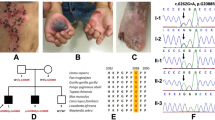
Abstract
We have earlier described a syndrome characterized by microcephaly, cutis verticis gyrata, retinitis pigmentosa, cataracts, hearing loss and mental retardation (Mendelian inheritance in man (MIM) no: 605685) in two brothers from a non-consanguineous Lebanese family. In view of the rarity of the disorder and the high rate of inbreeding in the Lebanese population, we assumed an autosomal recessive trait inherited from a common ancestor. A genomewide scan was performed. The single locus on the long arm of chromosome 8 that showed homozygosity by descent comprised the gene responsible for Cohen syndrome (CS), VPS13B. We then sequenced VPS13B in the patients and found a homozygous splice site mutation. Several possible explanations for the overlap between CS and the clinical features observed in our patients are discussed. Our data highlight the potential of high-resolution homozygosity mapping in small populations with a high rate of inbreeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Leonard H, Wen X : The epidemiology of mental retardation: challenges and opportunities in the new millennium. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2002; 8: 117–134.
Curry CJ, Stevenson RE, Aughton D et al: Evaluation of mental retardation: recommendations of a Consensus Conference: American College of Medical Genetics. Am J Med Genet 1997; 72: 468–477.
Megarbane A, Waked N, Chouery E et al: Microcephaly, cutis verticis gyrata of the scalp, retinitis pigmentosa, cataracts, sensorineural deafness, and mental retardation in two brothers. Am J Med Genet 2001; 98: 244–249.
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR : GRR: graphical representation of relationship errors. Bioinformatics 2001; 17: 742–743.
O’Connell JR, Weeks DE : PedCheck: a program for identification of genotype incompatibilities in linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 1998; 63: 259–266.
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR : Merlin – rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 2002; 30: 97–101.
Kruglyak L, Daly MJ, Reeve-Daly MP, Lander ES : Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 58: 1347–1363.
Strauch K, Fimmers R, Kurz T, Deichmann KA, Wienker TF, Baur MP : Parametric and nonparametric multipoint linkage analysis with imprinting and two-locus-trait models: application to mite sensitization. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 66: 1945–1957.
Gudbjartsson DF, Jonasson K, Frigge ML, Kong A : Allegro, a new computer program for multipoint linkage analysis. Nat Genet 2000; 25: 12–13.
Ruschendorf F, Nurnberg P : ALOHOMORA: a tool for linkage analysis using 10K SNP array data. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 2123–2125.
Thiele H, Nurnberg P : HaploPainter: a tool for drawing pedigrees with complex haplotypes. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 1730–1732.
Chandler KE, Kidd A, Al-Gazali L et al: Diagnostic criteria, clinical characteristics, and natural history of Cohen syndrome. J Med Genet 2003; 40: 233–241.
Kolehmainen J, Wilkinson R, Lehesjoki AE et al: Delineation of Cohen syndrome following a large-scale genotype-phenotype screen. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 122–127.
Hennies HC, Rauch A, Seifert W et al: Allelic heterogeneity in the COH1 gene explains clinical variability in Cohen syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 138–145.
Vogel F, Motulsky A : Human Genetics: Problems and Approaches, 3rd edn. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1997.
Ebermann I, Walger M, Scholl HP et al: Truncating mutation of the DFNB59 gene causes cochlear hearing impairment and central vestibular dysfunction. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 571–577.
Ebermann I, Elsayed SM, Abdel-Ghaffar TY et al: Double homozygosity for mutations of AGL and SCN9A mimicking neurohepatopathy syndrome. Neurology 2008; 70: 2343–2344.
Dahir GA, Miller LK, Butler MG : Survey of mentally retarded males for cutis verticis gyrata and chromosomal fragile sites. Am J Med Genet 1992; 44: 118–120.
Larsen F, Birchall N : Cutis verticis gyrata: three cases with different aetiologies that demonstrate the classification system. Australas J Dermatol 2007; 48: 91–94.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to the family that participated in this study. We thank Dr HC Hennies for kindly supplying VPS13B primers and Michaela Thoenes for technical assistance. This study was supported by the Pro Retina Deutschland, Pro-Re/KP/Bolz.1, and the Gertrud Kusen-Stiftung (HJB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mégarbané, A., Slim, R., Nürnberg, G. et al. A novel VPS13B mutation in two brothers with Cohen syndrome, cutis verticis gyrata and sensorineural deafness. Eur J Hum Genet 17, 1076–1079 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.273
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.273