Abstract
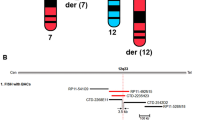
Mental retardation (MR) is not a common feature observed in patients with classical ectodermal dysplasias (EDs). Several genes responsible for EDs and MR have been identified. However, the causation has yet to be identified in a significant number of patients with either ED or MR. Here, we have molecularly characterized a de novo balanced translocation t(1;6)(p22.1;p22.1) in a female patient who had mild features of ED with hypodontia, microcephaly, and cognitive impairment. Mapping of the translocation breakpoints in the patient revealed no obvious causative gene for either ED or MR. Whole genome array CGH analysis unveiled two novel submicroscopic deletions at 2q12.2 and 6q22.3, unrelated to the translocation in the patient. The 2q12.2 deletion contains a known ED gene, ectodysplasin-A receptor (EDAR), and the loss of one copy of this gene is considered to be responsible for the ectodermal phenotype in the patient. It is plausible that a potential autosomal MR gene deleted at 2q12.2 or 6q22.3 is likely the cause of the neurodevelopmental defects in the patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ropers HH : X-linked mental retardation: many genes for a complex disorder. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2006; 16: 260–269.
Stevenson RE : Advances in X-linked mental retardation. Curr Opin Pediatr 2005; 17: 720–724.
Colleaux L, Rio M, Heuertz S et al: A novel automated strategy for screening cryptic telomeric rearrangements in children with idiopathic mental retardation. Eur J Hum Genet 2001; 9: 319–327.
Anderlid BM, Schoumans J, Anneren G et al: Subtelomeric rearrangements detected in patients with idiopathic mental retardation. Am J Med Genet 2002; 107: 275–284.
Kere J, Srivastava AK, Montonen O et al: X-linked anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia is caused by mutation in a novel transmembrane protein. Nat Genet 1996; 13: 409–416.
Srivastava AK, Montonen O, Saarialho-Kere U et al: Fine mapping of the EDA gene: a translocation breakpoint is associated with a CpG island that is transcribed. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 126–132.
Ezer S, Bayes M, Elomaa O, Schlessinger D, Kere J : Ectodysplasin is a collagenous trimeric type II membrane protein with a tumor necrosis factor-like domain and co-localizes with cytoskeletal structures at lateral and apical surfaces of cells. Hum Mol Genet 1999; 8: 2079–2086.
Headon DJ, Overbeek PA : Involvement of a novel Tnf receptor homologue in hair follicle induction. Nat Genet 1999; 22: 370–374.
Doffinger R, Smahi A, Bessia C et al: X-linked anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia with immunodeficiency is caused by impaired NF-kappaB signaling. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 277–285.
Schmidt-Ullrich R, Tobin DJ, Lenhard D, Schneider P, Paus R, Scheidereit C : NF-kappaB transmits Eda A1/EdaR signalling to activate Shh and cyclin D1 expression, and controls post-initiation hair placode down growth. Development 2006; 133: 1045–1057.
Nishioka E, Tanaka T, Yoshida H et al: Mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 plays an unexpected role in the development of mouse guard hair. J Invest Dermatol 2002; 119: 632–638.
Cui CY, Hashimoto T, Grivennikov SI, Piao Y, Nedospasov SA, Schlessinger D : Ectodysplasin regulates the lymphotoxin-beta pathway for hair differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 9142–9147.
Andl T, Reddy ST, Gaddapara T, Millar SE : WNT signals are required for the initiation of hair follicle development. Dev Cell 2002; 2: 643–653.
Durmowicz MC, Cui CY, Schlessinger D : The EDA gene is a target of, but does not regulate Wnt signaling. Gene 2002; 285: 203–211.
Cui CY, Schlessinger D : EDA signaling and skin appendage development. Cell Cycle 2006; 5: 2477–2483.
de Vries BB, Winter R, Schinzel A, van Ravenswaaij-Arts C : Telomeres: a diagnosis at the end of the chromosomes. J Med Genet 2003; 40: 385–398.
