Abstract
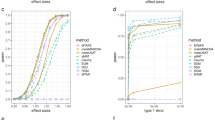
We propose an omnibus family-based association test (MFBAT) that can be applied to multiple markers and multiple phenotypes and that has only one degree of freedom. The proposed test statistic extends current FBAT methodology to incorporate multiple markers as well as multiple phenotypes. Using simulation studies, power estimates for the proposed methodology are compared with the standard methodologies. On the basis of these simulations, we find that MFBAT substantially outperforms other methods, including haplotypic approaches and doing multiple tests with single single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and single phenotypes. The practical relevance of the approach is illustrated by an application to asthma in which SNP/phenotype combinations are identified and reach overall significance that would not have been identified using other approaches. This methodology is directly applicable to cases in which there are multiple SNPs, such as candidate gene studies, cases in which there are multiple phenotypes, such as expression data, and cases in which there are multiple phenotypes and genotypes, such as genome-wide association studies that incorporate expression profiles as phenotypes. This program is available in the PBAT analysis package.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bonferroni C : Teoria statistica delle classi e calcolo delle probability Volime in Onore di Ricardo dlla Volta. Universita di Firenza, 1937.
Holm S : A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Statist 1979; 6: 65–70.
Hochberg Y : A sharper Bonferroni procedure for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika 1988; 75: 800–802.
Horvath S, Xu X, Lake SL, Silverman EK, Weiss ST, Laird NM : Family-based tests for associating haplotypes with general phenotype data: application to asthma genetics. Genet Epidemiol 2004; 26: 61–69.
Clayton D, Chapman J, Cooper J : Use of unphased multilocus genotype data in indirect association studies. Genet Epidemiol 2004; 27: 415–428.
Chapman JM, Cooper JD, Todd JA, Clayton DG : Detecting disease associations due to linkage disequilibrium using haplotype tags: a class of tests and the determinants of statistical power. Hum Hered 2003; 56: 18–31.
Rakovski CS, Xu X, Lazarus R, Blacker D, Laird NM : A new multimarker test for family-based association studies. Genet Epidemiol 2007; 31: 9–17.
Lange C, van Steen K, Andrew T et al: A family-based association test for repeatedly measured quantitative traits adjusting for unknown environmental and/or polygenic effects. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 2004; 3: 1–27.
Lange C, DeMeo D, Silverman EK, Weiss ST, Laird NM : PBAT: tools for family-based association studies. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 367–369.
Van Steen K, McQueen MB, Herbert A et al: Genomic screening and replication using the same data set in family-based association testing. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 683–691.
Van Steen K, Lange C : PBAT: a comprehensive software package for genome-wide association analysis of complex family-based studies. Hum Genomics 2005; 2: 67–69.
Rabinowitz D, Laird N : A unified approach to adjusting association tests for population admixture with arbitrary pedigree structure and arbitrary missing marker information. Hum Hered 2000; 50: 211–223.
Spielman RS, McGinnis RE, Ewens WJ : Transmission test for linkage disequilibrium: the insulin gene region and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Am J Hum Genet 1993; 52: 506–516.
O'Brien PC : Procedures for comparing samples with multiple endpoints. Biometrics 1984; 40: 1079–1087.
Wei L, Johnson W : Combining dependent tests with incomplete measurements. Biometrika 1985; 72: 359–364.
Lange C, Laird NM : On a general class of conditional tests for family-based association studies in genetics: the asymptotic distribution, the conditional power, and optimality considerations. Genet Epidemiol 2002; 23: 165–180.
Jiang H, Harrington D, Raby BA et al: Family-based association test for time-to-onset data with time-dependent differences between the hazard functions. Genet Epidemiol 2006; 30: 124–132.
Murphy A, Weiss ST, Lange C : Screening and replication using the same data set: testing strategies for family-based studies in which all probands are affected. PLoS Genet 2008; 4: e1000197.
Lange C, Silverman EK, Xu X, Weiss ST, Laird NM : A multivariate family-based association test using generalized estimating equations: FBAT-GEE. Biostatistics 2003; 4: 195–206.
Schaid DJ, Sinnwell JP, Thibodeau SN : Robust multipoint identical-by-descent mapping for affected relative pairs. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 128–138.
Long-term effects of budesonide or nedocromil in children with asthma: The Childhood Asthma Management Program Research Group. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1054–1063.
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC : Introduction to Quantitative Genetics. New York: Longman, 1997.
Litonjua AA, Lasky-Su J, Schneiter K et al: ARG1 is a novel bronchodilator response gene: screening and replication in four asthma cohorts. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008; 178: 688–694.
Acknowledgements
We thank all subjects for their ongoing participation in this study. We acknowledge the CAMP investigators and research team, supported by NHLBI, for collection of CAMP Genetic Ancillary Study data. All work on data collected from the CAMP Genetic Ancillary Study was conducted at the Channing Laboratory of the Brigham and Women's Hospital under appropriate CAMP policies and human subject's protections. The CAMP Genetics Ancillary Study is supported by U01 HL075419, U01 HL65899, P01 HL083069, R01 HL 086601, and T32 HL07427 from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute and the National Institute of Health. We would also like to acknowledge the support from the following grants: R01MH081862, P01 HL083069, U01 HL065899.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lasky-Su, J., Murphy, A., McQueen, M. et al. An omnibus test for family-based association studies with multiple SNPs and multiple phenotypes. Eur J Hum Genet 18, 720–725 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.221
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.221
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Statistically efficient association analysis of quantitative traits with haplotypes and untyped SNPs in family studies
BMC Genetics (2020)
-
Identifying pleiotropic genes in genome-wide association studies from related subjects using the linear mixed model and Fisher combination function
BMC Bioinformatics (2017)
-
Family-based association analysis: a fast and efficient method of multivariate association analysis with multiple variants
BMC Bioinformatics (2015)