Abstract
BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES:
The relationship between birth weight and body composition at later stages in life was not studied previously in anorexia nervosa (AN). The aim of the following brief report is to present results concerning the relationship between birth weight and later body composition specifically in AN, and to check if the programming of body composition from birth weight is still detected in severely emaciated AN patients.
SUBJECTS/METHODS:
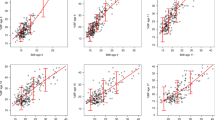
One hundred and fifty-one female AN patients aged between 13 and 44 were recruited from 11 inpatient treatment facilities in France. Birth weight, body weight and height were obtained. Body composition was measured using bioelectrical impedance. Birth weight was significantly correlated to lifetime maximum body mass index (BMI; r=0.211, P=0.009) and significantly correlated to fat-free mass index (r=0.190, P=0.027) but not to fat mass index (FMI).
RESULTS:
This report confirms that even in AN when patients are severely emaciated and where fat-free mass (FFM) and fat mass (FM) are low, a link between birth weight and FFM and BMI can still be identified, independently from age.
CONCLUSION:
Further studies are needed on larger samples exploring other factors, such as gender, puberty and ethnicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chomtho S, Wells JC, Williams JE, Lucas A, Fewtrell MS . Associations between birth weight and later body composition: evidence from the 4-component model. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 88, 1040–1048.
Kensara OA, Wootton SA, Phillips DI, Patel M, Jackson AA, Elia M . Fetal programming of body composition: relation between birth weight and body composition measured with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometric methods in older Englishmen. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82, 980–987.
Elia M, Betts P, Jackson DM, Mulligan J . Fetal programming of body dimensions and percentage body fat measured in prepubertal children with a 4-component model of body composition, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, deuterium dilution, densitometry, and skinfold thicknesses. Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86, 618–624.
Labayen I, Moreno LA, Blay MG, Blay VA, Mesana MI, Gonzalez-Gross M et al. Early programming of body composition and fat distribution in adolescents. J Nutr 2006; 136, 147–152.
Wells JC, Hallal PC, Wright A, Singhal A, Victora CG . Fetal, infant and childhood growth: relationships with body composition in Brazilian boys aged 9 years. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005; 29, 1192–1198.
Singhal A, Wells J, Cole TJ, Fewtrell M, Lucas A . Programming of lean body mass: a link between birth weight, obesity, and cardiovascular disease? Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 77, 726–730.
Murphy MJ, Metcalf BS, Jeffery AN, Voss LD, Wilkin TJ . Does lean rather than fat mass provide the link between birth weight, BMI, and metabolic risk? EarlyBird 23. Pediatr Diab 2006; 7, 211–214.
Loos RJ, Beunen G, Fagard R, Derom C, Vlietinck R . Birth weight and body composition in young women: a prospective twin study. Am J Clin Nutr 2002; 75, 676–682.
Beumont P, Hay P, Beumont D, Birmingham L, Derham H, Jordan A et al. Australian and New Zealand clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of anorexia nervosa. Aust NZ J Psychiatry 2004; 38, 659–670.
Foley DL, Neale MC, Kendler KS . Does intra-uterine growth discordance predict differential risk for adult psychiatric disorder in a population-based sample of monozygotic twins? Psychiatr Genet 2000; 10, 1–8.
Favaro A, Tenconi E, Santonastaso P . Perinatal factors and the risk of developing anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006; 63, 82–88.
Mattar L, Godart N, Melchior JC, Pichard C . Anorexia nervosa and nutritional assessment: contribution of body composition measurements. Nut Res Rev 2011; 24, 1–8.
Cooper Z, Cooper PJ, Fairburn CG . The validity of the eating disorder examination and its subscales. Br J Psychiatry 1989; 154, 807–812.
World Health Organization. Composite International Diagnostic Interview Version 2.1. WHO: Geneva, 1997.
UNICEF, WHO. Low Birth Weights: Country, Regional and Global Estimates. UNICEF, Editorial and publication section: NY, USA, 2004.
Probst M, Goris M, Vandereycken W, Van Coppenolle H . Body composition of anorexia nervosa patients assessed by underwater weighing and skinfold-thickness measurements before and after weight gain. Am J Clin Nutr 2001; 73, 190–197.