Kleefstra T, Smidt M, Banning MJ et al: Disruption of the gene euchromatin histone methyl transferase1 (Eu-HMTase1) is associated with the 9q34 subtelomeric deletion syndrome. J Med Genet 2005; 42: 299–306.
Froyen G, Corbett M, Vandewalle J et al: Submicroscopic duplications of the hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase HSD17B10 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase HUWE1 are associated with mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 432–443.
Asamoah A, Decker AB, Wiktor A, Van Dyke DL : Child with de novo t(1;6)(p22.1;p22.1) translocation and features of ectodermal dysplasia with hypodontia and developmental delay. Am J Med Genet A 2003; 118: 82–85.
Vervoort V, Beachmen M, Edwards P et al: AGTR2 mutations in X-linked mental retardation. Science 2002; 296: 2401–2403.
Griggs BL, Ladd S, Saul RA, DuPont BR, Srivastava AK : Dedicator of cytokinesis 8 is disrupted in two patients with mental retardation and developmental disabilities. Genomics 2008; 91: 195–202.
Monreal AW, Ferguson BM, Headon DJ, Street SL, Overbeek PA, Zonana J : Mutations in the human homologue of mouse dl cause autosomal recessive and dominant hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Nat Genet 1999; 22: 366–369.
Schuierer MM, Langmann T : Molecular diagnosis of ATP-binding cassette transporter-related diseases. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2005; 5: 755–767.
Imanaka T, Aihara K, Takano T et al: Characterization of the 70-kDa peroxisomal membrane protein, an ATP binding cassette transporter. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 11968–11976.
Paton BC, Heron SE, Nelson PV, Morris CP, Poulos A : Absence of mutations raises doubts about the role of the 70-kD peroxisomal membrane protein in zellweger syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 1997; 60: 1535–1539.
Valverde D, Riveiro-Alvarez R, Aguirre-Lamban J et al: Spectrum of the ABCA4 gene mutations implicated in severe retinopathies in Spanish patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48: 985–990.
Riveiro-Alvarez R, Valverde D, Lorda-Sanchez I et al: Partial paternal uniparental disomy (UPD) of chromosome 1 in a patient with stargardt disease. Mol Vis 2007; 13: 96–101.
Benarroch EE : Rho GTPases: role in dendrite and axonal growth, mental retardation, and axonal regeneration. Neurology 2007; 68: 1315–1318.
Saras J, Franzen P, Aspenstrom P, Hellman U, Gonez LJ, Heldin CH : A novel GTPase-activating protein for Rho interacts with a PDZ domain of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPL1. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 24333–24338.
Molinari F, Rio M, Meskenaite V et al: Truncating neurotrypsin mutation in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic mental retardation. Science 2002; 298: 1779–1781.
Cheunsuk S, Sparks R, Noveroske JK et al: Expression, genomic structure and mapping of the thymus specific protease prss16: a candidate gene for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus susceptibility. J Autoimmun 2002; 18: 311–316.
Gribble SM, Prigmore E, Burford DC et al: The complex nature of constitutional de novo apparently balanced translocations in patients presenting with abnormal phenotypes. J Med Genet 2005; 42: 8–16.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the patient and the parents for participation in this study. We thank Cindy Skinner for assistance in the collection of patient material and Rachel Griggs for technical assistance. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Self Regional Healthcare, the IRB of record for the GGC and was supported by a grant from NICHD (R01 HD39331) to AKS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griggs, B., Ladd, S., Decker, A. et al. Identification of ectodysplasin-A receptor gene deletion at 2q12.2 and a potential autosomal MR locus. Eur J Hum Genet 17, 30–36 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.183
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.183
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Novel interstitial 2q12.3q13 microdeletion predisposes to developmental delay and behavioral problems
neurogenetics (2021)
-
Detection of classical 17p11.2 deletions, an atypical deletion and RAI1 alterations in patients with features suggestive of Smith–Magenis syndrome
European Journal of Human Genetics (2012)