Abstract
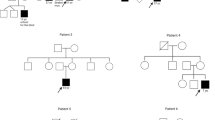
X-linked retinal dystrophies (XLRD) are listed among the most severe RD owing to their early onset, leading to significant visual loss before the age of 30. One-third of XLRD are accounted for by RP2 mutations at the Xp11.23 locus. Deletions of ca. 1.2 Mb in the Xp11.3-p11.23 region have been previously reported in two independent families segregating XLRD with intellectual disability (ID). Although the RD was ascribed to the deletion of RP2, the ID was suggested to be accounted for by the loss of ZNF674, which mutations were independently reported to account for isolated XLID. Here, we report deletions in the Xp11.3-p11.23 region responsible for the loss of ZNF674 in two unrelated families segregating XLRD, but no ID, identified by chromosomal microarray analysis. These findings question the responsibility of ZNF674 deletions in ID associated with X-linked retinal dystrophy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bird AC : X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol 1975; 59: 177–199.
Fishman GA : Retinitis pigmentosa. Genetic percentages. Arch Ophthalmol 1978; 96: 822–826.
Kaplan J, Bonneau D, Frézal J, Munnich A, Dufier JL : Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in retinitis pigmentosa. Hum Genet 1990; 85: 635–642.
Hartong DT, Berson EL, Dryja TP : Retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet 2006; 368: 1795–1809.
Schwahn U, Lenzner S, Dong J et al: Positional cloning of the gene for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa 2. Nat Genet 1998; 19: 327–332.
Meindl A, Dry K, Herrmann K et al: A gene (RPGR) with homology to the RCC1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor is mutated in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (RP3). Nat Genet 1996; 13: 35–42.
Roepman R, van Duijnhoven G, Rosenberg T et al: Positional cloning of the gene for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa 3: homology with the guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor RCC1. Hum Mol Genet 1996; 5: 1035–1041.
Pelletier V, Jambou M, Delphin N et al: Comprehensive survey of mutations in RP2 and RPGR in patients affected with distinct retinal dystrophies: genotype-phenotype correlations and impact on genetic counseling. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 81–91.
Aldred MA, Dry KL, Knight-Jones EB et al: Genetic analysis of a kindred with X-linked mental handicap and retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet 1994; 55: 916–922.
Zhang L, Wang T, Wright AF et al: A microdeletion in Xp11.3 accounts for co-segregation of retinitis pigmentosa and mental retardation in a large kindred. Am J Med Genet 2006; 140A: 349–357.
Lugtenberg D, Yntema HG, Banning MJG et al: ZNF674: a new Kruppel-associated box-containing zinc-finger gene involved in nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 78: 265–278. (Note: Erratum: Am J Hum Genet 2006; 78: 897.).
Casilli F, Di Rocco ZC, Gad S et al: Rapid detection of novel BRCA1 rearrangements in high-risk breast-ovarian cancer families using multiplex PCR of short fluorescent fragments. Hum Mutat 2002; 20: 218–226.
Dandekar SS, Ebenezer ND, Grayson C et al: An atypical phenotype of macular and peripapillary retinal atrophy caused by a mutation in the RP2 gene. Br J Ophthalmol 2004; 88: 528–532.
Medina R, Zaidi SK, Liu CG et al: MicroRNAs 221 and 222 bypass quiescence and compromise cell survival. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 2773–2780.
Olsen L, Klausen M, Helboe L, Nielsen FC, Werge T : MicroRNAs show mutually exclusive expression patterns in the brain of adult male rats. PLoS One 2009; 4: e7225.
Podolska A, Kaczkowski B, Busk PK et al: MicroRNA expression profiling of the porcine developing brain. PLoS One 2011; 6: e14494.
Chen W, Jensen LR, Gecz J et al: Mutation screening of brain-expressed X-chromosomal miRNA genes in 464 patients with nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Eur J Hum Genet 2007; 15: 375–378.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Association Retina France for its support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delphin, N., Hanein, S., Taie, L. et al. Intellectual disability associated with retinal dystrophy in the Xp11.3 deletion syndrome: ZNF674 on trial. Guilty or innocent?. Eur J Hum Genet 20, 352–356 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.217
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.217
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clinical findings and a DNA methylation signature in kindreds with alterations in ZNF711
European Journal of Human Genetics (2022)
-
Mapping the landscape of tandem repeat variability by targeted long read single molecule sequencing in familial X-linked intellectual disability
BMC Medical Genomics (2018)