Abstract
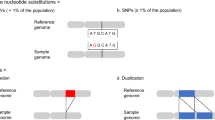
We used Affymetrix 6.0 GeneChip SNP arrays to characterize copy number variations (CNVs) in a cohort of 70 patients previously characterized on lower-density oligonucleotide arrays affected by idiopathic mental retardation and dysmorphic features. The SNP array platform includes ∼900 000 SNP probes and 900 000 non-SNP oligonucleotide probes at an average distance of 0.7 Kb, which facilitates coverage of the whole genome, including coding and noncoding regions. The high density of probes is critical for detecting small CNVs, but it can lead to data interpretation problems. To reduce the number of false positives, parameters were set to consider only imbalances >75 Kb encompassing at least 80 probe sets. The higher resolution of the SNP array platform confirmed the increased ability to detect small CNVs, although more than 80% of these CNVs overlapped to copy number ‘neutral’ polymorphism regions and 4.4% of them did not contain known genes. In our cohort of 70 patients, of the 51 previously evaluated as ‘normal’ on the Agilent 44K array, the SNP array platform disclosed six additional CNV changes, including three in three patients, which may be pathogenic. This suggests that about 6% of individuals classified as ‘normal’ using the lower-density oligonucleotide array could be found to be affected by a genomic disorder when evaluated with the higher-density microarray platforms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Feuk L, Carson AR, Scherer SW : Structural variation in the human genome. Nat Rev Genet 2006; 7: 85–97.
Chance PF, Abbas N, Lensch MW et al: Two autosomal dominant neuropathies result from reciprocal DNA duplication/deletion of a region on chromosome 17. Hum Mol Genet 1994; 3: 223–228.
Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR : Genome architecture, rearrangements and genomic disorders. Trends Genet 2002; 18: 74–82.
Cooper GM, Nickerson DA, Eichler EE : Mutational and selective effects on copy-number variants in the human genome. Nat Genet 2007; 39: S22–S29.
Perry GH, Tchinda J, McGrath SD et al: Hotspots for copy number variation in chimpanzees and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 8006–8011.
Sharp AJ, Locke DP, McGrath SD et al: Segmental duplications and copy-number variation in the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 77: 78–88.
Shaw CJ, Bi W, Lupski JR : Genetic proof of unequal meiotic crossovers in reciprocal deletion and duplication of 17p11.2. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1072–1081.
Emanuel BS, Saitta SC : From microscopes to microarrays: dissecting recurrent chromosomal rearrangements. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 869–883.
Carter NP : Methods and strategies for analyzing copy number variation using DNA microarrays. Nat Genet 2007; 39: S16–S21.
Fan YS, Jayakar P, Zhu H et al: Detection of pathogenic gene copy number variations in patients with mental retardation by genomewide oligonucleotide array comparative genomic hybridization. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 1124–1132.
Redon R, Ishikawa S, Fitch KR et al: Global variation in copy number in the human genome. Nature 2006; 444: 444–454.
Schoumans J, Ruivenkamp C, Holmberg E, Kyllerman M, Anderlid BM, Nordenskjold M : Detection of chromosomal imbalances in children with idiopathic mental retardation by array based comparative genomic hybridisation (array-CGH). J Med Genet 2005; 42: 699–705.
Sharp AJ, Cheng Z, Eichler EE : Structural variation of the human genome. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2006; 7: 407–442.
Trask BJ, Friedman C, Martin-Gallardo A et al: Members of the olfactory receptor gene family are contained in large blocks of DNA duplicated polymorphically near the ends of human chromosomes. Hum Mol Genet 1998; 7: 13–26.
van Karnebeek CD, Scheper FY, Abeling NG et al: Etiology of mental retardation in children referred to a tertiary care center: a prospective study. Am J Ment Retard 2005; 110: 253–267.
Rauch A, Hoyer J, Guth S et al: Diagnostic yield of various genetic approaches in patients with unexplained developmental delay or mental retardation. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140: 2063–2074.
Zahir F, Friedman JM : The impact of array genomic hybridization on mental retardation research: a review of current technologies and their clinical utility. Clin Genet 2007; 72: 271–287.
Shaikh TH : Oligonucleotide arrays for high-resolution analysis of copy number alteration in mental retardation/multiple congenital anomalies. Genet Med 2007; 9: 617–625.
Rauch A, Ruschendorf F, Huang J et al: Molecular karyotyping using an SNP array for genomewide genotyping. J Med Genet 2004; 41: 916–922.
Greshock J, Feng B, Nogueira C et al: A comparison of DNA copy number profiling platforms. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 10173–10180.
McCarroll SA, Kuruvilla FG, Korn JM et al: Integrated detection and population-genetic analysis of SNPs and copy number variation. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1166–1174.
Hehir-Kwa JY, Egmont-Petersen M, Janssen IM, Smeets D, van Kessel AG, Veltman JA : Genome-wide copy number profiling on high-density bacterial artificial chromosomes, single-nucleotide polymorphisms, and oligonucleotide microarrays: a platform comparison based on statistical power analysis. DNA Res 2007; 14: 1–11.
Wong KK, deLeeuw RJ, Dosanjh NS et al: A comprehensive analysis of common copy-number variations in the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 80: 91–104.
Koolen DA, Pfundt R, de Leeuw N et al: Genomic microarrays in mental retardation: a practical workflow for diagnostic applications. Hum Mutat 2009; 30: 283–292.
