Abstract
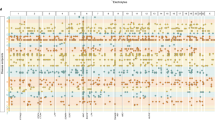
An investigation into fine-scale European population structure was carried out using high-density genetic variation on nearly 6000 individuals originating from across Europe. The individuals were collected as control samples and were genotyped with more than 300 000 SNPs in genome-wide association studies using the Illumina Infinium platform. A major East–West gradient from Russian (Moscow) samples to Spanish samples was identified as the first principal component (PC) of the genetic diversity. The second PC identified a North–South gradient from Norway and Sweden to Romania and Spain. Variation of frequencies at markers in three separate genomic regions, surrounding LCT, HLA and HERC2, were strongly associated with this gradient. The next 18 PCs also accounted for a significant proportion of genetic diversity observed in the sample. We present a method to predict the ethnic origin of samples by comparing the sample genotypes with those from a reference set of samples of known origin. These predictions can be performed using just summary information on the known samples, and individual genotype data are not required. We discuss issues raised by these data and analyses for association studies including the matching of case-only cohorts to appropriate pre-collected control samples for genome-wide association studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Clayton D, Walker N, Smyth D et al: Population structure, differential bias and genomic control in a large-scale, case-control association study. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 1243–1246.
Freedman M, Reich D, Penney K et al: Assessing the impact of population stratification on genetic association studies. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 388–393.
Marchini J, Cardon L, Phillips M, Donnelly P : The effects of human population structure on large genetic association studies. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 512–517.
Seldin MF, Shigeta R, Villoslada P et al: European population substructure: clustering of northern and southern populations. PLoS Genet 2006; 2: e143.
Tian C, Plenge RM, Ransom M et al: Analysis and application of European genetic substructure using 300 K SNP information. PLoS Genet 2008; 4: e4.
Price AL, Butler J, Patterson N et al: Discerning the ancestry of European Americans in genetic association studies. PLoS Genet 2008; 4: e236.
Bauchet M, McEvoy B, Pearson LN et al: Measuring European population stratification with microarray genotype data. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 80: 948–956.
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P : Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000; 155: 945–959.
Tang H, Coram M, Wang P, Zhu X, Risch N : Reconstructing genetic ancestry blocks in admixed individuals. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 79: 1–12.
Patterson N, Price AL, Reich D : Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet 2006; 2: e190.
Menozzi P, Piazza A, Cavalli-Sforza L : Synthetic maps of human gene frequencies in Europeans. Science 1978; 201: 786–792.
Li JZ, Absher DM, Tang H et al: Worldwide human relationships inferred from genome-wide patterns of variation. Science 2008; 319: 1100–1104.
Consortium IH, Frazer KA, Ballinger DG et al: A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature 2007; 449: 851–861.
Hung R, Mckay J, Gaborieau V et al: A susceptibility locus for lung cancer maps to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit genes on 15q25. Nature 2008; 452: 633–637.
Consortium WTCC: Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007; 447: 661–678.
Consortium WTCC, (TASC) A-A-ASC Burton PR, Clayton DG, Cardon LR et al: Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1329–1337.
Moffatt MF, Kabesch M, Liang L et al: Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature 2007; 448: 470–473.
Libioulle C, Louis E, Hansoul S et al: Novel Crohn disease locus identified by genome-wide association maps to a gene desert on 5p13.1 and modulates expression of PTGER4. PLoS Genet 2007; 3: e58.
Leon DA, Koupil I, Mann V et al: Fetal, developmental, and parental influences on childhood systolic blood pressure in 600 sib pairs: the Uppsala Family study. Circulation 2005; 112: 3478–3485.
Krawczak M, Nikolaus S, von Eberstein H, Croucher PJ, El Mokhtari NE, Schreiber S : PopGen: population-based recruitment of patients and controls for the analysis of complex genotype-phenotype relationships. Community genet 2006; 9: 55–61.
Bron C, Kerbosch J : Finding all cliques of an undirected graph. Commun ACM 1973; 16: 575–577.
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D : Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 904–909.
Sturm RA, Duffy DL, Zhao ZZ et al: A single SNP in an evolutionary conserved region within intron 86 of the HERC2 gene determines human blue-brown eye color. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 424–431.
Kayser M, Liu F, Janssens AC et al: Three genome-wide association studies and a linkage analysis identify HERC2 as a human iris color gene. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 411–423.
Eiberg H, Troelsen J, Nielsen M et al: Blue eye color in humans may be caused by a perfectly associated founder mutation in a regulatory element located within the HERC2 gene inhibiting OCA2 expression. Hum Genet 2008; 123: 177–187.
Herva R, de la Chapelle A : A large pericentric inversion of human chromosome 8. Am J Hum Genet 1976; 28: 208–212.
Giglio S, Broman KW, Matsumoto N et al: Olfactory receptor-gene clusters, genomic-inversion polymorphisms, and common chromosome rearrangements. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 68: 874–883.
Devlin B, Roeder K : Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics 1999; 55: 997–1004.
Devlin B, Roeder K, Wasserman L : Genomic control, a new approach to genetic-based association studies. Theor popul biol 2001; 60: 155–166.
Terwilliger JD, Haghighi F, Hiekkalinna TS, Göring HH : A bias-ed assessment of the use of SNPs in human complex traits. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2002; 12: 726–734.
Teare MD, Dunning AM, Durocher F, Rennart G, Easton DF : Sampling distribution of summary linkage disequilibrium measures. Ann Hum Genet 2002; 66: 223–233.
Novembre J, Stephens M : Interpreting principal component analyses of spatial population genetic variation. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 646–649.
Clark AG, Hubisz MJ, Bustamante CD, Williamson SH, Nielsen R : Ascertainment bias in studies of human genome-wide polymorphism. Genome Res 2005; 15: 1496–1502.
Paschou P, Ziv E, Burchard EG et al: PCA-correlated SNPs for structure identification in worldwide human populations. PLoS Genet 2007; 3: 1672–1686.
Acknowledgements
Funding for the genotyping for the eastern European data was provided by INCa, France and the CNG, France. Funding for the genotyping of the German Asthma case and control samples was provided by the GABRIEL European project. The CNG also provided support for genotyping all samples (including those described above) apart from the Wellcome Trust control samples, which were generated by the Wellcome Trust Case-Control Consortium. A full list of the investigators who contributed to the generation of the data is available from www.wtccc.org.uk. Funding for the project was provided by the Wellcome Trust under award 076113. Johanna Sandling is acknowldeged for managing the Uppsala Family Study samples. The longitudinal database of Uppsala Family Study is supported by the Swedish Research Council. The Popgen biobank is supported by the German Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) through the National Genome Research Network (NGFN). It also received infrastructure support through the DFG excellence cluster ‘Inflammation at Interfaces.’
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heath, S., Gut, I., Brennan, P. et al. Investigation of the fine structure of European populations with applications to disease association studies. Eur J Hum Genet 16, 1413–1429 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.210
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.210
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Performance of model-based multifactor dimensionality reduction methods for epistasis detection by controlling population structure
BioData Mining (2021)
-
The genetic history of France
European Journal of Human Genetics (2020)
-
Towards a fine-scale picture of European genetic diversity
European Journal of Human Genetics (2020)
-
Estimating the age of p.(Phe508del) with family studies of geographically distinct European populations and the early spread of cystic fibrosis
European Journal of Human Genetics (2018)
-
Between Lake Baikal and the Baltic Sea: genomic history of the gateway to Europe
BMC Genetics (2017)