:10207–10212.
Starr DA, Han M . A genetic approach to study the role of nuclear envelope components in nuclear positioning. Novartis Found Symp 2005; 264:208–219.
Luxton GG, Gomes ER, Folker ES, Worman HJ, Gundersen GG . TAN lines: a novel nuclear envelope structure involved in nuclear positioning. Nucleus 2011; 2:173–181.
Luxton G, Gomes ER, Folker ES, Vintinner E, Gundersen GG . Linear arrays of nuclear envelope proteins harness retrograde actin flow for nuclear movement. Science 2010; 329:956–959.
Taranum S, Vaylann E, Meinke P, et al. LINC complex alterations in DMD and EDMD/CMT fibroblasts. Eur J of Cell Biol 2012; 91:614–628.
Zhang Q, Bethmann C, Worth NF, et al. Nesprin-1 and -2 are involved in the pathogenesis of Emery Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and are critical for nuclear envelope integrity. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16:2816–2833.
Stewart-Hutchinson PJ, Hale CM, Wirtz D, Hodzic D . Structural requirements for the assembly of LINC complexes and their function in cellular mechanical stiffness. Exp Cell Res 2008; 314:1892–1905.
Ketema M, Wilhelmsen K, Kuikman I, et al. Requirements for the localization of nesprin-3 at the nuclear envelope and its interaction with plectin. J Cell Sci 2007; 120:3384–3394.
Padmakumar VC, Libotte T, Lu W, et al. The inner nuclear membrane protein Sun1 mediates the anchorage of Nesprin-2 to the nuclear envelope. J Cell Sci 2005; 118:3419–3430.
Rashmi RN, Eckes B, Glockner G, et al. The nuclear envelope protein Nesprin-2 has roles in cell proliferation and differentiation during wound healing. Nucleus 2011; 3:172–186.
Schaller MD . Cellular functions of FAK kinases: insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J Cell Sci 2010; 123:1007–1013.
Sieg DJ, Hauck CR, Schlaepfer DD . Required role of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) for integrin-stimulated cell migration. J Cell Sci 1999; 112:2677–2691.
Yu J, Lei K, Zhou M, et al. KASH protein Syne-2/Nesprin-2 and SUN proteins SUN1/2 mediate nuclear migration during mammalian retinal development. Hum Mol Genet 2011; 20:1061–1073.
Starr DA, Hermann GJ, Malone CJ, et al. unc-83 encodes a novel component of the nuclear envelope and is essential for proper nuclear migration. Development 2001; 128:5039–5050.
Lee KK, Starr D, Cohen M, et al. Lamin-dependent localization of UNC-84, a protein required for nuclear migration in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell 2002; 13:892–901.
Oda Y, Fukuda H . Dynamics of Arabidopsis SUN proteins during mitosis and their involvement in nuclear shaping. Plant J 2011; 66:629–641.
Malone CJ, Fixsen WD, Horvitz HR, Han M . UNC-84 localizes to the nuclear envelope and is required for nuclear migration and anchoring during C. elegans development. Development 1999; 126:3171–3181.
Sosa BA, Rothballer A, Kutay U, Schwartz TU . LINC complexes form by binding of three KASH peptides to domain interfaces of trimeric SUN proteins. Cell 2012; 149:1035–1047.
Chikashige Y, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y . Another way to move chromosomes. Chromosoma 2007; 116:497–505.
Schmitt J, Benavente R, Hodzic D, et al. Transmembrane protein Sun2 is involved in tethering mammalian meiotic telomeres to the nuclear envelope. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104:7426–7431.
Mans BJ, Anantharaman V, Aravind L, Koonin EV . Comparative genomics, evolution and origins of the nuclear envelope and nuclear pore complex. Cell Cycle 2004; 3:1612–1637.
Mislow JM, Holaska JM, Kim MS, et al. Nesprin-1alpha self-associates and binds directly to emerin and lamin A in vitro. FEBS Lett 2002; 525:135–140.
Chikashige Y, Tsutsumi C, Yamane M, et al. Meiotic proteins bqt1 and bqt2 tether telomeres to form the bouquet arrangement of chromosomes. Cell 2006; 125:59–69.
Penkner A, Tang L, Novatchkova M, et al. The nuclear envelope protein Matefin/SUN-1 is required for homologous pairing in C. elegans meiosis. Dev Cell 2007; 12:873–885.
Schoggins JW, Wilson SJ, Panis M, et al. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011; 472:481–485.
Buchkovich NJ, Maguire TG, Alwine JC . Role of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP, SUN domain proteins, and dynein in altering nuclear morphology during human cytomegalovirus infection. J Virol 2010; 84:7005–7017.
Otwinowski Z, Minor W . Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol 1997; 276:307–326.
Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkoczi G, et al. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2010; 66:213–221.
Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K . Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2010; 66:486–501.
Murshudov GN, Skubak P, Lebedev AA, et al. REFMAC5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2011; 67:355–367.
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff at BL17U of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for their help with the data collection. This work was supported by the 973 program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2010CB529701, 2012CB910204), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970566, 10979005, 30971647, 31171414) and Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (11JC14140000). ZZ is a scholar of the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Shi, Z., Jiao, S. et al. Structural insights into SUN-KASH complexes across the nuclear envelope. Cell Res 22, 1440–1452 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.126
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.126
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nuclear membrane protein SUN2 promotes replication of flaviviruses through modulating cytoskeleton reorganization mediated by NS1
Nature Communications (2024)
-
SUN1/2 controls macrophage polarization via modulating nuclear size and stiffness
Nature Communications (2023)
-
The N-terminal region of Jaw1 has a role to inhibit the formation of organized smooth endoplasmic reticulum as an intrinsically disordered region
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A human infertility-associated KASH5 variant promotes mitochondrial localization
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The meiotic TERB1-TERB2-MAJIN complex tethers telomeres to the nuclear envelope
Nature Communications (2019)