Abstract
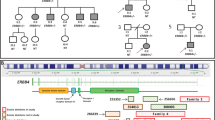
The tyrosine kinase receptor ErbB4 (erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4) plays a crucial role in numerous neurobiological processes in the developing and adult brain. Moreover, recent molecular genetics studies implicate ErbB4 in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. However, the phenotypic consequences of haploinsufficiency of ErbB4 are not known, as no coding mutations have been identified until now. Here, we present a patient with early myoclonic encephalopathy and profound psychomotor delay with a de novo reciprocal translocation t(2;6)(q34;p25.3), disrupting the ErbB4 gene. This patient represents the first case of haploinsufficiency for one of the ErbB family members of tyrosine kinase receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Panayiotopoulos CP : A Clinical guide to Epileptic Syndromes and their Treatment. Oxford: Bladon Medical Publishing, 2002.
Bruel H, Boulloche J, Chabrolle JP, Layet V, Poinsot J : Early myoclonic epileptic encephalopathy and non-ketotic hyperglycemia in the same family. Arch Pediatr 1998; 5: 397–399.
Britsch S : The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling system in development and disease. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 2007; 190: 1–65.
Junttila TT, Sundvall M, Maatta JA, Elenius K : Erbb4 and its isoforms: selective regulation of growth factor responses by naturally occurring receptor variants. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2000; 10: 304–310.
Srinivasan R, Poulsom R, Hurst HC, Gullick WJ : Expression of the c-erbB-4/HER4 protein and mRNA in normal human fetal and adult tissues and in a survey of nine solid tumour types. J Pathol 1998; 185: 236–245.
Gassmann M, Casagranda F, Orioli D et al: Aberrant neural and cardiac development in mice lacking the ErbB4 neuregulin receptor. Nature 1995; 378: 390–394.
Tidcombe H, Jackson-Fisher A, Mathers K, Stern DF, Gassmann M, Golding JP : Neural and mammary gland defects in ErbB4 knockout mice genetically rescued from embryonic lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 8281–8286.
Anton ES, Ghashghaei HT, Weber JL et al: Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB4 modulates neuroblast migration and placement in the adult forebrain. Nat Neurosci 2004; 7: 1319–1328.
Law AJ, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR, Weickert CS : Disease-associated intronic variants in the ErbB4 gene are related to altered ErbB4 splice-variant expression in the brain in schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16: 129–141.
Vermeesch JR, Melotte C, Froyen G et al: Molecular karyotyping: array CGH quality criteria for constitutional genetic diagnosis. J Histochem Cytochem 2005; 53: 413–422.
Luhn K, Wild MK, Eckhardt M, Gerardy-Schahn R, Vestweber D : The gene defective in leukocyte adhesion deficiency II encodes a putative GDP-fucose transporter. Nat Genet 2001; 28: 69–72.
Mechawar N, Lacoste B, Yu WF, Srivastava LK, Quirion R : Developmental profile of neuregulin receptor ErbB4 in postnatal rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 2007; 148: 126–139.
Golding JP, Trainor P, Krumlauf R, Gassmann M : Defects in pathfinding by cranial neural crest cells in mice lacking the neuregulin receptor ErbB4. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: 103–109.
Golub MS, Germann SL, Lloyd KC : Behavioral characteristics of a nervous system-specific erbB4 knock-out mouse. Behav Brain Res 2004; 153: 159–170.
Yau HJ, Wang HF, Lai C, Liu FC : Neural development of the neuregulin receptor ErbB4 in the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus: preferential expression by interneurons tangentially migrating from the ganglionic eminences. Cereb Cortex 2003; 13: 252–264.
Flames N, Long JE, Garratt AN et al: Short- and long-range attraction of cortical GABAergic interneurons by neuregulin-1. Neuron 2004; 44: 251–261.
Kitamura K, Yanazawa M, Sugiyama N et al: Mutation of ARX causes abnormal development of forebrain and testes in mice and X-linked lissencephaly with abnormal genitalia in humans. Nat Genet 2002; 32: 359–369.
Poirier K, Van Esch H, Friocourt G et al: Neuroanatomical distribution of ARX in brain and its localisation in GABAergic neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2004; 122: 35–46.
Kato M, Saitoh S, Kamei A et al: A longer polyalanine expansion mutation in the ARX gene causes early infantile epileptic encephalopathy with suppression-burst pattern (Ohtahara syndrome). Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 361–366.
Archer HL, Evans J, Edwards S et al: CDKL5 mutations cause infantile spasms, early onset seizures, and severe mental retardation in female patients. J Med Genet 2006; 43: 729–734.
Van Esch H, Jansen A, Bauters M, Froyen G, Fryns JP : Encephalopathy and bilateral cataract in a boy with an interstitial deletion of Xp22 comprising the CDKL5 and NHS genes. Am J Med Genet A 2007; 143: 364–369.
Bahi-Buisson N, Kaminska A, Boddaert N et al: The three stages of epilepsy in patients with CDKL5 mutations. Epilepsia 2008; 49: 1027–1037.
Weaving LS, Christodoulou J, Williamson SL et al: Mutations of CDKL5 cause a severe neurodevelopmental disorder with infantile spasms and mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 1079–1093.
Tao J, Van Esch H, Hagedorn-Greiwe M et al: Mutations in the X-linked cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5/STK9) gene are associated with severe neurodevelopmental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 1149–1154.
Pescucci C, Meloni I, Bruttini M et al: Chromosome 2 deletion encompassing the MAP2 gene in a patient with autism and Rett-like features. Clin Genet 2003; 64: 497–501.
Acknowledgements
We thank the family of the patients for their cooperation. LB is supported by the Geconcerteerde Onderzoeksactie 2006/12. HVE is a postdoctoral researcher of the Fund for Scientific Research Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen), Belgium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
URLs: Ensembl, http://www.ensembl.org/; ILAE, http://www.ilae-epilepsy.org; OMIM, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Backx, L., Ceulemans, B., Vermeesch, J. et al. Early myoclonic encephalopathy caused by a disruption of the neuregulin-1 receptor ErbB4. Eur J Hum Genet 17, 378–382 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.180
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.180
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Impairments of GABAergic transmission in hippocampus mediate increased susceptibility of epilepsy in the early stage of Alzheimer’s disease
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
ERBB4 exonic deletions on chromosome 2q34 in patients with intellectual disability or epilepsy
European Journal of Human Genetics (2021)
-
Calpain-Dependent ErbB4 Cleavage Is Involved in Brain Ischemia-Induced Neuronal Death
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)
-
Neuregulin 1-Induced AKT and ERK Phosphorylation in Patients with Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) and Intellectual Disability Associated with Obstetric Complications
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2014)
-
Considering specific clinical features as evidence of pathogenic copy number variants
Journal of Applied Genetics (2014)