Korn JM, Kuruvilla FG, McCarroll SA et al: Integrated genotype calling and association analysis of SNPs, common copy number polymorphisms and rare CNVs. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1253–1260.
Bernardini L, Castori M, Capalbo A et al: Syndromic craniosynostosis due to complex chromosome 5 rearrangement and MSX2 gene triplication. Am J Med Genet A 2007; 143A: 2937–2943.
Carbone A, Bernardini L, Valenzano F et al: Array-based comparative genomic hybridization in early-stage mycosis fungoides: recurrent deletion of tumor suppressor genes BCL7A, SMAC/DIABLO, and RHOF. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2008; 47: 1067–1075.
Wagenstaller J, Spranger S, Lorenz-Depiereux B et al: Copy-number variations measured by single-nucleotide-polymorphism oligonucleotide arrays in patients with mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 768–779.
Coe BP, Ylstra B, Carvalho B, Meijer GA, Macaulay C, Lam WL : Resolving the resolution of array CGH. Genomics 2007; 89: 647–653.
Vermeesch JR, Fiegler H, de Leeuw N et al: Guidelines for molecular karyotyping in constitutional genetic diagnosis. Eur J Hum Genet 2007; 15: 1105–1114.
Lee C, Iafrate AJ, Brothman AR : Copy number variations and clinical cytogenetic diagnosis of constitutional disorders. Nat Genet 2007; 39: S48–S54.
Hernandez-Martin A, Gonzalez-Sarmiento R, De Unamuno P : X-linked ichthyosis: an update. Br J Dermatol 1999; 141: 617–627.
Shaw-Smith C, Redon R, Rickman L et al: Microarray based comparative genomic hybridisation (array-CGH) detects submicroscopic chromosomal deletions and duplications in patients with learning disability/mental retardation and dysmorphic features. J Med Genet 2004; 41: 241–248.
Battaglia A, Hoyme HE, Dallapiccola B et al: Further delineation of deletion 1p36 syndrome in 60 patients: a recognizable phenotype and common cause of developmental delay and mental retardation. Pediatrics 2008; 121: 404–410.
Heilstedt HA, Ballif BC, Howard LA et al: Physical map of 1p36, placement of breakpoints in monosomy 1p36, and clinical characterization of the syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 72: 1200–1212.
Ballif BC, Yu W, Shaw CA, Kashork CD, Shaffer LG : Monosomy 1p36 breakpoint junctions suggest pre-meiotic breakage-fusion-bridge cycles are involved in generating terminal deletions. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 2153–2165.
Perry GH, Ben-Dor A, Tsalenko A et al: The fine-scale and complex architecture of human copy-number variation. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 685–695.
Froyen G, Van Esch H, Bauters M et al: Detection of genomic copy number changes in patients with idiopathic mental retardation by high-resolution X-array-CGH: important role for increased gene dosage of XLMR genes. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 1034–1042.
Wolff DJ, Schwartz S, Carrel L : Molecular determination of X inactivation pattern correlates with phenotype in women with a structurally abnormal X chromosome. Genet Med 2000; 2: 136–141.
Vrijenhoek T, Buizer-Voskamp JE, van der Stelt I et al: Recurrent CNVs disrupt three candidate genes in schizophrenia patients. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 83: 504–510.
Sudo K, Ito H, Iwamoto I, Morishita R, Asano T, Nagata K : SEPT9 sequence alternations causing hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy are associated with altered interactions with SEPT4/SEPT11 and resistance to Rho/Rhotekin-signaling. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 1005–1013.
Xie Y, Vessey JP, Konecna A, Dahm R, Macchi P, Kiebler MA : The GTP-binding protein Septin 7 is critical for dendrite branching and dendritic-spine morphology. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 1746–1751.
Buser AM, Erne B, Werner HB, Nave KA, Schaeren-Wiemers N : The septin cytoskeleton in myelinating glia. Mol Cell Neurosci 2009; 40: 156–166.
Zhang ZF, Ruivenkamp C, Staaf J et al: Detection of submicroscopic constitutional chromosome aberrations in clinical diagnostics: a validation of the practical performance of different array platforms. Eur J Hum Genet 2008; 16: 786–792.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Elaine Mansfield for helpful and valuable suggestions. This study was supported in part by grants from the PA Department of Health (SAP4100026302 to PF), the NIH (HL-69256 to SS), the Cardeza Foundation for Hematological Research (Philadelphia, PA to SS), the Kimmel Cancer Center (Philadelphia, PA to PF) and by grants from the Italian NIH (‘Rare Disease’ – Italy-USA Program n.526D/28) and the Italian Ministry of Health RC2008-2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernardini, L., Alesi, V., Loddo, S. et al. High-resolution SNP arrays in mental retardation diagnostics: how much do we gain?. Eur J Hum Genet 18, 178–185 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.154
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.154
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genomic Testing for Diagnosis of Genetic Disorders in Children: Chromosomal Microarray and Next—Generation Sequencing
Indian Pediatrics (2020)
-
The Molecular Karyotype of 25 Clinical-Grade Human Embryonic Stem Cell Lines
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Dandy-Walker malformation and Wisconsin syndrome: novel cases add further insight into the genotype-phenotype correlations of 3q23q25 deletions
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2013)
-
High-resolution SNP array analysis of patients with developmental disorder and normal array CGH results
BMC Medical Genetics (2012)
-
Delineation and Diagnostic Criteria of Oral-Facial-Digital Syndrome Type VI
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2012)