Piccoli A, Codognotto M, Di Pascoli L, Boffo G, Caregaro L . Body mass index and agreement between bioimpedance and anthropometry estimates of body compartments in anorexia nervosa. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2005; 29, 148–156.
Kyle UG, Bosaeus I, De Lorenzo AD, Deurenberg P, Elia M, Gomez JM et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis—part I: review of principles and methods. Clin Nutr 2004; 23, 1226–1243.
Mattar L, Godart N, Melchior JC, Falissard B, Kolta S, Ringuenet D et al. Underweight patients with anorexia nervosa: comparison of bioelectrical impedance analysis using five equations to dual X-ray absorptiometry. Clin Nutr 2011; 30, 746–752.
Deurenberg P, van der Kooy K, Leenen R, Weststrate JA, Seidell JC . Sex and age specific prediction formulas for estimating body composition from bioelectrical impedance: a cross-validation study. Int J Obes 1991; 15, 17–25.
VanItallie TB, Yang MU, Heymsfield SB, Funk RC, Boileau RA . Height-normalized indices of the body's fat-free mass and fat mass: potentially useful indicators of nutritional status. Am J Clin Nutr 1990; 52, 953–959.
Wells JC . A critique of the expression of paediatric body composition data. Arch Dis Child 2001; 85, 67–72.
Kyle UG, Schutz Y, Dupertuis YM, Pichard C . Body composition interpretation. Contributions of the fat-free mass index and the body fat mass index. Nutrition 2003; 19, 597–604.
Kyle UG, Bosaeus I, De Lorenzo AD, Deurenberg P, Elia M, Manuel Gomez J et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-part II: utilization in clinical practice. Clin Nutr 2004; 23, 1430–1453.
Godart N, Wallier J, Hubert T, Curt F, Gales O, Perdereau F et al. Determining factors for target weights in an anorexia nervosa inpatient program for adolescents and young adults: study on the links between theory-based hypotheses and the realities of clinical practice. Eat Weight Disord 2009; 14, e176–e183.
Rogers IS, Ness AR, Steer CD, Wells JC, Emmett PM, Reilly JR et al. Associations of size at birth and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry measures of lean and fat mass at 9 to 10 y of age. Am J Clin Nutr 2006; 84, 739–747.
Garnett SP, Cowell CT, Baur LA, Fay RA, Lee J, Coakley J et al. Abdominal fat and birth size in healthy prepubertal children. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25, 1667–1673.
Shephard R . Pathological disturbances of body composition. In: Lasker G M-TC, Roberts D (eds). Body Composition in Biological Anthropology. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1991, pp 226–241.
Goulding A, Taylor RW, Jones IE, Lewis-Barned NJ, Williams SM . Body composition of 4- and 5-year-old New Zealand girls: a DXA study of initial adiposity and subsequent 4-year fat change. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2003; 27, 410–415.
Cheek DB, Hill DE, Cordano A, Graham GG . Malnutrition in infancy: changes in muscle and adipose tissue before and after rehabilitation. Pediatr Res 1970; 4, 135–144.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the persons who helped in the recruitment and the assessments. We also thank the Eiffel Scholarship, the AP-HP PHRC grant, the CNAM-TS and the ANR programme jeune chercheur for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Appendix
EVAN group: group still under construction: Sylvie Berthoz, Laura Bignami, Stephanie Bioulac, Corinne Blanchet, Jennifer Carrere, Annaig Courty, Marc Delorme, Karine Doncieux, Jeanne Duclos, Catherine Fayollet, Claire Gayet, Priscille Gerardin, Christine Hassler, Sylvain Lambert, Sylvie Lebecq, Virginie Mourier, Clementine Nordon, Ludovic Place, Marc-Antoine Podlipski, Damien Ringuenet, Morgane Rousselet, Christelle Turuban, Jean-luc Venisse
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattar, L., Pichard, C., Godart, N. et al. Can birth weight predict later body composition in anorexia nervosa?. Eur J Clin Nutr 66, 964–967 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2012.21
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2012.21