Abstract
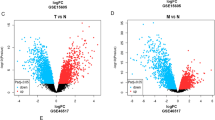
In most Dutch melanoma families, a founder deletion in the melanoma susceptibility gene CDKN2A (which encodes p16) is present. This founder deletion (p16-Leiden) accounts for a significant proportion of the increased melanoma risk. However, it does not account for the Atypical Nevus (AN) phenotype that segregates in both p16-Leiden carriers and non-carriers. The AN-affected p16-Leiden family members are therefore a unique valuable resource for unraveling the genetic etiology of the AN phenotype, which is considered both a risk factor and a precursor lesion for melanoma. In this study, we performed a genome-wide scan for linkage in four p16-Leiden melanoma pedigrees, classifying family members with five or more AN as affected. The strongest evidence for an atypical nevus susceptibility gene was mapped to chromosome band 7q21.3 (two-point LOD score=2.751), a region containing candidate gene CDK6.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Skolnick MH, Cannon-Albright LA, Kamb A : Genetic predisposition to melanoma. Eur J Cancer 1994; 30A: 1991–1995.
Lynch HT, Frichot III BC, Lynch JF : Familial atypical multiple mole-melanoma syndrome. J Med Genet 1978; 15: 352–356.
Kamb A, Gruis NA, Weaver-Feldhaus J et al: A cell cycle regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types. Science 1994; 264: 436–440.
Foulkes WD, Flanders TY, Pollock PM, Hayward NK : The CDKN2A (p16) gene and human cancer. Mol Med 1997; 3: 5–20.
Kefford R, Bishop JN, Tucker M et al: Genetic testing for melanoma. Lancet Oncol 2002; 3: 653–654.
Hussussian CJ, Struewing JP, Goldstein AM et al: Germline p16 mutations in familial melanoma. Nat Genet 1994; 8: 5–21.
Cannon-Albright LA, Meyer LJ, Goldgar DE et al: Penetrance and expressivity of the chromosome 9p melanoma susceptibility locus (MLM). Cancer Res 1994; 54: 6041–6044.
Bishop JA, Wachsmuth RC, Harland M et al: Genotype/phenotype and penetrance studies in melanoma families with germline CDKN2A mutations. J Invest Dermatol 2000; 114: 28–33.
Hille ET, van Duijn E, Gruis NA, Rosendaal FR, Bergman w, Vandenbroucke JP : Excess cancer mortality in six Dutch pedigrees with the familial atypical multiple mole-melanoma syndrome from 1830 to 1994. J Invest Dermatol 1998; 110: 788–792.
Gruis NA, Sandkuijl LA, Weber JL et al: Linkage analysis in Dutch familial atypical multiple mole-melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome families. Effect of naevus count. Melanoma Res 1993; 3: 271–277.
Gruis NA, Sandkuijl LA, van der Velden PA, Bergman W, Frants RR : CDKN2 explains part of the clinical phenotype in Dutch familial atypical multiple-mole melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome families. Melanoma Res 1995; 5: 169–177.
Puig S, Ruiz A, Castel T et al: Inherited susceptibility to several cancers but absence of linkage between dysplastic nevus syndrome and CDKN2A in a melanoma family with a mutation in the CDKN2A (P16INK4A) gene. Hum Genet 1997; 101: 359–364.
Gruis NA, van der Velden PA, Sandkuijl LA et al: Homozygotes for CDKN2 (p16) germline mutation in Dutch familial melanoma kindreds. Nat Genet 1995; 10: 351–353.
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR : GRR: graphical representation of relationship errors. Bioinformatics 2001; 17: 742–743.
Duffy DL : An integrated genetic map for linkage analysis. Behav Genet 2006; 36: 4–6.
Kong X, Murphy K, Raj T, He C, White PS, Matise TC : A combined linkage-physical map of the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 1143–1148.
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM : Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet 1984; 36: 460–465.
Lander E, Kruglyak L : Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet 1995; 11: 241–247.
Bishop DT, Demenais F, Goldstein AM et al: Geographical variation in the penetrance of CDKN2A mutations for melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94: 894–903.
Goldstein AM, Struewing JP, Fraser MC, Smith MW, Tucker MA : Prospective risk of cancer in CDKN2A germline mutation carriers. J Med Genet 2004; 41: 421–424.
Cramer SF : Atypical histologic features in melanocytic nevi. Am J Dermatopathol 2001; 23: 160–161.
Easton DF, Cox GM, Macdonald AM, Ponder BA : Genetic susceptibility to naevi – a twin study. Br J Cancer 1991; 64: 1164–1167.
Wachsmuth RC, Gaut RM, Barrett JH et al: Heritability and gene-environment interactions for melanocytic nevus density examined in a UK adolescent twin study. J Invest Dermatol 2001; 117: 348–352.
Goldstein AM, Tucker MA, Crutcher WA, Hartge P, Sagebiel RW : The inheritance pattern of dysplastic naevi in families of dysplastic naevus patients. Melanoma Res 1993; 3: 15–22.
Falchi M, Spector TD, Perks U, Kato BS, Bataille V : Genome-wide search for nevus density shows linkage to two melanoma loci on chromosome 9 and identifies a new QTL on 5q31 in an adult twin cohort. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 2975–2979.
Zhu G, Montgomery GW, James MR et al: A genome-wide scan for naevus count: linkage to CDKN2A and to other chromosome regions. Eur J Hum Genet 2007; 15: 94–102.
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to the family members for their past and recent participation in our research. FAS is supported by the Dutch Cancer Society (RUL 99-1932); NAG is a recipient of an Aspasia fellowship of the Netherlands organization for Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Snoo, F., Hottenga, JJ., Gillanders, E. et al. Genome-wide linkage scan for atypical nevi in p16-Leiden melanoma families. Eur J Hum Genet 16, 1135–1141 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.72
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.72
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Melanoma susceptibility as a complex trait: genetic variation controls all stages of tumor progression
Oncogene (2015)
-
Association of Genetic Variants in CDK6 and XRCC1 with the Risk of Dysplastic Nevi in Melanoma-Prone Families
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2014)