Abstract
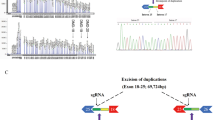
Mutations impacting on the splicing of pre-mRNA are one important cause of genetically inherited diseases. However, detection of splice mutations, that are mainly due to intronic variations, and characterization of their effects are usually not performed as a first approach during genetic diagnosis. X-linked recessive myotubular myopathy is a severe congenital myopathy due to mutations in the MTM1 gene encoding myotubularin. Here, we screened a male patient showing an unusually mild phenotype without respiratory distress by western blot with specific myotubularin antibodies and detected a strong reduction of the protein level.The disease was subsequently linked to a hemizygous point mutation affecting the acceptor splice site of exon 8 of MTM1, proven by protein, transcript and genomic DNA analysis. Detailed analysis of the MTM1 mRNA by RT-PCR, sequencing and quantitative PCR revealed multiple abnormal transcripts with retention of a truncated exon 8, and neighboring exons 7 and 9 but exclusion of several other exons, suggesting a complex effect of this mutation on the splicing of non-adjacent exons. We conclude that the analysis of RNA by RT-PCR and sequencing is an important step to characterize the precise impact of detected splice variants. It is likely that complex splice aberrations due to a single mutation also account for unsolved cases in other diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Jungbluth H, Wallgren-Pettersson C, Laporte J : Centronuclear (myotubular) myopathy. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2008; 3: 26.
Laporte J, Hu LJ, Kretz C et al: A gene mutated in X-linked myotubular myopathy defines a new putative tyrosine phosphatase family conserved in yeast. Nat Genet 1996; 13: 175–182.
Laporte J, Biancalana V, Tanner SM et al: MTM1 mutations in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Hum Mutat 2000; 15: 393–409.
Tsai TC, Horinouchi H, Noguchi S et al: Characterization of MTM1 mutations in 31 Japanese families with myotubular myopathy, including a patient carrying 240 kb deletion in Xq28 without male hypogenitalism. Neuromuscul Disord 2005; 15: 245–252.
Nishino I, Minami N, Kobayashi O et al: MTM1 gene mutations in Japanese patients with the severe infantile form of myotubular myopathy. NeuromusculDisord 1998; 8: 453–458.
Tanner SM, Laporte J, Guiraud-Chaumeil C, Liechti-Gallati S : Confirmation of prenatal diagnosis results of X-linked recessive myotubular myopathy by mutational screening, and description of three new mutations in the MTM1 gene. Hum Mutat 1998; 11: 62–68.
Tanner SM, Schneider V, Thomas NS, Clarke A, Lazarou L, Liechti-Gallati S : Characterization of 34 novel and six known MTM1 gene mutations in 47 unrelated X-linked myotubular myopathy patients. Neuromuscul Disord 1999; 9: 41–49.
Tosch V, Vasli N, Kretz C et al: Novel molecular diagnostic approaches for X-linked centronuclear (myotubular) myopathy reveal intronic mutations. Neuromuscul Disord 2010; 20: 375–381.
Desmet FO, Hamroun D, Lalande M, Collod-Beroud G, Claustres M, Beroud C : Human Splicing Finder: an online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: e67.
Cartegni L, Chew SL, Krainer AR : Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: exonic mutations that affect splicing. Nat Rev Genet 2002; 3: 285–298.
McEntagart M, Parsons G, Buj-Bello A et al: Genotype-phenotype correlations in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Neuromuscul Disord 2002; 12: 939–946.
Laporte J, Kress W, Mandel JL : Diagnosis of X-linked myotubular myopathy by detection of myotubularin. Ann Neurol 2001; 50: 42–46.
Komatsu A, Suzuki S, Inagaki T, Yamashita K, Hashizume K : A kindred with Cockayne syndrome caused by multiple splicing variants of the CSA gene. Am J Med Genet A 2004; 128A: 67–71.
Nissim-Rafinia M, Kerem B : Splicing regulation as a potential genetic modifier. Trends Genet 2002; 18: 123–127.
Targovnik HM, Edouard T, Varela V et al: Two novel mutations in the thyroglobulin gene as cause of congenital hypothyroidism: identification a cryptic donor splice site in the exon 19. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2012; 348: 313–321.
Aminoff M, Carter JE, Chadwick RB et al: Mutations in CUBN, encoding the intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor, cubilin, cause hereditary megaloblastic anaemia 1. Nat Genet 1999; 21: 309–313.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Charlotte Fugier and Nicolas Dondaine for technical assistance, Jean-Louis Mandel for support and the DNA and Cell Bank of Généthon (Evry, France) for cell lines. This study was supported by INSERM, CNRS, University of Strasbourg, Collège de France, and by grants from Association Française contre les Myopathies. JB was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasli, N., Laugel, V., Böhm, J. et al. Myotubular myopathy caused by multiple abnormal splicing variants in the MTM1 RNA in a patient with a mild phenotype. Eur J Hum Genet 20, 701–704 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.256
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.256